Survey of primary care physicians' beliefs on prescription drug abuse
2014-12-08
(Press-News.org) A survey of primary care physicians found the vast majority of practicing internists, family physicians and general practitioners consider prescription drug abuse to be a significant problem in their community and most physicians agreed opioids were overused to treat pain, according to a research letter published online by JAMA Internal Medicine.
Primary care physicians are critical in maximizing the safe use of opioid pain-relieving medications. It is because of this that Catherine S. Hwang, M.S.P.H., of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, and co-authors wanted to know more about physician beliefs and their self-reported prescribing practices for opioids. The authors conducted a nationally representative mail survey, resulting in 420 respondents.
The survey found that among physicians:
90 percent reported prescription drug abuse to be a "big" or "moderate" problem in their community
85 percent reported opioids are overused in clinical practice
45 percent reported being less likely to prescribe opioids compared with a year ago
"Our investigation suggests that most primary care physicians are aware of many risks of opioids and many have decreased their prescribing of these products during the past 12 months," the research letter concludes.
INFORMATION:
(JAMA Intern Med. Published online December 8, 2014. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.6520. Available pre-embargo to the media at http://media.jamanetwork.com.)
Editor's Note: Authors made conflict of interest disclosures. This work was supported by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Public Health Law Research Program and the Lipitz Public Health Policy Fund Award from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, financial disclosures, funding and support, etc.
Media Advisory: To contact corresponding author G. Caleb Alexander, M.D., M.S., call Stephanie Desmon at 410-955-7619 or email sdesmon1@jhu.edu.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-08
Smoking water pipe tobacco from hookahs and using the smokeless tobacco snus were associated with initiating cigarette smoking and smoking cigarettes in the past 30 days among previously nonsmoking teenagers and young adults, according to a study published online by JAMA Pediatrics.
The Food and Drug Administration regulates cigarettes, loose tobacco and smokeless tobacco products. However, the FDA does not regulate the manufacturing, distribution and marketing of other tobacco products, such as water pipe tobacco, and many of those products are used by teenagers and ...
2014-12-08
Salt Lake City - Develop 100 drugs in 10 years. That's the ambitious goal set by a group of scientists and engineers at the University of Utah, founders of Recursion Pharmaceuticals, a start-up company that is able to quickly and affordably identify unexpected ways a drug could be used by testing it on diseased cells.
The disruptive approach to drug development, aided by custom-designed software capable of tracking changes, or signs of healing, in cells, could speed discovery of therapies for so-called "orphan" diseases.
Scientists at Recursion have already identified ...
2014-12-08
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) -- Children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) were more than twice as likely to have been exposed in utero to preeclampsia, and the likelihood of an autism diagnosis was even greater if the mother experienced more severe disease, a large study by researchers with the UC Davis MIND Institute has found.
Women with preeclampsia experience hypertension during the latter half of their pregnancies, and may have increased levels of protein in their urine and edema, or fluid retention. Preeclampsia can develop into eclampsia, a life-threatening condition ...
2014-12-08
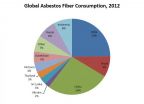
New York, NY, December 8, 2014 - Challenges to global health can evolve from policies and decisions that take years or decades to unfold. An article in the current issue of the Annals of Global Health describes the current state of asbestos use worldwide, a story that began over 100 years ago, and the real and contrived controversies regarding asbestos.
At the peak of asbestos use in 1972 in the United States, more than 775,000 tons of asbestos were used, much of it by the construction trades and shipbuilding industry, in addition to the manufacturing of many consumer ...
2014-12-08
There are strong economic incentives for governments to invest in early childhood nutrition, reports a new paper from the University of Waterloo and Cornell University. Published for the Copenhagen Consensus Centre, the paper reveals that every dollar spent on nutrition during the first 1,000 days of a child's life can provide a country up to $166 in future earnings.
"The returns on investments in nutrition have high benefit-cost ratios, especially in countries with higher income levels and a growing economy," said Professor Susan Horton, of the School of Public Health ...
2014-12-08
Older Latinos living in the U.S. who perceive their neighborhoods as safer and more walkable are less likely to develop severe depressive symptoms, and the effect may be long term, a new study suggests.
Researchers examined links between the onset of depressive symptoms in 570 older Latino adults and various characteristics of the Greater Los Angeles neighborhoods they lived in, including crime, the availability and quality of sidewalks, traffic safety and aesthetics.
Participants ranged in age from 60 to 90, and 351 of them screened positive for low levels of depression ...
2014-12-08
The opioid pain-reliever tramadol appears to be associated with an increased risk of hospitalization for hypoglycemia, a potentially fatal condition caused by low blood sugar, according to a report published online by JAMA Internal Medicine.
Tramadol hydrochloride is a weak opioid whose use has increased steadily worldwide. However, concerns have been raised about the drug and an increased risk for hypoglycemia.
Because of increasing use of the doctor-prescribed pain reliever, researchers at McGill University and the Lady Davis Institute at the Jewish General Hospital ...
2014-12-08
LOS ANGELES - (Dec. 8, 2014) - In the U.S. and around the globe, skin and soft tissue infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) continue to endanger the health and lives of patients and otherwise healthy individuals.
Treatment is difficult because MRSA is resistant to many antibiotics, and the infections can recur, placing family members and other close contacts at risk of infection.
A study reported online today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA holds new hope for preventing or reducing the severity of infections ...
2014-12-08
Everyday events are easy to forget, but unpleasant ones can remain engraved in the brain. A new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences identifies a neural mechanism through which unpleasant experiences are translated into signals that trigger fear memories by changing neural connections in a part of the brain called the amygdala. The findings show that a long-standing theory on how the brain forms memories, called Hebbian plasticity, is partially correct, but not as simple as was originally proposed.
The effort led by Joshua Johansen from ...
2014-12-08
A new genetic therapy not only helped blind mice regain enough light sensitivity to distinguish flashing from non-flashing lights, but also restored light response to the retinas of dogs, setting the stage for future clinical trials of the therapy in humans.
The therapy employs a virus to insert a gene for a common ion channel into normally blind cells of the retina that survive after the light-responsive rod and cone photoreceptor cells die as a result of diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa. Photoswitches - chemicals that change shape when hit with light -are then ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Survey of primary care physicians' beliefs on prescription drug abuse