New study showed spawning frequency regulates species population networks on coral reefs
UM Rosenstiel School scientists use computer model to uncover spawning strategies
2015-07-08
(Press-News.org) MIAMI - New research on tropical coral reef ecosystems showed that releasing larvae more often is beneficial for a species' network. The study on reproductive strategies is critical to assess the conservation of coral reef ecosystems worldwide.
Researchers from the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science used a computer model developed by UM Rosenstiel School scientist Claire Paris, known as the Connectivity Modeling System to track larval movements of three distinct reef species - the Carribean sea plume (Anthiellogorgia elisebeathae), the bicolor damselfish (Stegastes partitus) and the Caribbean spiny lobster (Panulirus argus). The three species, which have varying larval dispersal strategies, were simulated in a dynamic natural marine system over time to determine whether dispersal was driven by environmental or biological factors for the modeled species.
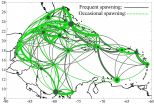
Many coral reef species live on separate habitat patches on coral reefs that are linked through larval dispersal into a larger population network. As a parent population spawns, the eggs and larvae are transported in the currents from their native location to another, more distant location. This exchange of larvae by currents between geographically separated populations create a network of connections, which is known as a connectivity network. The authors suggest that the more often an animal reproduces, the greater the variability in the ocean currents that larvae can experience, and the more potential habitats that a dispersing animal could be connected to.
"We found that the rate at which a species spawn drives the relatedness between distant populations," said Claire Paris, associate professor of ocean sciences at the UM Rosenstiel School. "Therefore more frequent spawning is more likely to stabilize the connectivity network."
"There is tremendous variability in how often reef animals reproduce and release eggs and larvae, yet they all find their way to coral reefs," said Andrew Kough, UM Rosenstiel School alumnus and lead author of the study. "Our study explored how changes in reproductive frequency shape an animal's connectivity network."
The researchers also found that larval behavior enhances the persistence of these network connections, when compared to passive transport by the ocean currents.
"For animals that reproduce infrequently, vertical swimming behavior during the larval stage helps control the dispersal network and is a vital part of marine ecology," said Kough.
The larval phase of a marine species is often the only time that coral reef inhabitants travel between habitat locations, an important early life history stage required to maintain healthy populations when environmental conditions fluctuate due to both natural and man-made factors.
"Our model has proved accurate enough to test important hypotheses in marine ecology, said Paris. "One hot topic has always been about the role of reproduction strategies on the structure of marine populations. We find a fine balance between spawning frequency and larval behavior in reef species."
INFORMATION:
The study, titled "The influence of spawning periodicity on population connectivity," was published in the Online First section of the journal Coral Reefs. The co-authors are Andrew S. Kough and Claire B. Paris.
About the University of Miami's Rosenstiel School
The University of Miami is one of the largest private research institutions in the southeastern United States. The University's mission is to provide quality education, attract and retain outstanding students, support the faculty and their research, and build an endowment for University initiatives. Founded in the 1940's, the Rosenstiel School of Marine & Atmospheric Science has grown into one of the world's premier marine and atmospheric research institutions. Offering dynamic interdisciplinary academics, the Rosenstiel School is dedicated to helping communities to better understand the planet, participating in the establishment of environmental policies, and aiding in the improvement of society and quality of life. For more information, visit: http://www.rsmas.miami.edu.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-07-08
Cancer cells defy the rules by which normal cells abide. They can divide without cease, invade distant tissues and consume glucose at abnormal rates.
Now a study by University of Pennsylvania researchers implicates defects in mitochondria, the energy-production centers of cells, as playing a key role in the transition from normal to cancerous. When the Penn scientists disrupted a key component of mitochondria, otherwise normal cells took on characteristics of cancerous tumor cells.
The research is published in the journal Oncogene and was led by members of the lab of ...
2015-07-08
Boulder, Colo., USA - Submarine landslides, also known as mass transport deposits (MTDs), are common in marine environments and pose risks to coastal communities and offshore infrastructure. This new 332-point database presented by Lorena Moscardelli and Lesli Wood is drawn from studies of multiple MTDs around the world. Understanding these MTDS, they write, will help determine the extent of ancient submarine landslides and contribute to the development geo-models for forecasting future submarine slides.
