This Week From AGU: Volcano hazards and the role of westerly wind bursts in El Niño
2014-11-11
(Press-News.org) From this week's Eos: Scientists Engage With the Public During Lava Flow Threat
On 27 June, lava from Kīlauea, an active volcano on the island of Hawai`i, began flowing to the northeast, threatening the residents in Pāhoa, a community in the District of Puna, as well as the only highway accessible to this area. Scientists from the U.S. Geological Survey's Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO) and the Hawai`i County Civil Defense have been monitoring the volcano's lava flow and communicating with affected residents through public meetings since 24 August. Eos recently spoke with Michael Poland, a geophysicist at HVO and a member of the Eos Editorial Advisory Board, to discuss how he and his colleagues communicated this threat to the public.
Drilling a Small Basaltic Volcano to Reveal Potential Hazards
Drilling into the Rangitoto Island Volcano in the Auckland Volcanic Field in New Zealand offers insight into a small monogenetic volcano, and may improve understanding of future hazards.
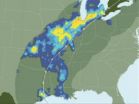
From AGU's journals: El Niño fades without westerly wind bursts
The warm and wet winter of 1997 brought California floods, Florida tornadoes, and an ice storm in the American northeast, prompting climatologists to dub it the El Niño of the century. Earlier this year, climate scientists thought the coming winter might bring similar extremes, as equatorial Pacific Ocean conditions resembled those seen in early 1997. But the signals weakened by summer, and the El Niño predictions were downgraded. Menkes et al. used simulations to examine the differences between the two years.
The El Niño-Southern Oscillation is defined by abnormally warm sea surface temperatures in the eastern Pacific Ocean and weaker than usual trade winds. In a typical year, southeast trade winds push surface water toward the western Pacific "warm pool"--a region essential to Earth's climate. The trade winds dramatically weaken or even reverse in El Niño years, and the warm pool extends its reach east.
Scientists have struggled to predict El Niño due to irregularities in the shape, amplitude, and timing of the surges of warm water. Previous studies suggested that short-lived westerly wind pulses (i.e. one to two weeks long) could contribute to this irregularity by triggering and sustaining El Niño events.
To understand the vanishing 2014 El Niño, the authors used computer simulations and examined the wind's role. The researchers find pronounced differences between 1997 and 2014. Both years saw strong westerly wind events between January and March, but those disappeared this year as spring approached. In contrast, the westerly winds persisted through summer in 1997.
In the past, it was thought that westerly wind pulses were three times as likely to form if the warm pool extended east of the dateline. That did not occur this year. The team says their analysis shows that El Niño's strength might depend on these short-lived and possibly unpredictable pulses.
INFORMATION:
The American Geophysical Union is dedicated to advancing the Earth and space sciences for the benefit of humanity through its scholarly publications, conferences, and outreach programs. AGU is a not-for-profit, professional, scientific organization representing more than 62,000 members in 144 countries. Join our conversation on Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, and other social media channels.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-11
The majority of people - including healthcare professionals - are unable to visually identify whether a person is a healthy weight, overweight or obese according to research by psychologists at the University of Liverpool.
Researchers from the University's Institute of Psychology, Health and Society asked participants to look at photographs of male models and categorise whether they were a healthy weight, overweight or obese according to World Health Organisation (WHO) Body Mass Index (BMI) guidelines.
They found that the majority of participants were unable to correctly ...
2014-11-11
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Tiny, thin microtubes could provide a scaffold for neuron cultures to grow so that researchers can study neural networks, their growth and repair, yielding insights into treatment for degenerative neurological conditions or restoring nerve connections after injury.
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and the University of Wisconsin-Madison created the microtube platform to study neuron growth. They posit that the microtubes could one day be implanted like stents to promote neuron regrowth at injury sites or to treat disease.
"This ...
2014-11-11
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Crop producers and scientists hold deeply different views on climate change and its possible causes, a study by Purdue and Iowa State universities shows.
Associate professor of natural resource social science Linda Prokopy and fellow researchers surveyed 6,795 people in the agricultural sector in 2011-2012 to determine their beliefs about climate change and whether variation in the climate is triggered by human activities, natural causes or an equal combination of both.
More than 90 percent of the scientists and climatologists surveyed said they ...
2014-11-11
Located hundreds of miles inland from the nearest ocean, the Midwest is unaffected by North Atlantic hurricanes.
Or is it?
With the Nov. 30 end of the 2014 hurricane season just weeks away, a University of Iowa researcher and his colleagues have found that North Atlantic tropical cyclones in fact have a significant effect on the Midwest. Their research appears in the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society.
Gabriele Villarini, UI assistant professor of civil and environmental engineering, studied the discharge records collected at 3,090 U.S. Geological Survey ...
2014-11-11
COLUMBIA, Mo. - Glycogen storage disorders, which affect the body's ability to process sugar and store energy, are rare metabolic conditions that frequently manifest in the first years of life. Often accompanied by liver and muscle disease, this inability to process and store glucose can have many different causes, and can be difficult to diagnose. Now, researchers at the University of Missouri who have studied enzymes involved in metabolism of bacteria and other organisms have catalogued the effects of abnormal enzymes responsible for one type of this disorder in humans. ...
2014-11-11
What if you researched your family's genealogy, and a mysterious stranger turned out to be an ancestor?
That's the surprising feeling had by a team of scientists who peered back into Europe's murky prehistoric past thousands of years ago. With sophisticated genetic tools, supercomputing simulations and modeling, they traced the origins of modern Europeans to three distinct populations.
The international research team published their September 2014 results in the journal Nature.
XSEDE, the Extreme Science and Engineering Discovery Environment, provided the computational ...
2014-11-11
Reston, Va. (November 11, 2014) - A novel study demonstrates the potential of a novel molecular imaging drug to detect and visualize early prostate cancer in soft tissue, lymph nodes and bone. The research, published in the November issue of the Journal of Nuclear Medicine, compares the biodistribution and tumor uptake kinetics of two Tc-99m labeled ligands, MIP-1404 and MIP-1405, used with SPECT and planar imaging.
Prostate cancer is the most commonly diagnosed non-skin cancer in the United States, and it is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer ...
2014-11-11
If you're a native of rural Mozambique who contracts HIV and becomes symptomatic, before seeking clinical testing and treatment, you'll likely consult a traditional healer.
Your healer may well conclude that your complaints are caused by a curse, perhaps placed upon you by a neighbor or by the spirit of an ancestor. To help you battle your predicament, the healer will likely cut your skin with a razor blade and rub medicinal herbs into the cut.
A recent survey of symptomatic HIV-positive people in rural Mozambique, led by Carolyn Audet, Ph.D., M.A., assistant professor ...
2014-11-11
New research from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health suggests that HIV-infected adults are at a higher risk for developing heart attacks, kidney failure and cancer. But, contrary to what many had believed, the researchers say these illnesses are occurring at similar ages as adults who are not infected with HIV.
The findings appeared online last month in the journal Clinical Infectious Diseases.
Researchers say these findings can help reassure HIV-infected patients and their health care providers.
"We did not find conclusive evidence to suggest that ...
2014-11-11
New Haven, Conn.--The phrase "tears of joy" never made much sense to Yale psychologist Oriana Aragon. But after conducting a series of studies of such seemingly incongruous expressions, she now understands better why people cry when they are happy.
"People may be restoring emotional equilibrium with these expressions," said Aragon, lead author of work to be published in the journal Psychological Science. "They seem to take place when people are overwhelmed with strong positive emotions, and people who do this seem to recover better from those strong emotions."
There ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] This Week From AGU: Volcano hazards and the role of westerly wind bursts in El Niño