(Press-News.org) Household pets can transmit infection to people, especially those with weak immune systems, young children, pregnant women and seniors, according to an article in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal). Health care providers and pet owners should be aware of this risk to prevent illness in vulnerable people.
Surveys suggest that the general public and people at high risk for pet-associated disease are not aware of the risks associated with high-risk pet practices or recommendations to reduce them; for example, 77% of households that obtained a new pet following a cancer diagnosis acquired a high-risk pet," states Dr. Jason Stull, assistant professor, Department of Veterinary Preventive Medicine, Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio.
The review explains the types of infections, how infections are transmitted from pets, prevention and the role of health care providers.
"Studies suggest physicians do not regularly ask about pet contact, nor do they discuss the risks of zoonotic diseases with patients, regardless of the patient's immune status ," writes writes Dr. Stull, with coauthors Dr. Jason Brophy, Children's Hospital of Eastern Ontario (CHEO) and Dr. J.S. Weese, Ontario Veterinary College.
All pets can transmit diseases to people. For instance, dogs, cats, rodents, reptiles and amphibians can transmit Salmonella, multidrug resistant bacteria (including Clostridium difficile), Campylobacter jejuni and other diseases. Parasites such as hookworm, roundworm and Toxoplasma can also be transmitted. Infection can be contracted from bites, scratches, saliva and contact with feces. Reptiles and amphibians can transmit disease indirectly, such as via contaminated surfaces.
"Reptiles and amphibians are estimated to be responsible for 11% of all sporadic Salmonella infections among patients less than 21 years of age, and direct contact with such animals is not required for zoonotic transmission," write the authors. "In one study, 31% of reptile-associated salmonellosis cases occurred in children less than 5 years of age and 17% occurred in children aged 1 year or younger; these findings highlight the heightened risk in children and the potential for reptile-associated Salmonella to be transmitted without direct contact with the animal or its enclosure."
For healthy people, the risk of pet-associated disease is low, but vulnerable people are at risk, including newborns, children with leukemia and adults with cancer.
"Given the health benefits of animal ownership and the reluctance of patients to give up their pets, resources highlight the importance of following specific precautions," states Dr. Stull. "Patients at high risk and their households should have increased vigilance of their pets' health and take precautions to reduce pathogen transmission." Simple steps can dramatically reduce the risk.
Recommendations for reducing transmission of infection include:
wearing protective gloves to clean aquariums and cages and remove feces
proper handwashing after pet contact
discouraging pets from face licking
covering playground boxes when not in use
avoiding contact with exotic animals
regular cleaning and disinfection of animal cages, feeding areas and bedding
locating litter boxes away from areas where eating and food preparation occur
waiting to acquire a new pet until immune status has improved
regularly scheduling veterinary visits for all pets.
Physicians and other health care providers should enquire about pets and repeat questions in light of illness in vulnerable people, as well as advise on the risks of pet ownership and how to reduce risks of disease.
The authors also recommend that veterinarians can be a resource for physicians seeking more information on zoonotic infections and risks associated with unusual pets.
INFORMATION:
La Jolla, Calif., April 20, 2015 - A new research study has shown that pancreatic cancer cells can be coaxed to revert back toward normal cells by introducing a protein called E47. E47 binds to specific DNA sequences and controls genes involved in growth and differentiation. The research provides hope for a new treatment approach for the more than 40,000 people who die from the disease each year in the United States.
"For the first time, we have shown that overexpression of a single gene can reduce the tumor-promoting potential of pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells and reprogram ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio--As new medical diagnostics become available, researchers are increasingly discovering situations in which pets can transmit diseases to humans--especially when an owner's immune system is compromised.
At The Ohio State University and partner institutions, researchers have compiled the latest information from more than 500 studies worldwide to make recommendations on how families can minimize the risk of disease transmission by choosing the right type of pet, or by making small changes in how they enjoy the pets they already have.
The review was published ...
A new diagnostic method, namely spectral histopathology, facilitates marker-free detection of individual subtypes of lung cancers. It was developed by researchers at the PURE consortium at Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB). They have successfully applied it in collaboration with clinicians at the Ruhrlandklinik in Essen. It is an automatable imaging process which, by classifying specific forms of lung cancer, facilitates a prognosis regarding a tumour's aggressiveness. The team, headed by RUB Prof Dr Klaus Gerwert, compares the results of traditional diagnostic procedures ...
CLEMSON, S.C. -- In a groundbreaking achievement led by an international team that includes Clemson scientist Chris Saski, the intricately woven genetic makeup of Upland cotton has been decoded for the first time in the ancient plant's history.
Saski participated in sequencing the genome, which is a crucial stepping-stone toward further advancements of understanding the inner workings of one of the most complex and treasured plants on the planet.
The future implications of Saski's research in the short and long terms are both financial and holistic. Upland cotton, which ...
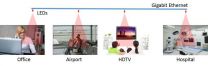
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Researchers at Oregon State University have invented a new technology that can increase the bandwidth of WiFi systems by 10 times, using LED lights to transmit information.
The technology could be integrated with existing WiFi systems to reduce bandwidth problems in crowded locations, such as airport terminals or coffee shops, and in homes where several people have multiple WiFi devices.
Experts say that recent advances in LED technology have made it possible to modulate the LED light more rapidly, opening the possibility of using light for wireless ...
NEW YORK (April 20, 2015) -- Genomic studies have illuminated the ways in which malfunctioning genes can drive cancer growth while stunting the therapeutic effects of chemotherapy and other treatments. But new findings from Weill Cornell Medical College investigators indicate that these genes are only partly to blame for why treatment that was at one point effective ultimately fails for about 40 percent of patients diagnosed with the most common form of non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.
The study, published April 20 in Nature Communications, suggests that global changes in cancer ...
A rigorous analysis of antimalarial drug quality conducted in Cambodia and Tanzania found no evidence of fake medicines, according to new research published in the American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene.
But researchers warn that routine surveillance is crucial as poor quality medicines exist, leaving malaria patients at risk of dying and increasing the risk of drug resistance.
Previous reports had suggested that up to one third of antimalarials could be fake. Researchers from the Artemisinin-based Combination Therapy (ACT) Consortium at the London School ...
Dispensing of prescription opioid pain relievers and prescription opioid overdoses both dropped substantially after abuse-deterrent extended-release oxycodone hydrochloride was introduced on the pharmaceutical market and the narcotic drug propoxyphene was withdrawn from the U.S. market in 2010, according to an article published online by JAMA Internal Medicine.
The abuse-deterrent OxyContin formulation is resistant to crushing and dissolving, actions that have been used to bypass the extended-release mechanism to get a quicker and more intense high. Propoxyphene (also ...
Children whose families and pediatricians were most faithful to an obesity intervention program that included computerized clinical decision support for physicians and health coaching for families experienced the greatest improvements in body mass index (BMI), according to an article published online by JAMA Pediatrics.
The prevalence of childhood obesity in the United States remains at historically high levels. Clinical approaches that are cost-effective and scalable for obesity reduction in children are a public health priority. However, interventions to improve BMI ...
(Boston) - Results of a new study led by Boston Medical Center (BMC) researchers, in collaboration with Harvard Medical School (HMS), indicate that the introduction of abuse-deterrent OxyContin, coupled with the removal of propoxyphene from the US prescription marketplace, may have played a role in decreasing opioid prescribing and overdoses. The findings, published in JAMA Internal Medicine, showed that these two changes led to a 19 percent drop in prescription opioid supply that was mirrored by a 20 percent drop in prescription opioid overdose between August 2010 and ...