(Press-News.org) OAK BROOK, Ill. -- Non-calcified arterial plaque is associated with diabetes, high systolic blood pressure and elevated 'bad' cholesterol levels in asymptomatic individuals, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology.
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the leading cause of death in men and women worldwide, accounting for 17 million deaths annually. Current treatment strategies focus on cardiovascular risk and serum cholesterol levels rather than direct assessment of extent of disease in the coronary arteries.
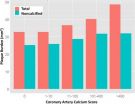
Plaque that forms in the arterial walls can restrict blood flow and, in some cases, rupture, leading to potentially fatal heart attacks. There is considerable evidence that calcified, or stable, plaque is less prone to rupture than non-calcified, or soft, plaque. Intravascular ultrasound can quantify non-calcified and calcified coronary artery plaque, but it is invasive and unsuitable for screening purposes. Coronary artery calcium (CAC) scoring with CT, a common noninvasive option, measures how much calcified plaque a person has, but it doesn't measure non-calcified plaque, and that's the component that tends to be dangerous. Despite treatment for hypercholesterolemia (high levels of cholesterol in the blood), CAC scores often paradoxically increase. Thus, researchers have searched for other plaque measures that can identify treatment response.
'Most information to date about coronary artery disease and cardiovascular risk factors in asymptomatic individuals has been derived from calcium scoring,' said the study's lead author, David A. Bluemke, M.D., Ph.D., from the NIH Clinical Center. 'We hypothesized that risk factors for the presence of non-calcified plaque may differ from those for calcified plaque.'
Coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) has emerged as a viable screening option for plaque, including non-calcified plaque. CCTA can capture the full anatomic map of the coronary arteries in a single heartbeat with low radiation dose and provide a complete picture of the total amount of plaque throughout the arteries of the heart.
For the study, Dr. Bluemke and colleagues used CCTA to assess the relationship between calcified and non-calcified coronary plaque burden in the coronary arteries and cardiovascular risk factors in low- to moderate-risk asymptomatic individuals.
The researchers recruited 202 asymptomatic men and women over age 55 who were eligible for statin therapy. CCTA was performed using a 320-detector row CT scanner and an intravenous contrast agent. Coronary wall thickness/plaque was evaluated, and analysis was performed to determine the relationship between risk factors and plaque.
Controlling for all risk factors, total coronary plaque index was greater in men than in women. Non-calcified plaque index was significantly associated with greater systolic blood pressure, diabetes, and elevated low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol level.
'These results highlight the potential of CCTA in quantifying plaque burden to assess progression or regression of coronary artery disease in low to moderate risk individuals,' Dr. Bluemke said.
INFORMATION:
'Coronary plaque burden at coronary CT angiography in asymptomatic men and women.' Collaborating with Dr. Bluemke were Karen Rodriguez, B.A., Alan C. Kwan, B.A., Shenghan Lai, M.D., João A. C. Lima, M.D., Davis Vigneault, B.S., Veit Sandfort, M.D., Puskar Pattanayak, M.D., Mark A. Ahlman, M.D., Marissa Mallek, R.N., and Christopher T. Sibley, M.D.
Radiology is edited by Herbert Y. Kressel, M.D., Harvard Medical School, Boston, Mass., and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc.
RSNA is an association of more than 54,000 radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Ill. (RSNA.org).
For patient-friendly information on CCTA, visit Radiology Info.
A new study shows that social and sensory overstimulation drives autistic behaviors. The study, conducted on rats exposed to a known risk factor in humans, supports the unconventional view of the autistic brain as hyper-functional, and offers new hope with therapeutic emphasis on paced and non-surprising environments tailored to the individual's sensitivity.
For decades, autism has been viewed as a form of mental retardation, a brain disease that destroys children's ability to learn, feel and empathize, thus leaving them disconnected from our complex and ever-changing ...
You might not need to remember those complicated e-mail and bank account passwords for much longer. According to a new study, the way your brain responds to certain words could be used to replace passwords.
