Scientists uncover how protein ensures reproductive success
Regulating DNA in sperm and eggs
2014-10-23
(Press-News.org) An international team of researchers from Japan and the UK has discovered how a single protein, called PP4, oversees the processing of DNA during sperm and egg generation for successful fertilization. This protein's activity becomes even more paramount during aging. The study, published in the journal PLOS Genetics, may one day help scientists to understand the mechanisms underlying age-related fertility declines in humans.
While a typical adult human cell contains 46 DNA strands, or chromosomes, that carry our complete genetic information, reproductive cells such as sperm and eggs receive half of this number during a highly intricate process known as "meiosis." How chromosomes are mixed, matched and distributed into reproductive cells accurately is essential for successful fertilization and the development of diverse new life. However, errors in the system can lead to infertility.
To understand which proteins help meiosis run smoothly, the researchers from Kyoto University's Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS) and Tohoku University in Japan, and Imperial College in London, used a tiny worm known as Caenorhabditis elegans to look into the role of PP4.
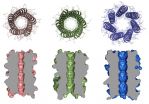
The researchers genetically engineered the worm so that PP4 was functionally disabled, and then observed the consequences of its absence on chromosome regulation during meiosis. The researchers used a super-resolution microscope, which takes pictures at twice the level of detail compared to a normal microscope.
"We found that when PP4 was missing, chromosomes failed to assemble correctly and DNA recombination, an important step for genetic diversity, did not occur," said Aya Sato-Carlton a researcher involved in the study from iCeMS. "The resulting eggs were defective, and the embryos inside could not survive after fertilization," added Sato-Carlton.
Surprisingly, the authors observed that the effects of defective PP4 became even worse as the worms aged, indicating an age-related dependence.
Because the PP4 DNA of worms is over 90% identical with that of humans, it is possible that the protein plays a similar role in all animals as a universal regulator of meiosis, particularly as an organism ages.
"However, it's too early to say for certain that PP4 has a similar kind of role in humans", said Peter Carlton, the principal investigator of the study from iCeMS. "The next step is to see whether we observe the same kind of phenomenon in mice."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-23
Research conducted at the highest-altitude Pleistocene archaeological sites yet identified in the world sheds new light on the capacity of humans to survive in extreme environments.
The findings, to be published in the Oct. 24 edition of the academic journal Science – co-authored by a team of researchers including University of Calgary archaeologist Sonia Zarrillo – were taken from sites in the Pucuncho Basin, located in the Southern Peruvian Andes.
The primary site, Cuncaicha is a rock shelter at 4,480 metres above sea level, with a stone-tool workshop ...
2014-10-23
Scientists working on islands in Florida have documented the rapid evolution of a native lizard species — in as little as 15 years — as a result of pressure from an invading lizard species, introduced from Cuba.
After contact with the invasive species, the native lizards began perching higher in trees, and, generation after generation, their feet evolved to become better at gripping the thinner, smoother branches found higher up.
The change occurred at an astonishing pace: Within a few months, native lizards had begun shifting to higher perches, and over ...
2014-10-23
When a solid material is immersed in a liquid, the liquid immediately next to its surface differs from that of the bulk liquid at the molecular level. This interfacial layer is critical to our understanding of a diverse set of phenomena from biology to materials science. When the solid surface is charged, just like an electrode in a working battery, it can drive further changes in the interfacial liquid. However, elucidating the molecular structure at the solid-liquid interface under these conditions has proven difficult.
Now, for the first time, researchers at the US ...
2014-10-23
Ferns are believed to be 'old' plant species – some of them lived alongside the dinosaurs, over 200 million years ago. However, a group of Andean ferns evolved much more recently: their completely new form and structure (morphology) arose and diversified within the last 2 million years. This novel morphology seems to have been advantageous when colonising the extreme environment of the high Andes.
Dr Patricia Sanchez-Baracaldo (Bristol) and Dr Gavin Thomas (Sheffield) used molecular and morphological data to study a group of ferns which grow in a unique ecosystem ...
2014-10-23
Proteins are long linear molecules that fold up to form well-defined 3D shapes. These 3D molecular architectures are essential for biological functions such as the elasticity of skin, the digestion of food, and the transport of oxygen in blood.
Despite the wide variety of tasks that natural proteins perform, they appear to use only a limited number of structural types, perhaps just a few thousand or so. These are used over and over again, being altered and embellished through evolution to generate many different functions. This raises the question: are more protein ...
2014-10-23
A Dartmouth study suggests that it may be possible to use Diffuse Optical Spectroscopic Tomographic imaging (DOST) to predict which patients will best respond to chemotherapy used to shrink breast cancer tumors before surgery. These findings could eliminate delays in effective early treatment for tumors unlikely to respond to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC). The study, "Predicting breast tumor response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with Diffuse Optical Spectroscopic Tomography prior to treatment," was published online in Clinical Cancer Research on October 7, 2014.
Breast ...
2014-10-23
BOSTON - New achievements in synthetic biology announced today by researchers at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering, which will allow complex cellular recognition reactions to proceed outside of living cells, will dare scientists to dream big: there could one day be inexpensive, shippable and accurate test kits that use saliva or a drop of blood to identify specific disease or infection — a feat that could be accomplished anywhere in the world, within minutes and without laboratory support, just by using a pocket–sized paper diagnostic ...
2014-10-23
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Volatile rainstorms drive complex landscape changes in deserts, particularly in dryland channels, which are shaped by flash flooding. Paradoxically, such desert streams have surprisingly simple topography with smooth, straight and symmetrical form that until now has defied explanation.
That paradox has been resolved in newly published research conducted by Michael Singer and Katerina Michaelides, associate researchers at UC Santa Barbara's Earth Research Institute. The pair show that simple topography in dryland channels is maintained ...
2014-10-23
DALLAS – Oct. 23, 2014 – A hormone seen as a popular target to develop weight-loss drugs works by directly targeting the brain and triggering previously unknown activity in the nervous system, UT Southwestern Medical Center obesity researchers have found.
The fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) hormone has been a key target for developing weight-loss drugs because the protein increases energy expenditure, causing the body to burn calories. But how the hormone worked wasn't known until now.
UT Southwestern researchers tracking the hormone discovered that ...
2014-10-23
DENVER – Sixteen institutions across Europe collaborated together to show for the first time that a semi-quantitative anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) protein expression test, immunohistochemistry (IHC), is reliable amongst several laboratories and reviewers when test methodology and result interpretation are strictly standardized and the scoring pathologists are appropriately trained on the test.
ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) shrink tumors and increase progression-free survival in late-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients positive for ALK as ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists uncover how protein ensures reproductive success
Regulating DNA in sperm and eggs