(Press-News.org) Parents and family make all the difference in creating the next generation of scientists, engineers and mathematicians, according to new research by George Mason University.
"We were surprised to learn that the family is more important than we ever thought in terms of igniting the passion of future scientists," says Lance Liotta, a study author and co-director of George Mason's Center for Applied Proteomics and Molecular Medicine.
The study, featured in CBE-Life Sciences Education, is the first peer-reviewed article of its kind to focus on what initially attracts young people to the science, technology, engineering and math (STEM) fields. The findings could shape public policy and encourage community-centered activities designed to foster a love for science in the pre-teen and preschool crowd, says Amy Adams, director of Mason's Aspiring Scientists Summer Internship Program and study co-author, along with Mason researchers Cara L. Frankenfeld, Jessica Bases and Virginia Espina.
The research team surveyed 149 participants in the Aspiring Scientists Summer Internship Program from classes from 2007 to 2013. This competitive internship attracts top high school and undergraduate students who work alongside Mason professors on real-world research.
The majority--65.5 percent--said science experiences with a family member or a childhood activity piqued their initial interest. Hands-down, 92.6 percent, of the students said hands-on lab experience cemented their decision to make a career in a STEM field.
Researchers say the message is clear: families play the leading role in building the next generation of scientists who may solve daunting problems facing our society. Only after the family, do schools and even colleges play a supporting role.
"As a mom of three children, I am inspired by the Aspiring Scientists' recollections of what initially got them interested in science," Adams says. "When I watch my two-year-old sit in a sea of blocks building creative structures or when his 10-year-old brother is amazed by the results of his chemistry experiment in the kitchen, I recognize, more than ever, that experiences like these may shape their interests in the future."
Liotta says the holiday season is a great time to play.
"I have four grandchildren and love to work on science projects with them during the holidays and on summer vacations," Liotta says. "Among many of the fun memories, we have made autonomous robots and held robot wars at Thanksgiving. We have also tested new micro airplanes and radio-controlled butterflies, and studied the behavior of cicadas."
The researchers recommend science gifts for the holiday season to help fuel the imagination of future scientists. Family activities are another way to inspire future scientists, the researchers say.
"Parents who see the spark of science talent in their kids should reinforce that talent through family projects and nature walks," says College of Science Dean Peggy Agouris.
INFORMATION:
Cool Science-Inspired Gifts:
Biology/Medicine: microscope, human body anatomy toy, insect farm, DNA extraction kit
Chemistry: slime lab kit, crystal-growing kit, chemistry set
Astronomy/Space Exploration: telescope, meteorite excavation kit
Environment/Weather: alternative energy kit, weather lab
Physics/Engineering: blocks, electrical circuits, robotics
Family Fun Things to Do During Winter Break
Visit a museum
Watch science-inspired television shows
Perform hands-on science experiments at home
Attend a science camp, class or party
Visit a nature park
Read science-inspired books
Play with interactive science apps
Practice coding skills with free online tools
AMHERST, Mass. - Using a new approach for determining the age at sexual maturity for wild stocks of western Atlantic bluefin tuna, researchers led by Molly Lutcavage of the University of Massachusetts Amherst and Gilad Heinisch of Israel's Oceanographic and Limnological Research Center, suggest that these fish mature at a considerably younger age than cuurently assumed. These findings could lead to changes in how fisheries scientists estimate the population.
Lutcavage says, "Whether a bluefin tuna or cod, for realistic fish stock assessments it's important to know at ...
December 2, 2014 - Now you don't even have live in Estonia to open a business there. A new program lets people purchase e-signatures that enable them to open bank accounts and run a domestic business without being physically present. But according to new research, people may not have the same trust in such businesses as they would others. A new paper finds that people are much more likely to discount the validity of an e-signature than a hand-signed document.
"Although e-signatures provide greater efficiency and convenience, they just seem a bit inauthentic," says Eileen ...
LOS ANGELES (Dec. 1, 2014) - Research scientists have developed a novel method to re-create brain and intestinal stem cells from patients who died decades ago, using DNA from stored blood samples to study the potential causes of debilitating illnesses such as inflammatory bowel disease.
The lab research, published in the journal STEM CELLS Translational Medicine, could yield new therapies for people who suffer from aggressive motor-neuron and gut-related conditions that proved fatal to the deceased patients who long-ago volunteered their blood samples.
"The potential ...
Philadelphia, PA, December 1, 2014 - "Triple-negative" breast cancer (TNBC) occurs in patients whose cells do not express receptors for estrogen, progesterone, and/or human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (ER/PR/HER2). Because of the absence of these predictive biomarkers, treatment assignment can be difficult. Now, researchers report that high levels of the microRNA miR-21 in the tumor microenvironment, but not in the tumor epithelia (cancer cells), are associated with worse clinical outcomes for patients with TNBC, thus identifying a possible ...
Research at the University of Adelaide has discovered cancer cells may be particularly susceptible to metabolic stress - opening the way for new targeted therapy that won't harm normal cells.
The researchers showed that chromosomal instability - which is a hallmark of rapidly dividing cancer cells - makes them stressed and vulnerable to mild metabolic disruption. Metabolism is the normal process by which the body turns food into energy.
"A common problem in treating cancers is that they don't respond to chemotherapy, or they respond for a while, but then come back," ...
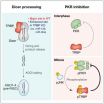
The research team of the Center for RNA Research at IBS has succeeded in revealing that the dsRNAs and Protein Kinase R (PKR) regulate division of mammalian cells.
This finding will provide important clues to understanding the process of tumor formation and the mechanism for suppressing cancer since the abnormal cell division marks the early events of cancer development.
For the first time, the IBS research team has found that during mitosis, the cellular dsRNAs activate PKR, an enzyme previously known as a trigger of immune response during virus infection. Activated ...
Inflammatory skin diseases such as psoriasis may result from abnormal activation of cell death pathways previously believed to suppress inflammation, a surprise finding that could help to develop new ways of treating these diseases.
Mr James Rickard, Associate Professor John Silke and colleagues from the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute made the discovery while investigating how cell death pathways are linked to inflammatory disease development. The study was published today in the journal eLife.
Infected cells, cancerous cells, or those that are simply unnecessary to ...
Vitamin D deficiency is not just harmful to physical health--it also might impact mental health, according to a team of researchers that has found a link between seasonal affective disorder, or SAD, and a lack of sunlight.
"Rather than being one of many factors, vitamin D could have a regulative role in the development of SAD," said Alan Stewart of the University of Georgia College of Education.
An international research partnership between UGA, the University of Pittsburgh and the Queensland University of Technology in Australia reported the finding in the November ...
URBANA, Ill. - A 12-year University of Illinois study shows that, although the use of cover crops does not improve crop yields, the practice does increase the amount of sequestered soil organic carbon using three different soil management systems.
U of I soil scientist Ken Olson evaluated plots that were subjected to no-till, chisel plow and moldboard plow treatments with and without hairy vetch and cereal rye cover crops.
"By 2012, we found that the soil tillage plots that had cover-crop treatments had more soil organic carbon stock than those without cover crops ...
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Most patients with triple-negative breast cancer should undergo genetic testing for mutations in known breast cancer predisposition genes, including BRCA1 and BRCA2, a Mayo Clinic-led study has found. The findings come from the largest analysis to date of genetic mutations in this aggressive form of breast cancer. The results of the research appear in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
"Clinicians need to think hard about screening all their triple-negative patients for mutations because there is a lot of value in learning that information, both in ...