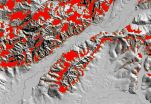
People's movement perturbed during, but similar after Hurricane Sandy
NYC residents resumed 'normal' mobility less than 24 hours after Hurricane Sandy
2014-11-19
(Press-News.org) New York City residents' movement around the city was perturbed, but resumed less than 24-hours after Hurricane Sandy, according to a study published November 19, 2014 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Qi Wang and John Taylor from Virginia Tech.
Tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons, are severe natural disasters that can cause tremendous loss of human life and suffering. Our knowledge of peoples' movements during natural disasters is so far limited due to a lack of data. The authors of this article studied human mobility using movement data from individuals active on Twitter in New York City for 12 days during and after Hurricane Sandy in 2012. They analyzed location data attached to over 700,000 tweets from over 53,000 people and mapped each location during 24-hour periods over the 12 days.
The researchers observed that peoples' locations covered nearly the entire mapped area and showed similar geographical and statistical distributions to 24-hour periods soon after the hurricane, including areas subject to mandatory evacuation. These results may indicate that New Yorkers were relatively resilient in terms of human mobility during Hurricane Sandy. While resilience could be vital for the city's post-disaster response and recovery, it may also be dangerous if people are moving through mandated evacuation areas during or immediately following extreme weather events like a hurricane. Understanding nuances of human mobility under the influence of such disasters will enable more effective evacuation, emergency response planning, and development of strategies and policies to minimize human fatality, injury, and economic loss.
INFORMATION:
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper: http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0112608
Citation: Wang Q, Taylor JE (2014) Quantifying Human Mobility Perturbation and Resilience in Hurricane Sandy. PLoS ONE 9(11): e112608. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0112608
Funding: This study is supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 1142379. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation. Open access publication of this article was supported by Virginia Tech's Open Access Subvention Fund. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-19
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Engineers have created a new way to use lidar technology to identify and classify landslides on a landscape scale, which may revolutionize the understanding of landslides in the U.S. and reveal them to be far more common and hazardous than often understood.
The new, non-subjective technology, created by researchers at Oregon State University and George Mason University, can analyze and classify the landslide risk in an area of 50 or more square miles in about 30 minutes - a task that previously might have taken an expert several weeks to months. It can ...
2014-11-19
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. -- A new study by a Florida State University biologist shows that bleaching events brought on by rising sea temperatures are having a detrimental long-term impact on coral.
Professor Don Levitan, chair of the Department of Biological Science, writes in the latest issue of Marine Ecology Progress Series that bleaching -- a process where high water temperatures or UV light stresses the coral to the point where it loses its symbiotic algal partner that provides the coral with color -- is also affecting the long-term fertility of the coral.
"Even corals ...
2014-11-19
New research has found that one of the world's most prolific bacteria manages to afflict humans, animals and even plants by way of a mechanism not before seen in any infectious microorganism -- a sense of touch. This unique ability helps make the bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa ubiquitous, but it also might leave these antibiotic-resistant organisms vulnerable to a new form of treatment.
Pseudomonas is the first pathogen found to initiate infection after merely attaching to the surface of a host, Princeton University and Dartmouth College researchers report in the journal ...
2014-11-19
A social sensing game created at Illinois allows researchers to study natural interactions between children, collect large amounts of data about those interactions and test theories about youth aggression and victimization.
The game's behavior analyses effectively identify classroom bullies, even revealing peer aggression that goes undetected by traditional research methods, the researchers say.
The game's developers say it is an improvement over traditional research methods, such as questionnaires, which do not assess interactions between youth in real time.
"What ...
2014-11-19
When the mouse and human genomes were catalogued more than 10 years ago, an international team of researchers set out to understand and compare the "mission control centers" found throughout the large stretches of DNA flanking the genes. Their long-awaited report, published Nov. 19 in the journal Nature suggests why studies in mice cannot always be reproduced in humans. Importantly, the scientists say, their work also sheds light on the function of DNA's regulatory regions, which are often to blame for common chronic human diseases.
"Most of the differences between mice ...
2014-11-19
Microbiologists at NYU Langone Medical Center say they have what may be the first strong evidence that the natural presence of viruses in the gut -- or what they call the 'virome' -- plays a health-maintenance and infection-fighting role similar to that of the intestinal bacteria that dwell there and make up the "microbiome."
In a series of experiments in mice that took two years to complete, the NYU Langone team found that infection with the common murine norovirus, or MNV, helped mice repair intestinal tissue damaged by inflammation and helped restore the gut's immune ...
2014-11-19
For years, scientists have considered the laboratory mouse one of the best models for researching disease in humans because of the genetic similarity between the two mammals. Now, researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine have found that the basic principles of how genes are controlled are similar in the two species, validating the mouse's utility in clinical research.
However, there are important differences in the details of gene regulation that distinguish us as a species.
"At the end of the day, a lot of the genes are identical between a mouse and ...
2014-11-19
For more than a century, the laboratory mouse (Mus musculus) has stood in for humans in experiments ranging from deciphering disease and brain function to explaining social behaviors and the nature of obesity. The small rodent has proven to be an indispensable biological tool, the basis for decades of profound scientific discovery and medical progress.
But in new findings published online Nov. 19 in the journal Nature, researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine and Ludwig Cancer Research, with colleagues across the country and world, have ...
2014-11-19
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. -- A new line of research from a team at Florida State University is pushing the limits on what the world knows about how human genetic material is replicated and what that means for people with diseases where the replication process is disrupted, such as cancer.
The team, lead by Department of Biological Sciences Professor David Gilbert and post-doctoral researcher Ben Pope, has taken an in-depth look at how DNA and the associated genetic material replicate and organize within a cell's nucleus. Their work could be especially crucial for doctors and ...
2014-11-19
BOSTON - November 19, 2014 - Each year in the Northern Hemisphere, levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) drop in the summer as plants inhale, and then climb again as they exhale and decompose after their growing season. Over the past 50 years, the size of this seasonal swing has increased by as much as half, for reasons that aren't fully understood. Now a team of researchers led by Boston University scientists has shown that agricultural production may generate up to a quarter of the increase in this seasonal carbon cycle, with corn playing a leading role.
"In the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] People's movement perturbed during, but similar after Hurricane Sandy
NYC residents resumed 'normal' mobility less than 24 hours after Hurricane Sandy