(Press-News.org) Online content creation has become easier than ever and is quickly reaching parity with content consumption. From writing a blog or social media post to letting an app turn your photos into a video montage, anyone with an Internet connection can publish these creations with the click of a button.
But in the age of Web publishing, it has become increasingly confusing for content creators to figure out how to protect their original works or to use other content legally -- such as for remixes or parodies -- on major websites for user-generated content, including YouTube and DeviantArt. These findings are from a new Georgia Tech study that found that copyright is a frequent topic of conversation -- and confusion -- in eight of the most popular creative online communities worldwide, which collectively have some 20 million publicly available forum posts on their sites.
The study notes that copyright law is navigated on a daily basis by Internet users, and that for amateur creative types publishing on the Web's largest creative venues, they often don't trust the websites to safeguard their art. The findings include user concerns about whether the websites can prevent others from copying their work without permission or outright pirating or plagiarizing. On the other end of the spectrum are those who want to legally reuse and remix content online but have no clear path on how to pursue this option. When seeking advice on when they are allowed to appropriate or remix content, users are sometimes discouraged from doing so, either by website policies or by other users interpreting the law too strictly. Researchers say this acts as a chilling effect, when users choose not to do something that is legally permitted for fear of getting into trouble.
"The dataset showed specific instances of chilling effects within these communities," says Casey Fiesler, a Ph.D. candidate in Human-Centered Computing and the primary investigator. "These include decisions by users not to upload their work onto YouTube due to improper takedown notices or creators being told that their work would definitely be infringing if they didn't get permission from the copyright holder."
For those seeking to publish original work online, several had concerns over whether the websites could enforce their own policies and protect the uploaded content. Fiesler says this acts as another type of chilling effect that has the same outcome of fewer amateur artists publishing on digital platforms.
With an initial dataset of 100,000 public forum posts from websites dedicated to user-generated video, writing, art and music, Georgia Tech researchers found that copyright had a prominent place in discussion threads. For example, at any given point an estimated 13 percent of the posts in YouTube help forums are about copyright. The posts were primarily Q&A threads under general topics since none of the sites offered dedicated copyright forums.
The researchers determined a list of 16 keywords (e.g. attorney, illegal, permission, license, copying) to filter the posts for the study, which resulted in a clear theme that permeated the user discussions:
"Over and over again, the prevalence of problems related to copyright was expressed by creators in the conversations," says Fiesler. "Most of the posts in our dataset could be labeled as expressing some sort of problem."
The five major problem or challenge areas identified were: (1) avoiding trouble and (2) dealing with consequences for artists seeking to appropriate or remix work, and (3) fear of infringement and (4) dealing with infringement for those seeking to protect their work. The fifth area was "incomplete information" where users simply didn't have clear details to help make an informed decision or have recourse for action.
To address these issues, the study gives potential solutions for online community designers such as recommending "plain English" copyright policies and having website owners monitor user conversations or answer copyright-related questions. Fiesler notes that some social norms adopted by the user base on each website could help inform how to shape policies for sharing and limiting reuse of content on the sites. She says in some cases, website policies that include user feedback go beyond the requirements of the law as it relates to copyright. Also, designing websites that prompt users to acknowledge whether work is their own or they found it elsewhere online serves as a simple copyright reminder at the time of upload.
The researchers conclude that copyright policy is deeply intertwined with any kind of creative activity online, especially in the context of sharing or collaboration. "This study reveals that copyright policy is an important aspect of interactions between creators in these online communities, and therefore should be an important part of the user model in design decisions," says Fiesler.
INFORMATION:
The Georgia Tech study, "Understanding Copyright Law in Online Creative Communities," will be presented at the 18th ACM Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing (CSCW 2015) taking place March 14-18, 2015.
New York (15 December 2014)--A study published today is the first detailed assessment of whether the 8-year Iraq War had an effect on childbearing. The study found that before the war, from 1997 to 2003, adolescent fertility in Iraq was stable at just below 70 births per 1,000 girls aged 15-19. However, soon after the beginning of the war, adolescent fertility rose by more than 30 percent, reaching over 95 births per 1,000 girls in 2010. The study is included in the December 2014 issue of Population and Development Review, a peer-reviewed journal published by the Population ...