FEATURED ARTICLE
Morphometry of mass transport deposits as a predictive ...
2015-07-08
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Southern Californians and writers love to blame the hot, dry Santa Ana winds for tense, ugly moods, and the winds have long been associated with destructive wildfires.
Now, a new study finds that on occasion, the winds have an accomplice with respect to fires, at least: Natural atmospheric events known as stratospheric intrusions, which bring extremely dry air from the upper atmosphere down to the surface, adding to the fire danger effects of the Santa Anas, and exacerbating some air pollution episodes.
The findings suggest that forecast models with ...
2015-07-08
AROUND half of all breast cancer patients could one day benefit from having the cheap and widely-available female hormone progesterone added to their treatment, according to Cancer Research UK funded research published in Nature today (Thursday)*.
Tumours fuelled by the female hormone oestrogen are treated with drugs like tamoxifen to block oestrogen receptors, which cause cancer cells to grow.
Women whose tumours have progesterone receptors as well are known to have a better outlook. But for decades scientists have been unable to pinpoint why.
Scientists at Cancer ...
2015-07-08
From a Glacier's Perspective
Big Four glacier & ice caves, WA: a short future?
Early summer melting led to the collapse of Washington ice caves, the death of one person, and the injury of five others. Mauri Pelto asks questions about the future of Washington's Big Four glacier on his blog From a Glacier's Perspective.
Eos.org
Learning geoscience by doing geoscience
A pilot project helps teachers bring scientific practice into the classroom.
New research papers
Response of the Amazon carbon balance to the 2010 drought derived with CarbonTracker South America, ...
2015-07-08
Researchers have developed a new approach for better integrating medical devices with biological systems. The researchers, led by Bozhi Tian, assistant professor in chemistry at the University of Chicago, have developed the first skeleton-like silicon spicules ever prepared via chemical processes.
"Using bone formation as a guide, the Tian group has developed a synthetic material from silicon that shows potential for improving interaction between soft tissue and hard materials," said Joe Akkara, a program director in the National Science Foundation materials research ...
2015-07-08
Tropical Depression 4E formed in the Eastern Pacific and crossed the 140 West longitude line as of the 0300 UTC time, which brought it into the Central Pacific Ocean. NOAA's GOES-West satellite captured an infrared image of the depression at 0900 UTC (5 a.m. EDT) on July 8 that showed the large storm in the Central Pacific.
At 8 p.m. PDT/11 p.m. EDT on July 7, (0300 UTC on July 8), the center of newly formed Tropical Depression Four-E was located near latitude 15.4 North, longitude 140.2 West. The depression was moving toward the west-northwest near 17 mph (28 kph) and ...
2015-07-08
Rice University researchers have built a simulation to show how cancerous tumors manipulate blood-vessel growth for their own benefit.
Like all cells, those in tumors need access to the body's fine network of blood vessels to bring them oxygen and carry away waste. Tumors have learned to game the process called angiogenesis in which new vessels sprout from existing ones, like branches from a tree.
But some details have been hidden until now.
The ability to stop tumors through anti-angiogenesis is one goal of cancer therapy. The new work by scientists at Rice's Center ...
2015-07-08
July 8, 2015 - A recent CDC report calls into question the widely reported belief that Black fathers are more absent in their children's lives than White fathers - showing that while more Black fathers live apart from their children, they are just as involved with their children as members of other racial groups in the same living situations. So why is it that messages about Black absentee fathers, such as Obama's 2008 Father's Day address, are so pervasive in society?
A new paper, published today in Social Psychological and Personality Science, suggests that such messages ...
2015-07-08
CAMBRIDGE, Mass--When you spill a bit of water onto a tabletop, the puddle spreads -- and then stops, leaving a well-defined area of water with a sharp boundary.
There's just one problem: The formulas scientists use to describe such a fluid flow say that the water should just keep spreading endlessly. Everyone knows that's not the case -- but why?
This mystery has now been solved by researchers at MIT -- and while this phenomenon might seem trivial, the finding's ramifications could be significant: Understanding such flowing fluids is essential for processes from the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New study showed spawning frequency regulates species population networks on coral reefs
UM Rosenstiel School scientists use computer model to uncover spawning strategies