(Press-News.org) Astronomers have captured the best image ever of planet formation around an infant star as part of the testing and verification process for the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array's (ALMA) new high-resolution capabilities.
This revolutionary new image reveals in astonishing detail the planet-forming disk surrounding HL Tau, a Sun-like star located approximately 450 light-years from Earth in the constellation Taurus.
ALMA uncovered never-before-seen features in this system, including multiple concentric rings separated by clearly defined gaps. These structures suggest that planet formation is already well underway around this remarkably young star.
"These features are almost certainly the result of young planet-like bodies that are being formed in the disk. This is surprising since HL Tau is no more than a million years old and such young stars are not expected to have large planetary bodies capable of producing the structures we see in this image," said ALMA Deputy Director Stuartt Corder.
All stars are believed to form within clouds of gas and dust that collapse under gravity. Over time, the surrounding dust particles stick together, growing into sand, pebbles, and larger-size rocks, which eventually settle into a thin protoplanetary disk where asteroids, comets, and planets form.
Once these planetary bodies acquire enough mass, they dramatically reshape the structure of their natal disk, fashioning rings and gaps as the planets sweep their orbits clear of debris and shepherd dust and gas into tighter and more confined zones.
The new ALMA image reveals these striking features in exquisite detail, providing the clearest picture to date of planet formation. Images with this level of detail were previously only seen in computer models and artist concepts. ALMA, living up to its promise, has now provided direct proof that nature and theory are very much in agreement.
"This new and unexpected result provides an incredible view of the process of planet formation. Such clarity is essential to understand how our own Solar System came to be and how planets form throughout the Universe," said Tony Beasley, director of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) in Charlottesville, Virginia, which manages ALMA operations for astronomers in North America.
HL Tau is hidden in visible light behind a massive envelope of dust and gas. Since ALMA observes at much longer wavelengths, it is able to peer through the intervening dust to study the processes right at the core of this cloud. "This is truly one of the most remarkable images ever seen at these wavelengths. The level of detail is so exquisite that it's even more impressive than many optical images. The fact that we can see planets being born will help us understand not only how planets form around other stars but also the origin of our own Solar System," said NRAO astronomer Crystal Brogan.
ALMA's new high-resolution capabilities were achieved by spacing the antennas up to 15 kilometers apart. This baseline at millimeter wavelengths enabled a resolution of 35 milliarcseconds, which is equivalent to a penny as seen from more than 110 kilometers away.
"Such a resolution can only be achieved with the long baseline capabilities of ALMA and provides astronomers with new information that is impossible to collect with any other facility, including the best optical observatories," noted ALMA Director Pierre Cox.
These long baselines fulfill one of ALMA's major objectives and mark an impressive technological and engineering milestone. Future observations at ALMA's longest possible baseline of 16 kilometers will produce even clearer images and continue to expand our understanding of the cosmos.
VIDEO:
This is an artist's animation of a protoplanetary disk. Newly formed planets can be seen traveling around the central host star, sweeping their orbits clear of dust and gas. These...
Click here for more information.
"This observation illustrates the dramatic and important results that come from NSF supporting world-class instrumentation such as ALMA," said Fleming Crim, the National Science Foundation assistant director for Mathematical and Physical Sciences. "ALMA is delivering on its enormous potential for revealing the distant Universe and is playing a unique and transformational role in astronomy."
INFORMATION:
[The National Science Foundation and the NRAO will expand on this news at a Google Hangout on Nov. 6 at 10:00 EST. Tune in at https://plus.google.com/events/ceul1hkj60se5uts2u75rgqe7rc.]
The National Radio Astronomy Observatory is a facility of the National Science Foundation, operated under cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc.
The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), an international astronomy facility, is a partnership of Europe, North America and East Asia in cooperation with the Republic of Chile. ALMA is funded in Europe by the European Southern Observatory (ESO), in North America by the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) in cooperation with the National Research Council of Canada (NRC) and the National Science Council of Taiwan (NSC) and in East Asia by the National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS) of Japan in cooperation with the Academia Sinica (AS) in Taiwan. ALMA construction and operations are led on behalf of Europe by ESO, on behalf of North America by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO), which is managed by Associated Universities, Inc. (AUI) and on behalf of East Asia by the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ). The Joint ALMA Observatory (JAO) provides the unified leadership and management of the construction, commissioning and operation of ALMA.
