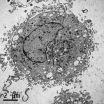
NASA's sun watching observatory sees mid-level solar flare on Dec. 16, 2014
2014-12-17
(Press-News.org) The sun emitted a mid-level solar flare, peaking at 11:50 p.m. EST on Dec. 16, 2014. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, which watches the sun constantly, captured an image of the event. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel.
To see how this event may affect Earth, please visit NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center at http://spaceweather.gov, the U.S. government's official source for space weather forecasts, alerts, watches and warnings.
This flare is classified as an M8.7-class flare. M-class flares are a tenth the size of the most intense flares, the X-class flares. The number provides more information about its strength. An M2 is twice as intense as an M1, an M3 is three times as intense, etc.
Updates will be provided as needed.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-17
In the first real-world trial of the impact of patient-controlled access to electronic medical records, almost half of the patients who participated withheld clinically sensitive information in their medical records from some or all of their health care providers.
This is the key finding of a new study by researchers from Clemson University, the Regenstrief Institute, Indiana University School of Medicine and Eskenazi Health published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine.
Kelly Caine, assistant professor in Clemson's School of Computing, and colleagues at Clemson ...
2014-12-17
A team of scientists, led by the University of Toronto's Barbara Sherwood Lollar, has mapped the location of hydrogen-rich waters found trapped kilometres beneath Earth's surface in rock fractures in Canada, South Africa and Scandinavia.
Common in Precambrian Shield rocks - the oldest rocks on Earth - the ancient waters have a chemistry similar to that found near deep sea vents, suggesting these waters can support microbes living in isolation from the surface.
The study, to be published in Nature on December 18, includes data from 19 different mine sites that were ...
2014-12-17
Chemical modifications to DNA's packaging -- known as epigenetic changes -- can activate or repress genes involved in autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) and early brain development, according to a new study to be published in the journal Nature on Dec. 18.
Biochemists from NYU Langone Medical Center found that these epigenetic changes in mice and laboratory experiments remove the blocking mechanism of a protein complex long known for gene suppression, and transitions the complex to a gene activating role instead.
Researchers say their findings represent the first link ...
2014-12-17
LA JOLLA, CA--December 17, 2014--Chemists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have invented a powerful method for joining complex organic molecules that is extraordinarily robust and can be used to make pharmaceuticals, fabrics, dyes, plastics and other materials previously inaccessible to chemists.
"We are rewriting the rules for how one thinks about the reactivity of basic organic building blocks, and in doing so we're allowing chemists to venture where none has gone before," said Phil S. Baran, the Darlene Shiley Chair in Chemistry at TSRI, whose laboratory reports ...
2014-12-17
Johns Hopkins and University of Alberta researchers have identified a single protein as the root of painful and dangerous allergic reactions to a range of medications and other substances. If a new drug can be found that targets the problematic protein, they say, it could help smooth treatment for patients with conditions ranging from prostate cancer to diabetes to HIV. Their results appear in the journal Nature on Dec. 17.
Previous studies traced reactions such as pain, itching and rashes at the injection sites of many drugs to part of the immune system known as mast ...
2014-12-17
Researchers found 53 existing drugs that may keep the Ebola virus from entering human cells, a key step in the process of infection, according to a study led by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and published today in the Nature Press journal Emerging Microbes and Infections.
Among the better known drug types shown to hinder infection by an Ebola virus model: several cancer drugs, antihistamines and antibiotics. Among the most effective at keeping the virus out of human cells were microtubule inhibitors ...
2014-12-17
Researchers from Intermountain Medical Center in Salt Lake City have identified a new "sliding scale" model used to rule out potentially deadly blood clots in the lungs, known as pulmonary embolisms, that is more accurate than current diagnostic methods.
The new model, which factors in a patient's age, more accurately identifies a patient's risk of the often-deadly blood clots and can more easily rule out the need for additional, more invasive tests, helping to reduce unnecessary costs.
The research is published in the medical journal, CHEST.
Pulmonary embolism is ...
2014-12-17
The engineered spring flood that brought water to previously dry reaches of the lower Colorado River and its delta resulted in greener vegetation, the germination of new vegetation along the river and a temporary rise in the water table, according to new results from the binational team of scientists studying the water's effects.
The experimental pulse flow of water was the result of a U.S.-Mexico agreement called Minute 319.
"The pulse flow worked," said Karl W. Flessa, co-chief scientist for the Minute 319 Science Team. "A small amount of water can have a big effect ...
2014-12-17
New research helps explain a paradoxical effect of certain antidepressants--that they may actually worsen symptoms before helping patients feel better. The findings, highlighted in a paper publishing online December 17 in the Cell Press journal Trends in Cognitive Sciences, may help investigators fix the problem as well as create new classes of drugs to treat depression.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are the most widely prescribed class of antidepressant drugs, and they work by increasing levels of a brain chemical called serotonin. While this boost ...
2014-12-17
In an article to be published in the January issue of BioScience, two philosophers tackle one of the most divisive arguments in modern biology: the value of the theory of "kin selection."
Kin selection is the idea that because genes influence behavior, and because an animal that helps its relatives helps to spread genes likely identical to its own, animals will evolve to favor kin. Researchers have spent decades testing this explanation for apparent animal altruism, but in recent years, critics, notably Martin Nowak of Harvard University and the famous naturalist and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NASA's sun watching observatory sees mid-level solar flare on Dec. 16, 2014