(Press-News.org) New big data methodology can analyse over 1 billion pieces of data
The methodology can potentially isolate the areas of the brain involved with other cognitive problems, including Obsessive Compulsive Disorder, ADHD and schizophrenia.
The functional differences between autistic and non-autistic brains have been isolated for the first time, following the development of a new methodology for analysing MRI scans.
Developed by researchers at the University of Warwick, the methodology, called Brain-Wide Association Analysis (BWAS), is the first capable of creating panoramic views of the whole brain and provides scientists with an accurate 3D model to study.
The researchers used BWAS to identify regions of the brain that may make a major contribution to the symptoms of autism.
BWAS does so by analysing 1,134,570,430 individual pieces of data; covering the 47,636 different areas of the brain, called voxels, which comprise a functional MRI (fMRI) scan and the connections between them.
Previous methodologies were process this level of data and were restricted to modelling only limited areas.
The ability to analyse the entire data set from an fMRI scan provided the Warwick researchers the opportunity to compile, compare and contrast accurate computer models for both autistic and non-autistic brains.
Led by BWAS developer Professor Jianfeng Feng, from the University of Warwick's Department of Computer Science, the researchers collected the data from hundreds of fMRI scans of autistic and non-autistic brains.
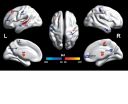
By comparing the two subsequent models the researchers isolated twenty examples of difference, where the connections between voxels of the autistic brain were stronger or weaker than the non-autistic .
The identified differences include key systems involved with brain functions relating to autism. Professor Feng explained the findings:
"We identified in the autistic model a key system in the temporal lobe visual cortex with reduced cortical functional connectivity. This region is involved with the face expression processing involved in social behaviour. This key system has reduced functional connectivity with the ventromedial prefrontal cortex, which is implicated in emotion and social communication".
The researchers also identified in autism a second key system relating to reduced cortical functional connectivity, a part of the parietal lobe implicated in spatial functions.
They propose that these two types of functionality, face expression-related, and of one's self and the environment, are important components of the computations involved in theory of mind, whether of oneself or of others, and that reduced connectivity within and between these regions may make a major contribution to the symptoms of autism.
The researchers argue that the methodology can potentially isolate the areas of the brain involved with other cognitive problems, including Obsessive Compulsive Disorder, ADHD and schizophrenia.
By using meta-analysis and a rigorous statistics approach the Warwick researchers were able to collect and use a big data set to obtain significant results, the likes of which have not been seen in autistic literature before. Professor Feng explains:
"We used BWAS to analyse resting state fMRI data collected from 523 autistic people and 452 controls. The amount of data analysed helped to achieve the sufficient statistical power necessary for this first voxel-based, comparison of whole autistic and non-autistic brains. Until the development of BWAS this had not been possible.
"BWAS tests for differences between patients and controls in the connectivity of every pair of voxels at a whole brain level. Unlike previous seed-based or independent components-based approaches, this method has the great advantage of being fully unbiased in that the connectivity of all brain voxels can be compared, not just selected brain regions."
INFORMATION:
The research, published in the journal Brain, is titled 'Autism: Reduced Connectivity between Cortical Areas Involved with Face Expression, Theory of Mind, and the Sense of Self'.
Notes for Editors:
The figure of 1,134,570,430 is reached by 47636 x 47635 / 2.
The researchers involved included: Wei Cheng, Edmund Rolls, Huaguang Gu, Jie Zhang
A cancer drug could be made 50 times more effective by a chemical found in stinging nettles and ants, new research finds.
Researchers at the University of Warwick found that when the chemical, Sodium Formate, is used in combination with a metal-based cancer treatment it can greatly increase its ability to shut down cancer cells.
Developed by Warwick's Department of Chemistry, the drug, a compound of the metal ruthenium called JS07, is capable of exploiting a cancer cell's natural weaknesses and disrupts its energy generation mechanism.
Laboratory tests on ovarian ...
In a world first, researchers have found that a naturally occurring chemical attracts pregnant malaria-transmitting mosquitoes - a discovery which could boost malaria control efforts.
