Study of Chile earthquake finds new rock structure that affects earthquake rupture
2014-11-01
(Press-News.org) Researchers from the University of Liverpool have found an unusual mass of rock deep in the active fault line beneath Chile which influenced the rupture size of a massive earthquake that struck the region in 2010.
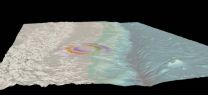
The geological structure, which was not previously known about, is unusually dense and large for this depth in the Earth's crust. The body was revealed using 3-D seismic images of Earth's interior based on the monitoring of vibrations on the Pacific seafloor caused by aftershocks from the magnitude 8.8 Chile earthquake. This imaging works in a similar way to CT scans that are used in hospitals.
Analysis of the 2010 earthquake also revealed that this structure played a key role in the movement of the fault, causing the rupture to suddenly slow down.
Seismologists think that the block of rock was once part of Earth's mantle and may have formed around 220 million years ago, during the period of time known as the Triassic.
Liverpool Seismologist, Stephen Hicks from the School of Environmental Sciences, who led the research, said: "It was previously thought that dense geological bodies in an active fault zone may cause more movement of the fault during an earthquake."
"However, our research suggests that these blocks of rock may in fact cause the earthquake rupture to suddenly slow down. But this slowing down can generate stronger shaking at the surface, which is more damaging to man-made structures."
"It is now clear that ancient geology plays a big role in the generation of future earthquakes and their subsequent aftershocks."
Professor Andreas Rietbrock, head of the Earthquake Seismology and Geodynamics research group added: "This work has clearly shown the potential of 3D 'seismic' images to further our understanding of the earthquake rupture process.
We are currently establishing the Liverpool Earth Observatory (LEO), which will allow us together with our international partners, to carry out similar studies in other tectonically active regions such as northern Chile, Indonesia, New Zealand and the northwest coast United States. This work is vital for understanding risk exposure in these countries from both ground shaking and tsunamis."
Chile is located on the Pacific Ring of Fire, where the sinking of tectonic plates generates many of the world's largest earthquakes.
The 2010 magnitude 8.8 earthquake in Chile is one of the best-recorded earthquakes, giving seismologists the best insight to date into the ruptures of mega-quakes.
INFORMATION:
The research, funded by the Natural Environment Research Council, is published in the journal Earth and Planetary Science Letters.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-31
New DNA sequencing technologies have greatly advanced genomic and metagenomic studies in plant biology. Scientists can readily obtain extensive genetic information for any plant species of interest, at a relatively low cost, rapidly accelerating the pace of genome sequencing.
However, since plant tissues harbor three separate genomes (nuclear, chloroplast, and mitochondrial), it can often be challenging to isolate the particular genome of interest from extracted DNA samples. Sequencing DNA containing all three genomes therefore results in a considerable amount of wasted ...
2014-10-31
After 17 years of groundbreaking 3-D images of rain and storms, the joint NASA and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) will come to an end next year. NASA predicts that science operations will cease in or about April 2015, based on the most recent analysis by mission operations at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland.
On July 8, 2014, pressure readings from the fuel tank indicated that TRMM was near the end of its fuel supply. As a result, NASA ceased station-keeping maneuvers that would keep the satellite at ...
2014-10-31
An active region on the sun – an area of intense and complex magnetic fields – rotated into view on Oct. 18, 2014. Labeled AR 12192, it soon grew into the largest such region in 24 years, and fired off 10 sizable solar flares as it traversed across the face of the sun. The region was so large it could be seen without a telescope for those looking at the sun with eclipse glasses, as many did during a partial eclipse of the sun on Oct. 23.
"Despite all the flares, this region did not produce any significant coronal mass ejections," said Alex Young a solar scientist ...
2014-10-31
AUSTIN, Texas— A new analysis of geologic history may help solve the riddle of the "Cambrian explosion," the rapid diversification of animal life in the fossil record 530 million years ago that has puzzled scientists since the time of Charles Darwin.
A paper by Ian Dalziel of The University of Texas at Austin's Jackson School of Geosciences, published in the November issue of Geology, a journal of the Geological Society of America, suggests a major tectonic event may have triggered the rise in sea level and other environmental changes that accompanied the apparent ...
2014-10-31
Rachel MacTavish is growing salt marsh plants in microcosms that replicate the tide. She assembled them in an outdoor greenhouse at the Sapelo Island National Estuarine Research Reserve in Georgia, USA, with buckets from a hardware store, aquarium tubing, and pumps. Her tidal simulation units could be an important tool for preserving and restoring environmentally important wetlands, because they enable researchers to investigate tidal marsh plant growth in a controlled setting.
"Tidal wetlands are often influenced by many factors, and controlled experiments allow researchers ...
2014-10-31
INDIANAPOLIS -- People with muscular dystrophy could one day assess the effectiveness of their medication with the help of a smartphone-linked device, a new study in mice suggests. The study used a new method to process ultrasound imaging information that could lead to hand-held instruments that provide fast, convenient medical information.
In the study presented Oct. 30 at the Acoustical Society of America's annual meeting, researchers determined how well muscles damaged by muscular dystrophy responded to a drug in mice with an animal form of the disease. They did so ...
2014-10-31
WASHINGTON — New research points to tau, not amyloid-beta (Abeta) plaque, as the seminal event that spurs neuron death in disorders such as Alzheimer's disease. The finding, which dramatically alters the prevailing theory of Alzheimer's development, also explains why some people with plaque build-up in their brains don't have dementia.
The study is published online today in the journal Molecular Neurodegeneration.
Neuronal death happens when tau, found inside neurons, fails to function. Tau's role is to provide a structure — like a train track —inside ...
2014-10-31
Contrary to popular belief, use of the supplement resveratrol (RSV) may not actually enhance the effects of high-intensity interval training (HIIT).
Many news outlets and health blogs have long recommended RSV as a complement to exercise and to enhance performance. However, results from a study by Queen's researcher Brendon Gurd suggest that RSV may actually impede the body's response to training.
"The easiest way to experience the benefits of physical activity is to be physically active," says Dr. Gurd, a professor in the School of Kinesiology and Health Studies. "The ...
2014-10-31
Where does HIV hide? Antiretroviral drugs can usually control the virus, but can't completely eliminate it. So any strategy to eradicate HIV from the body has to take into account not only the main group of immune cells the virus targets, called CD4 or helper T cells, but other infected cells as well.
New research from Yerkes National Primate Research Center, Emory University, sheds light on the question of which cells support viral replication and persistence, and the answers have implications for future efforts to eliminate HIV from the body in human patients.
The ...
2014-10-31
The pathogen Giardia duodenalis is present in mussels from freshwater run-off sites and from areas where California Sea Lions lounge along the coast of California, according to a team of researchers from the University of California, Davis. One of the G. duodenalis strains found is known to infect humans; the two others occur mostly in dogs and other canids. "Thus, the detection of these assemblages implies a potential public health risk if consuming fecally contaminated water or uncooked shellfish," says coauthor Woutrina Smith. The research is published ahead of print ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study of Chile earthquake finds new rock structure that affects earthquake rupture