National model of restoration: Nine Mile Run
Study by Pitt hydrologist shows that one of the largest urban-stream restorations in the United States has led to the recovery of fish and, more importantly, a groundswell of local support
2014-12-17
(Press-News.org) PITTSBURGH--A stream runs through it. A much nicer, healthier stream.
Pittsburgh's Frick Park is home to Nine Mile Run, a stream that had been known as "Stink Creek." From 2003 to 2006, the City of Pittsburgh and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers poured $7.7 million into restoring 2.2 miles of the stream and tributaries into waterways approximating what they were prior to urban development.
The project remains one of the largest urban-stream restorations undertaken in the United States.
What can this restoration teach us as we continue to deal with streams affected by urbanization?
The University of Pittsburgh's Dan Bain, assistant professor of hydrology and metal biogeochemistry in the Department of Geology and Planetary Science within the Kenneth P. Dietrich School of Arts and Sciences, says the project has made a difference and sets an example for other cities to follow. The evidence is tallied in Bain's paper, "Characterizing a Major Urban Stream Restoration Project: Nine Mile Run," published this month in the Journal of the American Water Resources Association.
Nine Mile Run, which is part of a watershed that drains 6.5 square miles of Wilkinsburg, Edgewood, Swissvale, Forest Hills, Squirrel Hill, and Point Breeze, had been truly abused by urbanization and industrialization. Toxins leached into the creek from a slag heap left over from the steelmaking process, sewer lines discharged into the water, and so much of the waterway had been buried in culverts or diverted from its natural path that Nine Mile Run had become toxic.
The three-year restoration project involved rerouting the creek to a natural pathway, reestablishing flora, creating areas to catch floodwater, and building natural "slash piles" and "snags" from cut-down trees to create bird and animal habitats. It also involved infrastructure interventions: adding rain barrels to individual's homes, preventing some storm water from overwhelming the stream, and fixing parts of the underlying sewers.
Some of the impediments remain, but neighbors and Frick Park users have been motivated to continue the work. Those inspired by the improving health of the stream have enlisted as volunteer Urban EcoStewards with the Nine Mile Run Watershed Association, a nonprofit that advocates for and monitors the area. These EcoStewards visit an assigned plot on a regular basis to remove invasive species, plant native flora, clean up trash, and install rain barrels on their property to reduce runoff and slow erosion.
In his paper, Bain reports that fish populations are improving as are populations of macroinvertebrates--insects, crustaceans, etc.--that fish feed on, though their recovery is coming along more slowly. However, the human response to this restoration has been vigorous--the rise in the number of volunteer hours as well as the number of rain barrels installed at private residences appears to be associated with the restoration of the stream. If replicated elsewhere, community involvement should be considered an important part of sustaining improvements in stream health.
"What we found is that, properly done, urban-stream restoration can create a citizen involvement in the process of appropriately managing urban streams and give us a greater opportunity to understand how restorations work in an urban system, particularly when compared with our ability to understand restoration success in less populated areas," Bain says.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-17
WASHINGTON - National Poison Control Center data from 2012 show that poisonings from prescription drugs are the leading cause of injury death in the United States, and that poisonings from "bath salts," synthetic marijuana and laundry detergent pods are emerging threats to public health. The paper was published online Monday in Annals of Emergency Medicine ("Poisoning in the United States: 2012 Emergency Medicine Report of the National Poison Data System").
"The poison center system can provide real-time advice and collect data regarding a variety of poisonings, including ...
2014-12-17
WASHINGTON -- Two related proteins exert a lethal double whammy effect against glioblastoma cells when activated with a small molecule, say researchers at Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center.
The scientists say when activated, one protein, called the short form, stops glioblastoma cells from replicating their DNA, and the other, called the long form, prevents cell division if the DNA has already been replicated, explains Rebecca Riggins, PhD, assistant professor of oncology at Georgetown Lombardi. The study was posted online Dec. 12 in the journal Cell Cycle.
Both ...
