(Press-News.org) A study by Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) researchers finds that body mass index (BMI) plays a role in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients' ability to achieve a sustained remission. Looking at patients who had received an RA diagnosis within the past 12 months, investigators found that those who were significantly underweight or overweight/obese were the least likely to remain in remission.
The study, titled, "Very Low or High Body Mass Index Negatively Affects Patients' Ability to Achieve Sustained Remission in Early RA in a Multicenter Canadian Cohort," was presented at the American College of Rheumatology annual meeting on November 16 in Boston.
Researchers set out to determine if early RA patients with a very low BMI ( END
Study: Rheumatoid arthritis patients' BMI linked to ability to stay in remission
Researchers find very low or high BMI makes it more difficult for rheumatoid arthritis patients to achieve sustained remission
2014-11-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study: Hip replacement an excellent option for young juvenile arthritis patients
2014-11-17
When you think of hip replacement surgery, you generally envision an older adult with painful osteoarthritis. But the procedure is also used for younger patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) whose joints have been severely damaged by the disease.
A new study by Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) researchers finds that total hip replacement (THR) is an excellent option for patients under age 35 when conservative treatments fail to provide relief.
The study, presented at the American College of Rheumatology annual meeting on November 16, found that hip replacement ...
Spiral laser beam creates quantum whirlpool
2014-11-17
Physicists have engineered a spiral laser beam and used it to create a whirlpool of hybrid light-matter particles called polaritons.
"Creating circulating currents of polaritons - vortices - and controlling them has been a long-standing challenge," said leader of the team, theoretician Dr Elena Ostrovskaya, from the Research School of Physics and Engineering at The Australian National University (ANU).
"We can now create a circulating flow of these hybrid particles and sustain it for hours."
Polaritons are hybrid particles that have properties of both matter and light. ...
DAPT study favored 30 over 12 months of DAPT for lower clot and heart attack risk
2014-11-17
CHICAGO and BOSTON - Nov. 16, 2014 - The Harvard Clinical Research Institute (HCRI) announced today results of the DAPT Study, a major international study that investigated the duration of dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT, the combination of aspirin and a thienopyridine/antiplatelet medication to reduce the risk of blood clots) following coronary stent implantation. The continuation of dual antiplatelet therapy beyond one year resulted in significant benefits compared with aspirin alone, including reducing the rare but serious problem of stent thrombosis and preventing heart ...
Extinction risk not the answer for reef futures
2014-11-17
Leading coral reef scientists in Australia and the USA say there needs to be a new approach to protecting the future of marine ecosystems, with a shift away from the current focus on extinction threat.
"Extinction is the final endpoint, but coral reefs are in deep trouble long before we get to that point. We need to take action much earlier," says Professor David Bellwood from the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies (Coral CoE) at James Cook University.
"The goal should be to maintain reefs that can support corals, fish and humans" Professor Bellwood says.
In ...
Readying the neural network
2014-11-17
VIDEO:
The neurons in this video contain a dye that fluoresces when it encounters calcium ions. When the neuron is excited, calcium floods into the cell and the neuron fluoresces. The...
Click here for more information.
Synapse, the name for the signal-receiving site on a neuron, comes from the Greek word for contact. Neuroscientists used to maintain that neurons form one-to-one relationship to contact one another. Yet more researchers are finding evidence that shows how neurons ...
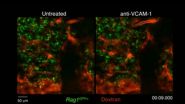
Infection-fighting B cells go with the flow
2014-11-17
VIDEO:
The movement of bone marrow B cells was limited in the absence of VCAM-1, as shown in this time-lapse video. B cells (green) were tracked before (left) and after (right)...
Click here for more information.
Newly formed B cells take the easy way out when it comes to exiting the bone marrow, according to a study published in The Journal of Experimental Medicine.
For infection-fighting T and B cells to defend the body, they must first leave their birthplace--the thymus for ...
Chlamydia knock out the body's own cancer defence
2014-11-17
This news release is available in German.
Infections due to the sexually transmitted bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis often remain unnoticed. The pathogen is not only a common cause of female infertility; it is also suspected of increasing the risk of abdominal cancer. A research team at the Max Planck Institute for Infection Biology in Berlin has now observed the breakdown of an important endogenous protective factor in the course of chlamydial infection. By activating the destruction of p53 protein, the bacterium blocks a key protective mechanism of infected cells, ...
Less sex plus more greens equals a longer life
2014-11-17
Doctors tell us that the frenzied pace of the modern 24-hour lifestyle -- in which we struggle to juggle work commitments with the demands of family and daily life -- is damaging to our health. But while life in the slow lane may be better, will it be any longer? It will if you're a reptile.
A new study by Tel Aviv University researchers finds that reduced reproductive rates and a plant-rich diet increases the lifespan of reptiles. The research, published in the journal Global Ecology and Biogeography, was led by Prof. Shai Meiri, Dr. Inon Scharf, and doctoral student ...
Climate capers of the past 600,000 years
2014-11-17
If you want to see into the future, you have to understand the past. An international consortium of researchers under the auspices of the University of Bonn has drilled deposits on the bed of Lake Van (Eastern Turkey) which provide unique insights into the last 600,000 years. The samples reveal that the climate has done its fair share of mischief-making in the past. Furthermore, there have been numerous earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. The results of the drilling project also provide a basis for assessing the risk of how dangerous natural hazards are for today's population. ...
Danger of repeat head injuries: Brain's inability to tap energy source
2014-11-17
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Two or more serious hits to the head within days of each other can interfere with the brain's ability to use sugar - its primary energy source - to repair cells damaged by the injuries, new research suggests.
The brain's ability to use energy is critical after an injury. In animal studies, Ohio State University scientists have shown that brain cells ramp up their energy use six days after a concussion to recover from the damage. If a second injury occurs before that surge of energy use starts, the brain loses its best chance to recover.
In mice, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Study: Rheumatoid arthritis patients' BMI linked to ability to stay in remissionResearchers find very low or high BMI makes it more difficult for rheumatoid arthritis patients to achieve sustained remission