New study analyzes 'thinspiration' images of women on social media sites
2015-05-08
(Press-News.org) Some of the most popular social media sites are filled with images of extremely thin women that might be harmful to those who view them -- whether they are seeking them or not, according to research from the University of California, Davis. The images were often cropped to remove heads or focus on just a few body parts.
Doctoral candidate Jannath Ghaznavi and associate professor Laramie Taylor in the Department of Communication examined about 300 photographs from Twitter and Pinterest postings that used the terms "thinspiration" and/or "thinspo" to tag images and ideas promoting extreme thinness and often casting eating disorders in a positive light.
Their paper "Bones, body parts, and sex appeal: An analysis of #thinspiration images on popular social media" was recently published in Body Image: An International Journal of Research.
"Imagine a teenage girl or even a young woman looking for inspiration using terms such as 'attractive,' 'fit,' or 'pretty,'" Ghaznavi said. "She will likely find images of headless, scantily clad, sexualized women and their body parts."
Images from Twitter, popular among younger audiences, were most likely to be cropped to remove heads and focus on specific body parts compared to Pinterest, according to the study.
The content analysis cannot speak to the effects of viewing the images, the researchers concede, but they point to studies that have shown repeated exposure to such content can result in body dissatisfaction and disordered eating attitudes.
"A young woman looking at these image may think that's what she should look like," Ghaznavi said. "That could prompt these girls and women to resort to extreme dieting, excessive exercise or other harmful behaviors in order to achieve this thin ideal."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-05-08
URBANA, Ill. - Much attention has been given to dedicated, perennial bioenergy crops to meet the revised Renewable Fuel Standard mandating production of 36 billion gallons of biofuel by the year 2022. Even so, concern remains over the impending need to convert as much as 30 million acres of U.S. crop land, which would include food crops, to land for perennial energy crops in order to meet that demand.
Researchers realize that biomass feedstocks will need to come from many different sources, including crop residues, forest residues, and municipal waste, for example, said ...
2015-05-08
Livermore - New results from the NASA NuSTAR telescope show that a supernova close to our galaxy experienced a single-sided explosion.
A team of scientists including Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers found that X-ray emissions taken with the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) show that the Supernova 1987A explosion was highly asymmetric. The results appear in the May 8 edition of the journal, Science.
NuSTAR observations, including those of 1987A, provide strong and compelling observational evidence that supernovae are not symmetric.
Supernova ...
2015-05-08
El Salvador, Niger, and Pakistan are performing better in improving water and sanitation for their citizens than industrial giants like Russia and Brazil according to the new WaSH Performance Index developed by The Water Institute at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill's Gillings School of Global Public Health. The new index to be released Friday, May 8 during a live webcast shows which countries are leaders in improving access to water and sanitation for their citizens. Sub-Saharan Africa countries including Mali, South Africa, and Ethiopia are also among the ...
2015-05-08
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. -- May 8, 2015) St. Jude Children's Research Hospital scientists have gained ground toward developing more targeted therapies for the most common childhood brain tumor. The findings appear today in the Journal of Molecular Biology.
The findings involve the DDX3X gene. In 2012, the St. Jude Children's Research Hospital -- Washington University Pediatric Cancer Genome Project highlighted DDX3X as a promising focus for efforts to develop targeted therapies against medulloblastoma. Such treatments target the genetic mistakes that give rise to the brain tumor's ...
2015-05-08
PITTSBURGH -- Scientists have been manipulating genes for a while. The University of Pittsburgh's Alexander Deiters just found a way to control the process with higher precision.
By using light.
Deiters and his group are the first to achieve this. The resulting paper was recently published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Since 2013, scientists have used a gene-editing tool called CRISPR/Cas9. The method employs a bacterially derived protein (Cas9) and a synthetic guide RNA to induce a double-strand break at a specific location in the genome. This ...
2015-05-08
Object recognition -- determining what objects are where in a digital image -- is a central research topic in computer vision.
But a person looking at an image will spontaneously make a higher-level judgment about the scene as whole: It's a kitchen, or a campsite, or a conference room. Among computer science researchers, the problem known as "scene recognition" has received relatively little attention.
Last December, at the Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, MIT researchers announced the compilation of the world's largest database of images ...
2015-05-08
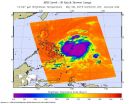
The Philippines warning center has raised a #2 warning for its citizens in the Luzon province of Catanduanes. This warning indicates, among other things, that the tropical cyclone will affect the locality and that winds of greater than 100 kph up to 185 kph (62 to 114 mph) may be expected in at least 18 hours.
Philippines know the storm as Dodong and have also raised warning #1 for the areas of Luzon provinces of Sorsogon. Albay, Camarines Norte, Camarines Sur, Quezon, Polillo Island, Aurora, Quirino, Isabela and the Visayas provinces of Northern and Eastern Samar.
Warning ...
2015-05-08
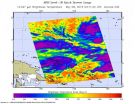
Forecasters expect Tropical Depression 07W which is riding behind Typhoon Noul to intensify to typhoon strength within the next five days. Currently 07W is located 298 miles southeast of Pohnopei, one of the Federated States of Micronesia. It is moving at a slow 5 knots on a east northeast trajectory with maximum sustained winds of 30 knots gusting to 40 (18 to 24 mph). Maximum wave height is 11 feet. 07W is moving east, but will turn round to a northwesterly course.
A tropical storm WARNING is in force for Kosrae, Pingelap and Mokil in Pohnpei State. A tropical storm ...
2015-05-08
For the last decade, scientists have deployed increasingly capable underwater robots to map and monitor pockets of the ocean to track the health of fisheries, and survey marine habitats and species. In general, such robots are effective at carrying out low-level tasks, specifically assigned to them by human engineers -- a tedious and time-consuming process for the engineers.
When deploying autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), much of an engineer's time is spent writing scripts, or low-level commands, in order to direct a robot to carry out a mission plan. Now a new ...
2015-05-08
The EU-funded MycoSynVac project combines gene engineering and biotechnology to design a novel veterinary vaccine chassis based on the bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
By combining their systems biology expertise with cutting-edge synthetic biology methodologies, researchers will engineer a universal chassis, which will be free of virulence and optimized for fast growth in a serum-free medium.
This chassis will be used to create specific vaccines against two highly detrimental pathogens that are causing suffering in livestock animals and large financial losses to the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New study analyzes 'thinspiration' images of women on social media sites