(Press-News.org) Recently, a team of astronomers reported discovering a pulsating star that appears to shine with the energy of 10 million suns. The find, which was announced in Nature, is the brightest pulsar – a type of rotating neutron star that emits a bright beam of energy that regularly sweeps past Earth like a lighthouse beam – ever seen. But what are the odds finding another one?
According to one of the paper's authors, chances are good now that they know what to look for.
Professor Deepto Chakrabarty of the Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology says he is optimistic that astronomers will find additional ultra-bright pulsars now that they know such objects exist.
"Detecting pulsations in faint sources is challenging, because the X-ray data are not always collected with sufficiently high time-resolution to make the measurement," he says. "Our discovery will now justify the additional effort required to make such timing observations."
Astronomers previously thought that this type of "ultraluminous X-ray source" was likely to be made up of black holes five to 50 times more massive than our sun, radiating energy as they pull in nearby matter. This discovery that at least one ULX source is in fact a pulsar brings that understanding into question.
"Black holes are unable to produce coherent pulsations like what we are seeing here," Chakrabarty says.
The discovery is even more surprising because pulsars by nature are not very massive objects and so have always been assumed capable of only relatively moderate X-ray signals. The newly discovered pulsar is far brighter than previously thought possible.
Chakrabarty says he believes the mysteries of how a pulsar could beam so bright can be solved through additional experimental observations – and with the assistance of theorists.
"It is clear that some sort of specialized beaming may be going on here, but coming up with a sensible and self-consistent picture may be a challenge," he says. "Observing some more examples of ULX pulsars could be very helpful in sorting this out, giving us some different sets of system parameters to work with."
INFORMATION:
More of Deepto Chakrabarty's thoughts on how this new result can align with current knowledge of both ULX sources and pulsars can be found in this Kavli Foundation conversation: http://www.kavlifoundation.org/kavli-news/bright-star-shines-light-mysterious-x-ray-sources-qa-mkis-deepto-chakrabarty
Tremendously bright pulsar may be 1 of many
2014-10-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Emergent behavior lets bubbles 'sense' environment
2014-10-27
VIDEO:
A collection of artificial lipid bubbles cycle through changes in their membranes as the surrounding environment changes. As the osmotic potential changes, different lipids in the membranes form patchy domains...
Click here for more information.
Tiny, soapy bubbles can reorganize their membranes to let material flow in and out in response to the surrounding environment, according to new work carried out in an international collaboration by biomedical engineers at the ...
One drop will do: UBC researchers develop simple new test for vitamin B12 deficiency
2014-10-27
Researchers at the University of British Columbia have developed a novel method to test for vitamin B12 deficiency that is sensitive enough to work on anyone, including newborn babies and large swaths of the general population.
Vitamin B12 deficiency can be tested with a single drop of blood collected from a finger prick, then blotted and dried overnight on a card consisting of filter paper. The UBC study made dried blood spot card analysis sensitive enough to measure the amount of methylmalonic acid (MMA), an indicator of a person's B12 level.
"This minimally invasive ...
International research group publishes updated criteria for diagnosing multiple myeloma
2014-10-27
ROCHESTER, Minn. –The International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG) today announced that it has updated the criteria for diagnosing multiple myeloma. A paper outlining the new criteria was published in the journal Lancet Oncology. Multiple myeloma is a blood cancer that forms in a type of white blood cell called a plasma cell.
"Our group, which includes more than 180 myeloma researchers worldwide, has updated the definition of multiple myeloma for diagnostic purposes to include validated biomarkers in addition to the current clinical symptoms used for diagnosis which ...
Diabetes patients report better outcomes with improved physician accessibility
2014-10-27
LOS ANGELES — A new model of delivering primary care studied by Keck Medicine of the University of Southern California (USC) researchers has the potential to improve the health of patients with type 2 diabetes.
The model encourages doctors to be more of a "medical home" for their patients by being accessible to patients in person and by phone, developing good ongoing relationships with their patients, and being more proactive in helping coordinate care for patients with difficult health problems.
Gregory Stevens, Ph.D., associate professor of family medicine ...
Clinical results indicate vaccine candidate highly efficacious against bacterial diarrhea
2014-10-27
Washington, DC, October 27, 2014—New results from a safety and immunogenicity study, which included a challenge phase to test efficacy, indicate that a live attenuated enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) vaccine candidate, given in combination with a novel adjuvant, provided significant protection against disease. This represents the first efficacy data for this vaccine/adjuvant combination, which was 58.5 percent efficacious in protecting against diarrhea of any severity using a highly rigorous ETEC human challenge model. The vaccine/adjuvant combination was ...
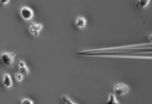
How cells know which way to go
2014-10-27
VIDEO:
In this video, lab-grown human leukemia cells move toward a pipette tip holding an attractive chemical.
Click here for more information.
Amoebas aren't the only cells that crawl: Movement is crucial to development, wound healing and immune response in animals, not to mention cancer metastasis. In two new studies from Johns Hopkins, researchers answer long-standing questions about how complex cells sense the chemical trails that show them where to go — and the ...
The Ebola epidemic: Is there a way out?
2014-10-27
Berlin, 27 October 2014. Not everyone who contracts the Ebola virus dies, the survival rate is around 30% suggesting that some kind of immunity to the disease is possible. Experimental treatments and vaccines against Ebola exist but have not yet been tested in large groups for safety and efficacy (phase 2 trials).
The International Union of Immunology Societies (IUIS) published a statement today in its official journal, Frontiers in Immunology calling for urgent and adequate funding of vaccine candidates in clinical trials and speedy implementation of immunisation in ...
Chest radiation to treat childhood cancer increases patients' risk of breast cancer
2014-10-27
A new study has found that patients who received chest radiation for Wilms tumor, a rare childhood cancer, face an increased risk of developing breast cancer later in life due to their radiation exposure. Published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, the findings suggest that cancer screening guidelines might be re-evaluated to facilitate the early diagnosis and prompt treatment of breast cancer among Wilms tumor survivors.
Wilms tumor is a rare childhood kidney cancer that can spread to the lungs. When this spread occurs, patients ...
Latest bone research abstracts summarized in slides and videos
2014-10-27
Today, the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) has published an educational slide deck highlighting 60 original scientific abstracts presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research (ASBMR) in September 2014.
The succinct slide kit can be downloaded free of charge by all individual IOF members (free sign up on the IOF website).
CEO Judy Stenmark stated, "IOF is pleased to provide this informative resource for healthcare professionals interested in the latest advances in bone and mineral research. While 10% of the featured ...
It's better for memory to make mistakes while learning
2014-10-27
Toronto, Canada – Making mistakes while learning can benefit memory and lead to the correct answer, but only if the guesses are close-but-no-cigar, according to new research findings from Baycrest Health Sciences.
"Making random guesses does not appear to benefit later memory for the right answer , but near-miss guesses act as stepping stones for retrieval of the correct information – and this benefit is seen in younger and older adults," says lead investigator Andrée-Ann Cyr, a graduate student with Baycrest's Rotman Research Institute and the Department ...