Tiny extensions on cells, cilia, play an important role in insulin release, according to a new study, which is published in Nature Communications. The researchers report that the cilia of beta cells in the pancreas are covered with insulin receptors and that changed ciliary function can be associated with the development of type 2 diabetes.
Cilia are tiny extensions on cells and they are credited with many important functions, including transduction of signals in cells. Defects in cilia have been implied in several diseases and pathological conditions. Thus, scientists ...
VIDEO:
A 10-day-old zebrafish gets its stripes over the next 30 days, one image taken a day.
Click here for more information.
Within weeks of publishing surprising new insights about how zebrafish get their stripes, the same University of Washington group is now able to explain how to "erase" them.
The findings – the first published Aug. 28 in Science and the latest in the Nov. 6 issue of Nature Communications – give new understanding about genes and cell behaviors ...
Berlin, Germany (November, 2014) – Closely related groups can differ dramatically in their diversity, but why this happens is a fundamental question in evolutionary biology, dating back to Darwin's observation that a few hyper-diverse groups dominate the modern biota. One of the most extreme examples of this observation is found in the comparison of rodents (Rodentia) and rabbits (Lagomorpha). These two mammalian orders are sister groups, but while rodents have diversified to over 2000 living species and an enormous range of body sizes, lagomorphs (rabbits, hares, ...
ATLANTA, GA (November 7, 2014) – Many people don't realize allergies and asthma go hand-in-hand, and about 90 percent of kids with asthma also have allergies. Even more important, when asthma is undiagnosed or poorly controlled, children are at risk for suffering difficult-to-treat allergic reactions to food.
According to a study presented at the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI) Annual Scientific Meeting, a two and-a-half year-old girl in Pennsylvania suffered a life-threatening allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) to eating an orange – ...
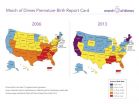
WHITE PLAINS, N.Y., Nov. 6, 2014 – The national preterm birth rate fell to 11.4 percent in 2013 – the lowest in 17 years -- meeting the federal Healthy People 2020 goal seven years early. Despite this progress, the U.S. still received a "C" on the 7th annual March of Dimes Premature Birth Report Card because it fell short of the more-challenging 9.6 percent target set by the March of Dimes, the group said today.
"Achieving the Healthy People 2020 goal is reason for celebration, but the U.S. still has one of the highest rates of preterm birth of any high ...
WASHINGTON - Airport security agents using a new conversation-based screening method caught mock airline passengers with deceptive cover stories more than 20 times as often as agents who used the traditional method of examining body language for suspicious signs, according to new research published by the American Psychological Association.
In experiments spanning eight months, security agents at eight international airports in Europe detected dishonesty in 66 percent of the deceptive mock passengers using the new screening method, compared to just 3 percent for agents ...
New Rochelle, NY, November 6, 2014—Screening large cell culture collections containing plant samples obtained from diverse geographic regions, climates, and soil and growing conditions for biological activity can reveal a wealth of natural compounds with potential applications for crop improvement and protection. The capability to do reproducible screening and genomic analysis of the more than 2,000 plant cell lines maintained in culture at the Institute of Cell Biology and Genetic Engineering, in Kiev, Ukraine is describe in an article in Industrial Biotechnology, ...
A recently launched European satellite could reveal tens of thousands of new planets within the next few years, and provide scientists with a far better understanding of the number, variety and distribution of planets in our galaxy, according to research published today.
Researchers from Princeton University and Lund University in Sweden calculated that the observational satellite Gaia could detect as many as 21,000 exoplanets, or planets outside of Earth's solar system, during its five-year mission. If extended to 10 years, Gaia could detect as many as 70,000 exoplanets, ...
November 5, 2014, Hong Kong, China –Today, the international open-access open-data journal GigaScience (a BGI and BioMed Central journal) announced publication of an article that presents GWATCH1, a new web-based platform that provides visualization tools for identifying disease-associated genetic markers from privacy-protected human data without risk to patient privacy. This dynamic online tool, developed by an international team of researchers from Russia, Australia, Canada, and the US, allows and facilitates disease gene discovery via automation and presentation ...
Fast, on-the-spot tests for bacterial infections may help to reduce excessive antibiotic use. A systematic review published in The Cochrane Library, found that when doctors tested for the presence of bacterial infections they prescribed fewer antibiotics.
Antibiotics treat infections caused by bacteria but not those caused by viruses. Most patients who visit their doctors with acute respiratory infections are suffering from viral infections like the common cold. However, because doctors usually have no immediate way of knowing whether an infection is bacterial or viral, ...