INFORMATION:
Media Contact:
Dr Beverly Mühlhäusler
Senior Research Fellow
FOODplus Research Centre
School of Agriculture, Food and Wine
The University of Adelaide
Phone: +61 8 8313 0848
Mobile: +61 402 143 949
beverly.muhlhausler@adelaide.edu.au
Dr Jessica Gugusheff
Post-doctoral researcher
School of Agriculture, Food and Wine
The University of Adelaide
Phone: +61 8313 6857
Mobile: +61 478 178 704
jessica.gugusheff@adelaide.edu.au
Robyn Mills
Media and Communications Officer
The University of Adelaide
Phone: +61 8 8313 6341
Mobile: +61 410 689 084
robyn.mills@adelaide.edu.au
Critical windows to turn away junk food craving
2015-04-02
(Press-News.org) University of Adelaide researchers have shown there are two critical windows during the developmental pathway to adulthood when exposure to junk food is most harmful, particularly for female offspring.
This work leads on from earlier findings which showed that mothers who eat junk food while pregnant are programming their babies to be addicted to a high fat, high sugar diet by the time they are weaned.
Their latest laboratory studies reveal there may be a chance to turn around this junk food addiction in two critical windows--equating to late pregnancy and in adolescence in humans.
"Our research suggests that too much junk food consumed late in pregnancy for humans has the potential to be more harmful to the child than excess junk food early in the pregnancy," says Dr Jessica Gugusheff, post-doctoral researcher in the School of Agriculture, Food and Wine.
"Importantly, it also indicates that if excess junk food was consumed by the mother in those early stages of pregnancy, there may be a chance to reduce those negative effects on the baby by eating a healthy diet in late pregnancy.
"The second critical window is adolescence and we've found differences between males and females. Our experiments showed that eating a healthy diet during adolescence could reverse the junk-food preference in males but not females."
The junk food preference is believed to result from a desensitisation of the normal reward system (the opioid and dopamine signalling pathway) fuelled by highly palatable high fat, high sugar diets. Offspring with less sensitive reward systems need more fat and sugar to get the same "good feeling".
"This brain area grows at its fastest during these critical windows and is therefore most susceptible to alteration at these times," says project leader Dr Beverly Mühlhäusler, Senior Research Fellow with the University's FOODplus Research Centre.
The researchers believe their work will ultimately allow pregnant women to be better informed about the lasting effect their diet has on the development of their child's life-long food preferences.
"It will help mothers to make better, more informed, decisions about their diet choices by narrowing down the window of when exposure to a bad diet is most harmful to the child," says Dr Mühlhäusler. "It will also enable us to target dietary interventions to times in development when they will be most beneficial."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Services users and their needs to be at the center of health-care services
2015-04-02
The use of technology in daily life is getting easier all the time as people accumulate knowledge and skills in information and communications technology. However, the most important thing in developing health care services, for example, is to take into account people's day to day lives and their subjective experience of the utility of using services. For example, people's previous bad experience of using a service is reflected for a long time in their use of the service in the future, and thus the dissemination of new service models is a lot slower than might be imagined. ...
Depression and insomnia are strongest risk factors for frequent nightmares
2015-04-02
DARIEN, IL - A new study suggests that symptoms of depression and insomnia are the strongest predictors of having frequent nightmares.
Results show that 3.9 percent of participants reported having frequent nightmares during the previous 30 days, including 4.8 percent of women and 2.9 percent of men. Frequent nightmares were reported by 28.4 percent of participants with severe depressive symptoms and 17.1 percent of those with frequent insomnia. Further analysis that adjusted for potential confounders found that the strongest independent risk factors for nightmares were ...
Liver injury in NASH leads to a leaky gut
2015-04-02
Bethesda, MD (April 2, 2015) -- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), the more severe form of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) that can progress to liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, is associated with leakiness of the intestinal wall, which in turn may worsen liver disease, according to research1 published in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the new basic science journal of the American Gastroenterological Association.
