(Press-News.org) Bethesda, MD, April 20, 2015: The Association for Molecular Pathology (AMP), the premier global, non-profit organization serving molecular diagnostic professionals, today published a special article in The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics titled, "Do Circulating Tumor Cells, Exosomes, and Circulating Tumor Nucleic Acids Have Clinical Utility?" The report provides a thorough overview of research to-date on the minimally invasive "liquid biopsy" approaches to cancer diagnostics.
"As a group of molecular diagnostic experts, we were intrigued and excited by the emerging technologies that are likely to find utility in patient management," said co-author Milena Cankovic, PhD, Henry Ford Health System and past AMP Clinical Practice Committee member. "We set out to review and compile the leading research literature as a primary reference source for continued exploration."
More than 200 studies are cited in the paper, providing a substantial digest of research to-date. "Our literature survey concluded that measuring circulating tumor cell burden in metastatic breast and prostate cancer has already crossed a prognostic threshold for clinical utility. That's why the FDA cleared a device for this purpose. It's likely that several other analytes, like circulating tumor DNA, will meet this threshold in the next few years,"
said first author, Bert Gold, PhD, National Cancer Institute.
In general, the article supports the notion that this type of diagnostic testing in and of itself allows for earlier diagnosis, faster and more targeted treatment, reduced costs, and increased quality of life and even increased lifespan for the patient. The article also includes recommendations for future trials that will ultimately lead to demonstrating the clinical utility of the referenced minimally invasive approaches. "These areas of cancer molecular diagnostics have been promising for quite a while," said senior author, Christopher D. Gocke, MD, Johns Hopkins University. "We hope that researchers will take this review of circulating tumor nucleic acids and circulating tumor cells as a spur to do the large studies needed to push the technology across the finish line. This would be a win for the field, for our patients, and for the concept of precision medicine."
While many of the studies referenced were smaller and examined only one or a few markers, progress has already been made in testing methods to increase accuracy and validity of samples. The initial results are promising, according to the authors.
INFORMATION:
ABOUT AMP:
The Association for Molecular Pathology (AMP) was founded in 1995 to provide structure and leadership to the emerging field of molecular diagnostics. AMP's 2,300+ members include individuals from academic and community medical centers, government, and industry; including pathologist and doctoral scientist laboratory directors; basic and translational scientists; technologists; and trainees. Through the efforts of its Board of Directors, Committees, Working Groups, and members, AMP is the primary resource for expertise, education, and collaboration in one of the fastest growing fields in healthcare. AMP members influence policy and regulation on the national and international levels, ultimately serving to advance innovation in the field and protect patient access to high quality, appropriate testing. For more information, visit http://www.amp.org.
CONTACT:
Nicole Litchfield, on behalf of AMP
Bioscribe Life Science Communications
Nicole@bioscribe.com
415-793-6468
Hasbro Children's Hospital study finds link between adverse childhood experiences and pediatric asthma
Children who experience violence, substance abuse at home
report significantly higher rates of asthma
PROVIDENCE, R.I. - Robyn Wing, M.D., an emergency medicine physician at Hasbro Children's Hospital, recently led a study that found children who were exposed to an adverse childhood experience (ACE) were 28 percent more likely to develop asthma. The rate of asthma occurrence further increased in children with each additional ACE exposure. The study, recently published ...
Scientists have for the first time captured live images of the process of taste sensation on the tongue.
The international team imaged single cells on the tongue of a mouse with a specially designed microscope system.
"We've watched live taste cells capture and process molecules with different tastes," said biomedical engineer Dr Steve Lee, from The Australian National University (ANU).
There are more than 2,000 taste buds on the human tongue, which can distinguish at least five tastes: salty, sweet, sour, bitter and umami.
However the relationship between the ...
Rather than slowing down, ants speed up in response to a higher density of traffic on their trails, according to new research published in Springer's journal The Science of Nature - Naturwissenschaften. When the researchers increased the supply of food by leaving food next to the trail, ants accelerated their speed by 50 percent. This was despite more than double the density of traffic.
When food increases in supply, more forager ants are sent out to carry it back to the nest. With this increase in ant density, the number of encounters between outbound and incoming individuals ...
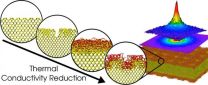
The ability of materials to conduct heat is a concept that we are all familiar with from everyday life. The modern story of thermal transport dates back to 1822 when the brilliant French physicist Jean-Baptiste Joseph Fourier published his book "Théorie analytique de la chaleur" (The Analytic Theory of Heat), which became a corner stone of heat transport. He pointed out that the thermal conductivity, i.e., ratio of the heat flux to the temperature gradient is an intrinsic property of the material itself.
The advent of nanotechnology, where the rules of classical ...
Scientists at The University of Manchester have made an important finding that could help develop an early test for kidney disease.
Dr Rachel Lennon from the Wellcome Trust Centre for Cell-Matrix Research has been studying why some people are more susceptible to kidney disease because of their race and gender.
She explains: "It's well known that impaired kidney function is more common in Afro-Caribbean individuals compared to those from a Caucasian background, and in men compared to women. However, the reasons for the difference in susceptibility are only just being ...
This news release is available in German.
The size of the neonatal skull is large relative to the dimensions of the birth canal in the female pelvis. This is the reason why childbirth is slower and more difficult in humans than in most other primates. Scientists from the Universities of Oslo and Vienna, identified adaptations in the morphology of the human body, which were unknown so far. The results of this new study appeared in the current edition of PNAS.
Upright walking and difficult birth
In hominids, upright walking evolved 4-5 million years ago. The ...
Is it possible to prevent mental health problems in higher education students? The answer is "yes" according to a team of psychologists from Loyola University Chicago who conducted a careful, systematic review of 103 universal interventions involving over 10,000 students enrolled in 2- and 4-year colleges and universities and graduate programs. The findings appear in the May 2015 issue of Prevention Science, published by Springer.
Researchers indicated that universal prevention interventions - that is, programs targeting general students, not just students who are at ...
Researchers from Plymouth University Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry are part of a team led by the University of Oxford, who have carried out new research that suggests mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) could provide an alternative non-drug treatment for people who do not wish to continue long-term antidepressant treatment.
The results are published in "The Lancet".
The results come from the first ever large study to compare MBCT - structured training for the mind and body which aims to change the way people think and feel about their experiences ...
Fragments of asteroids regularly land on Earth as meteorites. If you examine such a find, you can see that it comprises millimetre-sized round stones, known as chondrules. These small particles are believed to be the original building blocks of the solar system. However, the research community has not previously been able to explain how the chondrules formed asteroids. A new study shows that asteroids were formed by capturing chondrules with the help of gravitational force.
"The chondrules are of exactly the right size to be slowed down by the gas that orbited the young ...
Researchers at the Institut Hospital del Mar d'Investigacions Mèdiques (IMIM) have identified a new way of treating colorectal cancer. In the study published in the journal Science Signaling, the team led by LLuís Espinosa, investigator of IMIM's research group into stem cells and cancer, have shown that inhibition of endosomal activity is a potential therapeutic strategy for the treatment of cancers with the BRAF mutated gene. This discovery is an important step in the personalisation of the treatment of colorectal cancer, as the presence of this mutation is ...