In "Brainprint," a newly published study in academic journal Neurocomputing, researchers from Binghamton University observed the brain signals of 45 volunteers as they read a list of 75 acronyms, such as FBI and DVD. They recorded the brain's reaction to each group of letters, focusing on the part of the brain associated with reading and recognizing words, and found ...
San Antonio -- June 2, 2015 -- A close-up of Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko by NASA's ultraviolet instrument surprised scientists by revealing that electrons close to the comet's surface -- not photons from the Sun as had been believed -- cause the rapid breakup of water and carbon dioxide molecules spewing from the surface.
Since last August, the European Space Agency's Rosetta spacecraft has orbited within a hundred miles of the comet in this historic mission. The spectrograph onboard, named Alice, specializes in the far-ultraviolet wavelength band and was developed ...
Menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) given to recently postmenopausal women in the US for up to four years does not improve cognition, but may have some positive benefits for some mood symptoms, according to a study published by Carey Gleason and colleagues from the University of Wisconsin, Madison, USA, in this week's PLOS Medicine.
The researchers reached these conclusions by conducting a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial (the KEEPS-Cog trial), including 693 recently postmenopausal women living in the US who were randomly assigned to receive either oral estrogen ...
What if your doctor told you that your weight is somewhere between 100 and 400 lbs.? With any ordinary scale every patient can do better at home. Yet, one patient can't: the Milky Way. Even though today we peer deeper into space than ever before, our home galaxy's weight is still unknown to about a factor of four. Researchers at Columbia University's Astronomy Department have now developed a new method to give the Milky Way a more precise physical checkup.
The Milky Way consists of roughly 100 billion stars that form a huge stellar disk with a diameter of 100-200 thousand ...
PHILADELPHIA--(June 2, 2015)--Senescence, a phenomenon in which cells cease to divide and grow, can be caused by everything from natural DNA damage to treatment with chemotherapy. However, several mechanisms allow for cells to bypass senescence and grow out of control, eventually becoming cancerous. Now, scientists at The Wistar Institute have identified how a specific variant of a key protein complex found in human cells called condensin can reorganize a cell's genetic architecture in such a way as to promote senescence, making it an important facilitator in a cell's ...
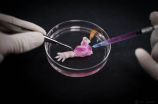
A team of Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigators has made the first steps towards development of bioartificial replacement limbs suitable for transplantation. In their report, which has been published online in the journal Biomaterials, the researchers describe using an experimental approach previously used to build bioartificial organs to engineer rat forelimbs with functioning vascular and muscle tissue. They also provided evidence that the same approach could be applied to the limbs of primates
"The composite nature of our limbs makes building a functional ...
Who says you can't do two things at once and do them both well?
A new University of Florida study challenges the notion that multi-tasking causes one or both activities to suffer. In a study of older adults who completed cognitive tasks while cycling on a stationary bike, UF researchers found that participants' cycling speed improved while multi-tasking with no cost to their cognitive performance.
Results of the study, which was supported by a grant from the National Institute on Aging, were published May 13 in the journal PLOS ONE.
The discovery was a surprise finding ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - A new nationwide study reveals that the kind of cities that attract college graduates has changed since the 1990s.
In the 1990s, grads were moving to cities with fast-growing "smart" industries in fields like high tech, the study found. But since 2000, with a less vibrant national economy, college graduates are flocking toward the biggest cities with the biggest labor markets and the best chances of landing a job.
In fact, the effect of city population size in attracting college grads was nearly four times as large in the 2000s as it was in the 1990s, ...
(New York, NY, June 1, 2015)-- The Big Apple is one of the most walkable cities in the nation, providing many opportunities for physical activity, and New Yorkers are more likely to exercise regularly than the average U.S. adult. But they are also sitting far more than what is considered healthy.
According to a new study published by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in its journal Preventing Chronic Disease, the average New York City resident sits more than seven hours a day--greatly exceeding the three hours or more per day that is associated with ...