"Our study strengthens the clinical association between intestinal permeability and NASH, although we were unable to identify ...
Accurate blood pressure measurement fundamental to early diagnosis in pregnancy
2015-04-02
Accurate blood pressure measurement (BP) is fundamental to the early diagnosis of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy, says a review published 1 April, 2015, in The Obstetrician & Gynaecologist (TOG).
The diagnosis and management of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy, as well as obstetric haemorrhage, sepsis and safe abortion, are guided in part by the measurement of BP. These conditions contribute to more than half of all maternal deaths globally, so the accuracy of BP measurement is vital, the review concludes.
The review explains that BP monitoring is the most ...
LSU professor's neurological research featured in the Journal of Neuroscience
2015-04-02
BATON ROUGE - LSU Psychology Professor Megan H. Papesh was part of a research team whose study appeared in the online-first edition of the Journal of Neuroscience on Wednesday, April 1.
The research, jointly conducted by scientists from the Barrow Neurological Institute and Arizona State University, involves recording single-neuron activity in the brains of epilepsy patients who require electrodes implanted to monitor seizures. With the electrodes in place, processes such as perception and memory can be studied at the level of individual neurons.
The research focused ...
Ocean-scale dataset allows broad view of human influence on Pacific coral reef ecosystems
2015-04-02
As man-made threats to coral reefs mount and interest in conserving reef ecosystems grows, scientists have turned to studying extremely remote and uninhabited reefs in an effort to understand what coral reefs would be like in the absence of humans. A number of islands and atolls in the Pacific Ocean remain virtually untouched by human influence, situated hundreds of kilometers from the nearest human populations.
A study published today by scientists at the University of Hawai'i at Mānoa (UHM) School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), the National ...
Plowing prairies for grains: Biofuel crops replace grasslands nationwide
2015-04-02
MADISON, Wis. - Clearing grasslands to make way for biofuels may seem counterproductive, but University of Wisconsin-Madison researchers show in a study today (April 2, 2015) that crops, including the corn and soy commonly used for biofuels, expanded onto 7 million acres of new land in the U.S. over a recent four-year period, replacing millions of acres of grasslands.
The study -- from UW-Madison graduate student Tyler Lark, geography Professor Holly Gibbs, and postdoctoral researcher Meghan Salmon -- is published in the journal Environmental Research Letters and addresses ...
Rapid increase in neonicotinoid insecticides driven by seed treatments
2015-04-02
Use of a class of insecticides, called neonicotinoids, increased dramatically in the mid-2000s and was driven almost entirely by the use of corn and soybean seeds treated with the pesticides, according to researchers at Penn State.
"Previous studies suggested that the percentage of corn acres treated with insecticides decreased during the 2000s, but once we took seed treatments into account we found the opposite pattern," said Margaret Douglas, graduate student in entomology. "Our results show that application of neonicotinoids to seed of corn and soybeans has driven ...
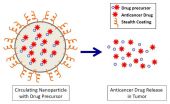
Nanoparticles may exploit tumor weaknesses to selectively attack cancers
2015-04-02
Delving into the world of the extremely small, researchers are exploring how biodegradable nanoparticles can precisely deliver anticancer drugs to attack neuroblastoma, an often-deadly children's cancer.
By bringing together experts in pediatric oncology with experts in nanotechnology, researchers at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia aim to thread the needle of delivering effective doses of cancer-killing agents while avoiding toxicity in healthy tissues. The team's new research shows that this approach inhibits tumor growth and markedly prolongs survival in animal ...
Physical activity benefits lung cancer patients and survivors
2015-04-02
DENVER - Exercise and physical activity should be considered as therapeutic options for lung cancer as they have been shown to reduce symptoms, increase exercise tolerance, improve quality of life, and potentially reduce length of hospital stay and complications following surgery for lung cancer.
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States with an estimated 160,000 deaths each year and worldwide there are 1.4 million deaths. In the last two decades lung cancer therapy has improved, but the overall 5-year survival rate is still quite low at 17%. ...