(Press-News.org) UK research collaboration develops a new bioinformatics pipeline that enables automated primer design for multiple genome species, significantly reducing turnaround time.
With a rising global population leading to increased pressure on food resources, it is becoming ever more essential that crop breeding programmes work to enhance the security of global food sources.
A key aspect of this is utilising breakthroughs in genomics research to guide the selection of the individuals to incorporate in breeding schemes. It is possible to relate the DNA of a species to its physical characteristics or phenotypes, and identify areas of DNA responsible for desirable traits such as high yield or disease resistance.
Crop breeding programmes can make use of this genetic information to ensure that the preferred trait is inherited by future crop yields, helping to secure future food supply. However, the majority of tools for the analysis of DNA are designed for diploid organisms, such as humans, with one set of chromosomes, and perform poorly when applied to polyploid species such as bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) which has multiple sets of chromosomes.
Scientists from The Genome Analysis Centre (TGAC) and John Innes Centre have developed a bioinformatics pipeline, PolyMarker that facilitates the design of genomic specific primers for polyploid species. Once identified, these primers can be used to ascertain whether or not an individual organism has the genetic variation associated with a given trait.
As an open access tool, researchers and crop breeders can submit their own data to PolyMarker and the online tool will return suggested design primers to identify genetic variations that tag vital traits in their crop samples, with a significantly reduced turnaround time compared to the current manual method.
"The process of manually designing primers to validate in hexaploid wheat is time consuming, with PolyMarker we have reduced the design time from around a week to twenty minutes," said lead author Ricardo Ramirez-Gonzalez, PhD student at TGAC.
"PolyMarker has already demonstrated its value having been developed and applied in a research project where it identified genetic markers that signal resistance to the wheat yellow rust pathogen (Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici). This disease is responsible for devastating bread wheat crops and has developed 'Warrior' strains capable of infecting individuals previously believed to have tolerance."
Mario Caccamo, senior author of the paper, said: "The development of PolyMarker is a great example of the benefits of multidisciplinary research. In one new software tool, we have applied expertise in advanced algorithm development, knowledge on genetics and principles of genome architecture."
This innovative online tool has been used to generate putative KASP probes for the 820K markers designed by the CerealsDB project from the BBSRC funded WISP programme (a collaboration between John Innes Centre, the University of Bristol, Rothamsted Research, NIAB and University of Nottingham). Polymarker has also been used to design probes for the 90K iSelect markers set.
The paper, titled: "PolyMarker: A fast polyploid primer design pipeline" is published in Bioinformatics.
INFORMATION:
The destruction of the Brazilian rainforest has slowed significantly. With around 5000 square kilometers annually, the loss is now about 80% lower than in 2004. Led by the Center for Development Research (ZEF) at the University of Bonn, an international team of researchers has evaluated the effectiveness of forest law enforcement in the Brazilian Amazon. In some federal states of the Brazilian Amazon region enforcement has been more effective than in others. The results are presented in the journal "PLOS ONE".
Deforestation of the Amazon rainforest featured in international ...
Could the mundane action of switching on an energy saving light bulb still hold secrets? It does, at least for physicists. These bulbs are interesting because they contain low-temperature plasma - a gas containing charges from ions and electrons. Now, a German team has developed a method that could be used for measuring the increase in the plasma force on the inner side of such a light bulb when the light is switched on. These findings from Thomas Trottenberg and colleagues from Christian-Albrechts University in Kiel, Germany, have just been published in EPJ D. They have ...
The research group of the neurofibromatosis of the Catalan Institute of Oncology (ICO), the Institute of Biomedical Research of Bellvitge (IDIBELL) and the Institute of Medicicina Predictive and Personalized Cancer (IMPPC) has developed new mouse models for the study of principal malignant tumor associated with neurofibromatosis type 1.
Details of the development and characterization of new animal models have been published in EMBO Molecular Medicine.
Neurofibromatosis, a rare and minority
The neurofibromatosis are disorders of the nervous system that primarily affect ...
A new study is a rare look into the delicate dynamics of social movement, and shows how people avoid bumping into each other while doing complementary, coordinated tasks such as dancing. The research reveals that people fall into a specific pattern to avoid a collision. The study led by Michael J. Richardson, a University of Cincinnati associate professor of psychology, is published in the highly ranked Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, a journal of the American Psychological Association.
The study involved 12 pairs of two participants ...
The exchange of words, speaking and listening in conversation, may seem unremarkable for most people, but communicating with others is a challenge for people who have aphasia, an impairment of language that often happens after stroke or other brain injury. Aphasia affects about 1 in 250 people, making it more common than Parkinson's Disease or cerebral palsy, and can make it difficult to return to work and to maintain social relationships. A new study published in the journal Nature Communications provides a detailed brain map of language impairments in aphasia following ...
Three or more hours of walking per week can boost the vitality and health of prostate cancer survivors. Men and women who have survived colorectal cancer and are regular walkers as well report lower sensations of burning, numbness, tingling or loss of reflexes that many often experience post-treatment. These are among the findings of two studies published in Springer's Journal of Cancer Survivorship that highlight the benefits of exercise for cancer survivors.
In the first, a group of American researchers led by Siobhan Phillips of Northwestern University weighed up the ...
One of the immune system's most critical challenges is to differentiate between itself and foreign invaders -- and the number of recognized autoimmune diseases, in which the body attacks itself, is on the rise. But humans are not the only organisms contending with "friendly fire."
Even single-celled bacteria attack their own DNA. What protects these bacteria, permitting them to survive the attacks?
A new study published in Nature by a team of researchers at Tel Aviv University and the Weizmann Institute of Science now reveals the precise mechanism that bacteria's defense ...
(PHILADELPHIA) - As cesarean section rates continue to climb in the United States, researchers are looking to understand the factors that might contribute. There has been debate in the field about whether non-medically required induction of labor leads to a greater likelihood of C-section, with some studies showing an association and others demonstrating that inductions at full term can actually protect both the mothers and babies. In order to tease apart the evidence, a new analysis pooled the results from five randomized controlled trials including 844 women, and found ...
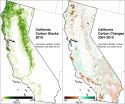
Berkeley - A new study quantifying the amount of carbon stored and released through California forests and wildlands finds that wildfires and deforestation are contributing more than expected to the state's greenhouse gas emissions.
The findings, published online today (Wednesday, April 15), in the journal Forest Ecology and Management, came from a collaborative project led by the National Park Service and the University of California, Berkeley. The results could have implications for California's efforts to meet goals mandated by the state Global Warming Solutions Act, ...
Researchers at the Angiocardioneurology Department of the Neuromed Scientific Institute for Research, Hospitalisation and Health Care of Pozzilli (Italy), have found, in animal models, that the absence of a certain enzyme causes a syndrome resembling the Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). The study, published in the international journal EMBO Molecular Medicine, paves the way for a greater understanding of this childhood and adolescent disease, aiming at innovative therapeutic approaches.
Described for the first time in 1845, but came to the fore only in ...