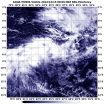
Tropical Cyclone Bakung ran into adverse conditions in the Southern Indian Ocean that weakened it to a remnant low pressure system when NASA's Aqua satellite spotted it on Dec. 15.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard Aqua captured a visible picture of Bakung's elongated remnants on Dec. 5 at 08:05 UTC (3:05 a.m. EST). The storm appeared to be stretched out from west to east in the visible image.
The last advisory on the tropical cyclone came on Dec. 13 when the storm was still a tropical storm with maximum sustained ...
WASHINGTON (Dec. 15, 2014)--Over prescription of antibiotics is a major factor driving one of the biggest public health concerns today: antibiotic resistance. In a first-of-its-kind study, research led by the George Washington University suggests that public health educational materials may not address the misconceptions that shape why patients expect antibiotics, driving doctors to prescribe them more. The research appeared in October in the journal Medical Decision Making.
Researchers from George Washington, Cornell and Johns Hopkins universities surveyed 113 patients ...
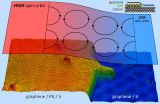
Researchers in Spain have discovered that if lead atoms are intercalated on a graphene sheet, a powerful magnetic field is generated by the interaction of the electrons' spin with their orbital movement. This property could have implications in spintronics, an emerging technology promoted by the European Union to create advanced computational systems.
Graphene is considered the material of the future due to its extraordinary optical and electronic mechanical properties, especially because it conducts electrons very quickly. However, it does not have magnetic properties, ...
To the casual observer, the colonies of social insects like bees and ants appear to be harmonious societies where individuals work together for the common good. But appearances can be deceiving.
In fact, individuals within nests compete over crucial determinants of fitness such as reproductive dominance and production of male eggs. The intensity of competition often depends on the level of kinship between colony members. This is because selfish individuals lose indirect fitness when their behavior harms close relatives. A new study by Eva Schultner and colleagues from ...
Just in time for Christmas, Simon Fraser University computing science professor Richard Zhang reveals how to print a 3D Christmas tree efficiently and with zero material waste, using the world's first algorithm for automatically decomposing a 3D object into what are called pyramidal parts.
A pyramidal part has a flat base with the remainder of the shape forming upwards over the base with no overhangs, much like a pyramid. A pyramidal shape is optimal for 3D printing because it incurs no material waste and saves print time.
The algorithm promises to become a big deal in ...
DALLAS - Dec. 15, 2014 - UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers have identified a possible therapy to treat neurofibromatosis type 1 or NF1, a childhood neurological disease characterized by learning deficits and autism that is caused by inherited mutations in the gene encoding a protein called neurofibromin.
Researchers initially determined that loss of neurofibromin in mice affects the development of the part of the brain called the cerebellum, which is responsible for balance, speech, memory, and learning.
The research team, led by Dr. Luis F. Parada, Chairman ...
Irvine, Calif., Dec. 15, 2014 - Dangerously high levels of air pollutants are being released in Mecca during the hajj, the annual holy pilgrimage in which millions of Muslims on foot and in vehicles converge on the Saudi Arabian city, according to findings reported today at the American Geophysical Union meeting in San Francisco.
"Hajj is like nothing else on the planet. You have 3 to 4 million people - a whole good-sized city - coming into an already existing city," said Isobel Simpson, a UC Irvine research chemist in the Nobel Prize-winning Rowland-Blake atmospheric ...
Early discoveries by NASA's newest Mars orbiter are starting to reveal key features about the loss of the planet's atmosphere to space over time.
The findings are among the first returns from NASA's Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) mission, which entered its science phase on Nov. 16. The observations reveal a new process by which the solar wind can penetrate deep into a planetary atmosphere. They include the first comprehensive measurements of the composition of Mars' upper atmosphere and electrically charged ionosphere. The results also offer an unprecedented ...
A breast cancer specialist and clinical researcher at Women & Infants Hospital of Rhode Island presented research yesterday at the 2014 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium showing that adding either the chemotherapy drug carboplatin or the blood vessel-targeting drug bevacizumab to the standard treatment of chemotherapy before surgery helped women who have the basal-like subtype of triple-negative breast cancer.
"We found that adding either carboplatin or bevacizumab to standard preoperative chemotherapy increased pathologic complete response rates for women with basal-like ...