2014-12-17
New Rochelle, NY, December 17, 2014-The Sunni Islamist terror organization known as the Islamic State, or ISIS, uses extreme violence and brutality against anyone it perceives as a threat to its goal of expansion and restoration of an Islamic Caliphate. The significant behavioral aspects of this unparalleled violence and its implications for the future are explored in a compelling Review article published in Violence and Gender, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Violence and Gender website at http://online.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/vio.2014.0037 ...
2014-12-17
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. - Dec. 17, 2014 - While people of Mexican ancestry are nearly twice as likely to develop Type 2 diabetes as people of European heritage, the majority of research in this area has focused on those of European origin.
In an effort to understand why Mexicans are disproportionately affected by the disease, researchers at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center led the largest study to date to examine the underlying causes. The study is published in the Dec. 17 issue of Diabetes.
"Type 2 diabetes is really about how you dispose of your glucose - how long it ...
2014-12-17
DAVIS, Calif. -- The 2013 Rim Fire, the largest wildland fire ever recorded in the Sierra Nevada region, is still fresh in the minds of Californians, as is the urgent need to bring forests back to a more resilient condition. Land managers are using fire as a tool to mimic past fire conditions, restore fire-dependent forests, and reduce fuels in an effort to lessen the potential for large, high-intensity fires, like the Rim Fire. A study led by the U.S. Forest Service's Pacific Southwest Research Station (PSW) and recently published in the journal Forest Ecology and Management ...
2014-12-17
The U.S. continues to look at the use and regulation of phthalates, which have been associated with health problems. Of particular concern is the safety of these plastic additives to children. A new study aims to improve our understanding of one possible exposure route for babies: vinyl crib mattress covers. Scientists report in ACS' Environmental Science & Technology that as these covers warm up, they emit more phthalates into the air.
Ying Xu and Yirui Liang note that previous studies have linked phthalates, which soften plastics, to potential health effects, including ...
2014-12-17
A new study by a team of researchers that includes University of Notre Dame scientists Joshua Shrout and Mark Alber provides new insights into the behavior of an important bacterial pathogen.
Alber, Vincent J. Duncan Family Professor of Applied Mathematics, and Schrout, an associate professor of civil and environmental engineering and earth sciences, studied Pseudomonas aeruginosa, an opportunistic pathogen responsible for both acute and persistent infections.
"While this ubiquitous environmental bacterium rarely infects healthy people, it is a common pathogen among ...
2014-12-17
ALAMEDA, Calif. - December 17, 2014 - Penumbra, Inc., the market leader in intra-arterial stroke treatment, announced that an independent study published online today in the New England Journal of Medicine found that intra-arterial stroke treatment, including the company's clot extraction technology, was shown to be significantly more effective than medical management with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), which is the current standard of care. The findings of this randomized, controlled comparative effectiveness trial of stroke treatment have the potential to change ...
2014-12-17
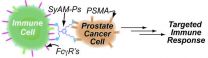
New Haven, Conn. - A Yale University lab has crafted the first synthetic molecules that have both the targeting and response functions of antibodies.
The new molecules -- synthetic antibody mimics (SyAMs) -- attach themselves simultaneously to disease cells and disease-fighting cells. The result is a highly targeted immune response, similar to the action of natural human antibodies.
"Unlike antibodies, however, our molecules are synthetic organic compounds that are approximately one-twentieth the size of antibodies," said David A. Spiegel, a professor of chemistry at ...
2014-12-17
Promising treatments known as biologics are on the market and under development for many serious illnesses such as cancer, but some of them come with high risks, even lethal ones. Now scientists have produced a novel class of molecules that could be as effective but without the dangerous side effects. They report their work on these compounds, which they tested on prostate cancer cells, in ACS' Journal of the American Chemical Society.
David A. Spiegel and colleagues explain that biologics are protein-based therapies that have revolutionized cancer treatment over the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] National model of restoration: Nine Mile Run
Study by Pitt hydrologist shows that one of the largest urban-stream restorations in the United States has led to the recovery of fish and, more importantly, a groundswell of local support