(Press-News.org) There are strong economic incentives for governments to invest in early childhood nutrition, reports a new paper from the University of Waterloo and Cornell University. Published for the Copenhagen Consensus Centre, the paper reveals that every dollar spent on nutrition during the first 1,000 days of a child's life can provide a country up to $166 in future earnings.
"The returns on investments in nutrition have high benefit-cost ratios, especially in countries with higher income levels and a growing economy," said Professor Susan Horton, of the School of Public Health and Health Systems and the Department of Economics at Waterloo.
Children who are undernourished during the first 1,000 days of their lives typically show stunted growth patterns by the age of three and have poorer cognitive skills than their well-fed peers. As adults they are less educated, earn lower wages and have more health problems throughout their lives.
"Height-for-age is a much better measure of health than weight-for-age. It is also predictive of economic outcomes," said Professor Horton, also chair in global health economics at the Centre for International Governance Innovation. She analyzed height and income data from a longitudinal nutrition study from Guatemala for the report. "Good childhood nutrition produces people who can contribute more and help boost economic growth."
Studies of a range of low- and middle-income countries suggest that 1 cm more of adult height for men is associated with an increase in their earnings of 2.4 per cent.
"Over an adult's working life, we can expect that one dollar spent on early childhood nutrition will on average have $45 worth of benefits in low and middle-income countries," said Horton.
The paper looked at the effects of stunting on low- and middle-income countries such as Ethiopia, Kenya, Yemen and India. The cost-benefit ratio was the greatest in Indonesia, where every dollar spent on early childhood nutrition could provide the country $166 in future earnings.
"It really is a compelling economic argument for nutrition interventions," said Horton. "If we can reduce stunting through better early nutrition, we can improve quality of life not only for individuals, but nations as a whole."
Currently, the World Health Organization is aiming to reduce stunting among children under age five by 40 per cent as part of its 2025 nutrition goals, and it is widely expected that the rate of stunting will also be included in its Sustainable Development Goals, which will be announced in 2015.
INFORMATION:
To view the study, please visit http://www.copenhagenconsensus.com/post-2015-consensus/nutrition
Older Latinos living in the U.S. who perceive their neighborhoods as safer and more walkable are less likely to develop severe depressive symptoms, and the effect may be long term, a new study suggests.
Researchers examined links between the onset of depressive symptoms in 570 older Latino adults and various characteristics of the Greater Los Angeles neighborhoods they lived in, including crime, the availability and quality of sidewalks, traffic safety and aesthetics.
Participants ranged in age from 60 to 90, and 351 of them screened positive for low levels of depression ...
The opioid pain-reliever tramadol appears to be associated with an increased risk of hospitalization for hypoglycemia, a potentially fatal condition caused by low blood sugar, according to a report published online by JAMA Internal Medicine.
Tramadol hydrochloride is a weak opioid whose use has increased steadily worldwide. However, concerns have been raised about the drug and an increased risk for hypoglycemia.
Because of increasing use of the doctor-prescribed pain reliever, researchers at McGill University and the Lady Davis Institute at the Jewish General Hospital ...
LOS ANGELES - (Dec. 8, 2014) - In the U.S. and around the globe, skin and soft tissue infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) continue to endanger the health and lives of patients and otherwise healthy individuals.
Treatment is difficult because MRSA is resistant to many antibiotics, and the infections can recur, placing family members and other close contacts at risk of infection.
A study reported online today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA holds new hope for preventing or reducing the severity of infections ...
Everyday events are easy to forget, but unpleasant ones can remain engraved in the brain. A new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences identifies a neural mechanism through which unpleasant experiences are translated into signals that trigger fear memories by changing neural connections in a part of the brain called the amygdala. The findings show that a long-standing theory on how the brain forms memories, called Hebbian plasticity, is partially correct, but not as simple as was originally proposed.
The effort led by Joshua Johansen from ...
A new genetic therapy not only helped blind mice regain enough light sensitivity to distinguish flashing from non-flashing lights, but also restored light response to the retinas of dogs, setting the stage for future clinical trials of the therapy in humans.
The therapy employs a virus to insert a gene for a common ion channel into normally blind cells of the retina that survive after the light-responsive rod and cone photoreceptor cells die as a result of diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa. Photoswitches - chemicals that change shape when hit with light -are then ...
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. (December 8, 2014) - Long known for its ability to help organisms successfully adapt to environmentally stressful conditions, the highly conserved molecular chaperone heat-shock protein 90 (HSP90) also enables estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancers to develop resistance to hormonal therapy.
This HSP90-mediated evolutionary mechanism of drug resistance, reported by Whitehead Institute scientists in this week's online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), provides a strong therapeutic rationale for combining HSP90 ...
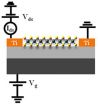
Two-dimensional (2D) layered materials are now attracting a lot of interest due to their unique optoelectronic properties at atomic thicknesses. Among them, graphene has been mostly investigated, but the zero-gap nature of graphene limits its practical applications. Therefore, 2D layered materials with intrinsic band gaps such as MoS2, MoSe2, and MoTe2 are of interest as promising candidates for ultrathin and high-performance optoelectronic devices.
Here, Pil Ju Ko and colleagues at Toyohashi University of Technology, Japan have fabricated back-gated field-effect phototransistors ...
Hummingbirds' remarkable ability to hover in place is highly contingent on the tiny bird having a completely stationary visual field, according to University of British Columbia research published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
UBC zoologists Benjamin Goller and Douglas Altshuler projected moving spiral and striped patterns in front of free-flying hummingbirds attempting to feed from a stationary feeder.
Even minimal background pattern motion caused the hummingbirds to lose positional stability and drift. Giving the birds time to get used ...
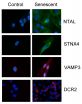
A new advance in biomedical research at the University of Leicester could have potential in the future to assist with tackling diseases and conditions associated with ageing - as well as in treating cancer.
The research, which has shown promise in clinical samples, has been published in the prestigious scientific journal, Cell Death and Disease.
The group of scientists coordinated by Dr Salvador Macip from the Mechanisms of Cancer and Ageing Lab and the Department of Biochemistry of the University of Leicester carried out the study to find new ways of identifying old ...
You don't have to be a jerk to come up with fresh and original ideas, but sometimes being disagreeable is just what's needed to sell your brainchild successfully to others. However, difficult or irritating people should be aware of the social context in which they are presenting their ideas. A pushy strategy will not always be equally successful, warn Samuel Hunter of Pennsylvania State University and Lily Cushenbery of Stony Brook University in the US, in an article in Springer's Journal of Business and Psychology.
People are often labelled as jerks if they are disagreeable ...