(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of Birmingham have identified the role of an enzyme in muscle wasting, and associated age-related problems. They believe that inhibiting it could hold the key to developing ways of preventing, or reversing, the adverse effects.
The research, published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, is a significant step in understanding the role played by the enzyme '11β-HSD1' in the degenerative effects of ageing - including sarcopenia (age related muscle wasting).
The expression of 11β-HSD1, responsible for activating the steroid hormone cortisol, was increased in the muscles of older females.
134 healthy volunteers, aged between 20-80, underwent physical and biochemical tests at a clinical research facility, including body composition analysis by DEXA, jump plate mechanography, grip strength analysis, baseline biochemical profiling, urine collection, and vastus lateralis muscle biopsy.
The findings show that expression of 11β-HSD1 in skeletal muscles is increased 2.72-fold in women aged over 60 years of age, compared to those aged between 20 and 40. In male participants, no difference was seen.
High levels of the enzyme aligned with increased levels of cortisol, reduced grip strength, insulin resistance and a poorer body composition profile.
Dr Zaki Hassan-Smith, from the University of Birmingham, said, "As yet, we don't know why it appears to only occur in women, it is obviously an interesting area for further research. We are planning to look at whether hormones such as estrogens could be involved."
With many countries seeing emerging healthcare problems associated with an ageing population, the research team wanted to investigate novel ways of increasing the healthy life span - the years in which people can maintain active lifestyles without the debilitating impact of muscle wasting.
The research team were able to draw on expertise from both the University of Birmingham and Queen Elizabeth Hospitals Birmingham, and apply their knowledge of Cushing's Syndrome to a new problem.
Dr Hassan-Smith explained, "Looking at this particular enzyme seemed like an intriguing way forward. We knew how it works in relation to Cushing's Syndrome, which is characterised by similar symptoms, and thought it would be worthwhile applying what we knew to the ageing population."
Cushing's Syndrome is a rare disease caused by high cortisol levels, and those who suffer from the syndrome see marked changes in their body composition. The effects can be devastating for patients who can develop features such as muscle wasting and weakness, weight gain, thinning of the bones, diabetes, high blood pressure and heart disease.
At present there is no accepted pharmacological treatment for sarcopenia but pharmaceutical companies are developing and testing inhibitors of 11β-HSD1 with a focus on treatments for such conditions as diabetes.
The team is excited about taking the results of their study forward into future research, with one eye on adapting the inhibitors already in development to combat muscle ageing.
Dr Hassan Smith added, "The next stage is a 'proof of concept' study to look at the effects of these inhibitive pharmaceuticals on muscle function, before opening it up into a clinical trial. It's an as yet unexplored area that could yield beneficial results for a problem that is becoming more prevalent as our lifespans increase."
INFORMATION:
Use of cholesterol lowering drugs is associated with a one third lower risk of stroke in older adults without previous disease, finds a study published in The BMJ this week.
In high income countries, a growing proportion of heart disease and stroke occur in the oldest people. In France, for instance, people aged 85 years and over accounted for 43% of deaths from coronary heart disease and 49% of deaths from stroke in 2010.
Yet very few people over the age of 70 take part in trials testing cardiovascular drugs, so their benefit in the oldest people remains uncertain. ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - A new study in animals suggests that skipping meals sets off a series of metabolic miscues that can result in abdominal weight gain.
In the study, mice that ate all of their food as a single meal and fasted the rest of the day developed insulin resistance in their livers - which scientists consider a telltale sign of prediabetes. When the liver doesn't respond to insulin signals telling it to stop producing glucose, that extra sugar in the blood is stored as fat.
These mice initially were put on a restricted diet and lost weight compared to controls ...
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) -- Many of those who should get it, don't. And many of those who shouldn't, do. That's the story of a common screening test for osteoporosis, according to new research from UC Davis Health System.
The study, published online today in the Journal of General Internal Medicine, found that screening rates increased sharply among women at age 50, despite guidelines suggesting screening at age 65 unless risk factors are present. The presence of risk factors only had a modest influence on screening decisions.
Osteoporosis causes bone density to diminish ...
A dramatic video has captured the behaviour of cytotoxic T cells - the body's 'serial killers' - as they hunt down and eliminate cancer cells before moving on to their next target.
In a study published today in the journal Immunity, a collaboration of researchers from the UK and the USA, led by Professor Gillian Griffiths at the University of Cambridge, describe how specialised members of our white blood cells known as cytotoxic T cells destroy tumour cells and virally-infected cells. Using state-of-the-art imaging techniques, the research team, with funding from the ...
Decades' worth of textbook precepts about how our immune systems manage to avoid attacking our own tissues may be wrong.
Contradicting a long-held belief that self-reactive immune cells are weeded out early in life in an organ called the thymus, a new study by Stanford University School of Medicine scientists has revealed that vast numbers of these cells remain in circulation well into adulthood.
"This overturns 25 years of what we've been teaching," said Mark Davis, PhD, professor of microbiology and immunology and director of Stanford's Institute for Immunity, Transplantation ...
Scientists are reporting development of a new way to modify interleukin-2 (IL-2), a substance known as a cytokine that plays key roles in regulating immune system responses, in order to fine-tune its actions. Harnessing the action of IL-2 in a controllable fashion is of clinical interest with potential benefit in a range of situations, including transplantation and autoimmune disease. The modified IL-2 molecules inhibited the actions of endogenous IL-2, potentially more effectively than existing agents, as well as inhibited the actions of another interleukin, IL-15, with ...
A team led by researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and the Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT and Harvard has found that the most common bacterial community in the genital tract among healthy South Africa women not only is significantly different from that of women in developed countries but also leads to elevated levels of inflammatory proteins. In a paper in the May 19 issue of Immunity, the investigators describe finding potential mechanisms by which particular bacterial species induce inflammation and show that the presence of those species and of elevated ...
Ever since single-layer graphene burst onto the science scene in 2004, the possibilities for the promising material have seemed nearly endless. With its high electrical conductivity, ability to store energy, and ultra-strong and lightweight structure, graphene has potential for many applications in electronics, energy, the environment, and even medicine.
Now a team of Northwestern University researchers has found a way to print three-dimensional structures with graphene nanoflakes. The fast and efficient method could open up new opportunities for using graphene printed ...
HIV infections continue to rise in a new generation of young, gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with men (YMSM) despite three decades of HIV prevention as well as recent availability of biomedical technologies to prevent infection. In the U.S., it is estimated that 63% of incident HIV infections in 2010 were among YMSM despite the fact that they represent a very small portion of the population. Given this heightened risk for HIV seroconversion among YMSM, researchers at New York University's Center for Health, Identity, Behavior & Prevention Studies (CHIBPS) sought ...
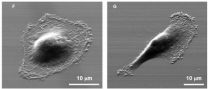
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- Why do some cancer cells break away from a tumor and travel to distant parts of the body? A team of oncologists and engineers from the University of Michigan teamed up to help understand this crucial question.
Cancer becomes deadly when it spreads, or metastasizes. Not all cells have the same ability to travel through the body, but researchers don't understand why.
In a paper published in Scientific Reports, researchers describe a new device that is able to sort cells based on their ability to move. The researchers were then able to take the sorted ...