Six times more expensive to travel by car than by bicycle: Study
2015-05-12
(Press-News.org) It is six times more expensive for society - and for you individually - if you travel by car instead of cycling. This has been shown in a Lund University study of Copenhagen, a city of cyclists. It is the first time a price has been put on car use as compared to cycling.
In the comparative study, Stefan Gössling from Lund University and Andy S. Choi from the University of Queensland have investigated a cost-benefit analysis that the Copenhagen Municipality uses to determine whether new cycling infrastructure should be built.
It considers how much cars cost society and how they compare to bicycles in terms of air pollution, climate change, travel route, noise, road wear, health and congestion in Copenhagen.
The study concluded that cars have a greater negative impact on the economy than bicycles:
If the costs to society and the costs to private individuals are added together, the impact of the car is EUR 0.50 per kilometre and the impact of the bicycle is EUR 0.08 per kilometre.
The study by Stefan Gössling and his colleague also shows that if we only look at costs/benefits for society, one kilometre by car costs EUR 0.15, whereas society earns EUR 0.16 on every kilometre cycled.
"The cost-benefit analysis in Copenhagen shows that investments in cycling infrastructure and bike-friendly policies are economically sustainable and give high returns", says Stefan Gössling.
Cost-benefit analysis is a method used to calculate the benefits to society of infrastructure investments.
INFORMATION:
WATCH VIDEO: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t0fe_hvWVF0
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-05-12
Offenders enrolled in alcohol treatment programmes as part of their sentence are significantly less likely to be charged or reconvicted in the 12 months following their programme, a study led by Plymouth University has shown.
Researchers from the University's School of Psychology led a project, supported by the European Social Fund, which saw males with alcohol problems related to offending being assigned to a range of different treatments when convicted.
They then calculated the participants' charged and reconviction rates over the following year, with the results ...
2015-05-12
This news release is available in German.
Mainz-based researchers have made significant advances with regard to the development of individualized immunotherapy strategies for treating cancer. They have managed to identify the relevant genetic changes or mutations associated with various types of cancer and have determined their individual blueprints. This makes it possible for the scientists to readily produce customized cancer vaccines of the kind that have already been demonstrated to be effective in animal models. Here they have proven effective in the regression ...
2015-05-12
PITTSBURGH--Bragging to coworkers about a recent promotion, or posting a photo of your brand new car on Facebook, may seem like harmless ways to share good news.
However, a new study from City University London, Carnegie Mellon University and Bocconi University shows that self-promotion or a "humblebrag" often backfires.
Published in Psychological Science, Irene Scopelliti, George Loewenstein and Joachim Vosgerau wanted to find out why so many people frequently get the trade-off between self-promotion and modesty wrong. They found that self-promoters overestimate how ...
2015-05-12
Pollution from historic mining activities in south west England has led to a reduction in genetic diversity of brown trout according to new research from the University of Exeter. The findings, which will be published on Friday 15 May in the journal Evolutionary Applications, indicate that human activity can alter the genetic patterns of wild populations - an important issue in modern conservation.
The prevalence of metal contaminants in rivers across the south west of England is directly linked to mining activities dating back hundreds of years. Exposure to high concentrations ...
2015-05-12
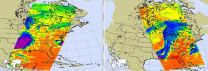
Today's imagery from NASA's AIRS instrument on the Aqua satellite indicates more severe weather is in store for the Midwest from Texas to Michigan. There is another extremely strong storm that is stretching from south to north and into Canada, and that system can be seen in this AIRS image from May 11, 2015. The first image (left) was taken at 3:35 am EDT, by the time the second image (right) was taken at 2:41 pm EDT the system had come together and was stretching across the nation vertically across the country.
Current weather forecasting predicts that Monday evening ...
2015-05-12
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Researchers have discovered why many animal species can spend their whole lives outdoors with no apparent concern about high levels of solar exposure: they make their own sunscreen.
The findings, published today in the journal eLife by scientists from Oregon State University, found that many fish, amphibians, reptiles, and birds can naturally produce a compound called gadusol, which among other biologic activities provides protection from the ultraviolet, or sun-burning component of sunlight.
The researchers also believe that this ability may have ...
2015-05-12
Using a smart tablet and a red beam of light, Georgia Institute of Technology researchers have created a system that allows people to control a fleet of robots with the swipe of a finger. A person taps the tablet to control where the beam of light appears on a floor. The swarm robots then roll toward the illumination, constantly communicating with each other and deciding how to evenly cover the lit area. When the person swipes the tablet to drag the light across the floor, the robots follow. If the operator puts two fingers in different locations on the tablet, the machines ...
2015-05-12
Diet exerts a major impact on health and ageing. The nervous system plays an important role in this process but, thus far, how food signals are interpreted by the nervous system has been a mystery. This is an important question because the perception of food by the nervous system impacts not just ageing, but also other processes associated with health and disease, including metabolism, reproduction, and development.
A new study published in eLife by researchers from the MRC Centre for Developmental Neurobiology (MRC CDN) at the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience ...
2015-05-12
To measure distances in the Universe, astronomers use Cepheids, a family of variable stars whose luminosity varies with time. Their role as distance calibrators has brought them attention from researchers for more than a century. While it was thought that nearly everything was known about the prototype of Cepheids, named Delta Cephei, a team of researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), the Johns Hopkins University, and the European Space Agency (ESA), have now discovered that this star is not alone, but that it has a hidden companion. A revelation published in The ...
2015-05-12
MADISON, Wis. -- Expansion of cattle pastures has led to the destruction of huge swaths of rain forest in Brazil, home to the world's largest herd of commercial beef cattle. But a new study led by the University of Wisconsin-Madison's Holly Gibbs shows that market-driven "zero deforestation agreements" have dramatically influenced the behavior of ranchers and the slaughterhouses to which they sell.
Publishing today [May 12, 2015] in the journal Conservation Letters, the research team - including other UW-Madison scientists, the National Wildlife Federation, and IMAZON ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Six times more expensive to travel by car than by bicycle: Study