The chemical, cedrol, found in mosquito breeding sites near Africa's Lake Victoria, could be used in traps that would 'attract and kill' the female mosquito, preventing reproduction before she lays hundreds of eggs.
A child dies every minute from malaria, according to World Health Organization estimates. In Africa, malaria parasites carried by the female Anopheles gambiae mosquito are ...
Trauma is responsible for more global deaths annually than HIV, malaria and tuberculosis combined. Yet healthcare systems in many countries are missing out on life-saving treatments learnt on the battlefield, according to a review by King's College London and published today in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine.
Medical advancements made by the military in times of conflict, are increasingly seen in the hospitals of high income countries but are being missed in poorer countries, where trauma is the leading cause of death in young people. Many innovations by ...
Highlights
Compared with uninfected (HIV-/HCV-) kidney transplant recipients, mono-infected HIV+ (HIV+/HCV-) recipients had similar 5-year and 10-year kidney survival rates, while HIV+ recipients co-infected with HCV (HIV+/HCV+) had worse kidney survival rates.
Patient survival among mono-infected HIV+ recipients was similar to uninfected recipients but was significantly lower for co-infected recipients.
Over the last decade there has been a 10-fold increase in the number of kidney transplants performed in HIV+ patients.
Washington, DC (March 19, 2015) -- HIV+ ...
PHILADELPHIA - Greening vacant lots may be associated with biologic reductions in stress, according to a new study from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Residents who walked near newly greened vacant lots had significantly lower heart rates compared to walking near a blighted, or neglected, vacant lot.
"Our goal was to scientifically explore the connection between city environments and stress," said the study's lead author, Eugenia C. South, MD, MHSP, a physician in the department of Emergency Medicine at Penn. "We used heart rate as ...
In a paper published online today (Thursday, March 19), scientists report that the incidence of diagnosed autism was twice as high for assisted reproductive technology (ART) as non-ART births among the nearly 6 million children in their study, born in California from 1997 through 2007. However, much of the association between ART and autism was explained by age and education of the mother as well as adverse perinatal outcomes, especially multiple births. After accounting for these factors, the study showed an elevated risk only for mothers ages 20-34.
Notably, the study ...
Half a century ago, a concentrated global effort nearly wiped a disfiguring tropical disease from the face of the earth. Now, says Case Western Reserve's James W. Kazura, MD, it's time to complete the work.
In a perspective column in the Feb.19 New England Journal of Medicine, Kazura responded to a research article that demonstrated positive results from a single oral dose of azithromycin to 83.8 percent (13,302) of 16,092 residents of Lihir Island, Papua New Guinea.
"We have the medical knowledge to achieve global eradication, and new evidence establishes proof of ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Incessant mountain rain, snow and melting glaciers in a comparatively small region of land that hugs the southern Alaska coast and empties fresh water into the Gulf of Alaska would create the sixth largest coastal river in the world if it emerged as a single stream, a recent study shows.
Since it's broken into literally thousands of small drainages pouring off mountains that rise quickly from sea level over a short distance, the totality of this runoff has received less attention, scientists say. But research that's more precise than ever before is making ...
Both patients and physicians may benefit from a "work flow" system developed at military medical facilities and tested at a Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center clinic, according to results of an efficiency study.
The study evaluates a work flow method developed by the U.S. Air Force; Johns Hopkins researchers Shereef Elnahal, M.D., M.B.A. and Joseph Herman, M.D.; and consulting firm ProcessProxy Corporation. Called the Military Acuity Model, the method examines tasks performed by physicians and nurses and identifies jobs that can be safely assigned to support staff. For ...
By genomic sequencing of leukemia cells from relapsed patients at different stages, scientists have discovered key details of how acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cells mutate to survive chemotherapy. These mutations enable the cells to proliferate, causing relapse and often death.
The findings are important because ALL is a leading cause of cancer deaths in children, with 15 percent of ALL patients relapsing with poor survival. The researchers said their findings will lead to new tests to monitor children in remission and to detect signs of relapse.
The research ...