Light propagation in solar cells made visible
2014-12-05
(Press-News.org) This news release is available in German.
How can light which has been captured in a solar cell be examined in experiments? Jülich scientists have succeeded in looking directly at light propagation within a solar cell by using a trick. The photovoltaics researchers are working on periodic nanostructures that efficiently capture a portion of sunlight which is normally only poorly absorbed.
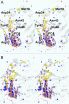
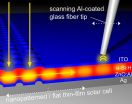
Until recently, light trapping within periodically nanostructured solar cells could only be analysed using indirect methods, as captured light is not visible from outside of the solar cell. However, the quantum mechanical tunnelling effect of light allows it to be tracked if a light-conducting component is brought extremely close to the cell's surface. Through use of a glass fibre tip, the researchers were able to measure the amount of light that had actually been captured in the solar cell using a method called near-field optical microscopy.
Light trapping plays a particular important role in optimizing thin-film solar cells. These solar cells are easier to manufacture and require less material than conventional crystalline solar cells, but they are not yet as efficient. The layer in which energy conversion takes place is only about one thousandth of a millimetre thick. Therefore, longer wavelengths in the infrared region are only poorly absorbed when the cell is exposed to direct sunlight.
Periodically nanopatterned interface layers allow for better absorption of the incident light. These interfaces couple incident light into the thin silicon layer. Based on the new experimental approach, scientists from the Institute of Energy and Climate Research at Forschungszentrum Jülich showed that there is a direct link between the nature of the nanostructure, the absorption of specific wavelengths of light, and in particular the efficiency of the solar cell. The approach, presented in the specialist journal Nano Letters (DOI: 10.1021/nl503249n), also opens a range of new possibilities for investigating applied nano-optical components.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-05
Radio frequency identification (RFID) tags--devices that can transmit data over short distances to identify objects, animals or people--have become increasingly popular for tracking everything from automobiles being manufactured on an assembly line to zoo animals in transit to their new homes. Now, thanks to a new NIST report, the next beneficiaries of RFID technology may soon be law enforcement agencies responsible for the management of forensic evidence.
A typical RFID system consists of a microchip programmed with identifying data--the "tag"--and a two-way radio transmitter-receiver, ...
2014-12-05
A study of more than 9,000 men with fertility problems has revealed a correlation between the number of different defects in a man's semen and the likelihood that the man has other health problems.
The study, conducted by investigators at the Stanford University School of Medicine, also links poor semen quality to a higher chance of having various specific health conditions, such as hypertension, and more generally to skin and endocrine disorders.
The findings, to be published online Dec. 10 in Fertility and Sterility, may spur more-comprehensive approaches to treating ...
2014-12-05
Nagoya, Japan - Professor Stephan Irle and Yoshio Nishimoto at the Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules (ITbM) of Nagoya University and Dr. Dmitri Fedorov of the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST, Tsukuba) have developed a novel ultrafast quantum chemical method enabling rapid simulations of molecules containing more than a million atoms without detrimental loss in accuracy. This method consists of a combination of the Fragment Molecular Orbital (FMO) approach and the Density-Functional Tight-Binding (DFTB) method, called FMO-DFTB ...
2014-12-05
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- A "Viewpoint" published in JAMA urges readers to be patient with the new federal Open Payments Program database. The site, designed to report drug and device industry payments to physicians, debuted substantially incomplete, the authors wrote, but it is too important to dismiss before its shortcomings are addressed.
"Viewed in the abstract, the value inherent in the transparency offered by the OPP database is beyond dispute," wrote Dr. Eli Y. Adashi, former dean of medicine and biological sciences at Brown University, and Sachin ...
2014-12-05
A research team led by physicists at the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee (UWM) has proven a method that makes it possible to find the atomic structure of proteins in action by producing "snapshots" of them with unprecedented spatial and temporal resolution.
What made it possible were the ultra-short X-ray pulses of a Free Electron Laser (XFEL).
Physics professor Marius Schmidt and doctoral student Jason Tenboer recently completed the experiment with the XFEL at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC) in California.
It confirms that the XFEL imaging method, ...
2014-12-05
LOS ANGELES (Dec. 4, 2014) - Genetics may play a larger role in causing Lou Gehrig's disease than previously believed, potentially accounting for more than one-third of all cases, according to one of the most comprehensive genetic studies to date of patients who suffer from the condition also known as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS.
The study, conducted by investigators at Cedars-Sinai and Washington University in St. Louis, also showed that patients with defects in two or more ALS-associated genes experience disease onset about 10 years earlier than patients ...
2014-12-05
A team of scientists that included researchers from UCLA has discovered a novel mechanism of RNA regulation in embryonic stem cells. The findings are strong evidence that a specific chemical modification, or "tag," on RNA plays a key role in determining the ability of embryonic stem cells to adopt different cellular identities.
The team also included scientists from Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital and Stanford University.
Published in the journal Cell Stem Cell, the research reveals that depleting or knocking out a key component of the machinery ...
2014-12-05
Friday, December 5, 2014 - London, UK - The Biogerontology Research Foundation (BGRF), a UK-based charity founded to support ageing research and address the challenges of a rapidly ageing population, will present new economic longevity research at the second Big Data Science in Medicine congress in Oxford on December 8.
The research, "Longevity expectations in the pension fund, insurance, and employee benefits industry", was recently published in the open-access journal Psychology Research and Behavior Management, and details an extensive survey of International Employee ...
2014-12-05
A group of UCL researchers (Louvain Drug Research Institute) identified an unsuspected mechanism impacting the development of obesity and diabetes type 2 after following a diet with a high dose of fat nutrition. The team of Professor Patrice D. Cani - in direct collaboration with two French teams, a Swedish expert as well as other UCL-researchers (LDRI and Ludwig Institute) - made an important discovery related to the essential role of the intestinal immune system regarding the control of the energy metabolism.
Today, the work of Doctor Amandine Everard (in charge of ...
2014-12-05
Vienna, Austria - 5 December 2014: New 3D printed heart technology could reduce the number of heart surgeries in children with congenital heart disease, according to Dr Peter Verschueren who spoke on the topic today at EuroEcho-Imaging 2014.1 Dr Verschueren brought 3D printed models of the heart to his lecture including models used to plan real cases in patients.
EuroEcho-Imaging is the annual meeting of the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI), a branch of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), and is held 3-6 December in Vienna, Austria.
Dr Verschueren ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Light propagation in solar cells made visible