This week from AGU: Ice cave collapse, learning geoscience and 4 new research papers
2015-07-08
(Press-News.org) From a Glacier's Perspective
Big Four glacier & ice caves, WA: a short future?
Early summer melting led to the collapse of Washington ice caves, the death of one person, and the injury of five others. Mauri Pelto asks questions about the future of Washington's Big Four glacier on his blog From a Glacier's Perspective.
Eos.org
Learning geoscience by doing geoscience
A pilot project helps teachers bring scientific practice into the classroom.
New research papers
Response of the Amazon carbon balance to the 2010 drought derived with CarbonTracker South America, Global Biogeochemical Cycles
CO2 outgassing from the Yellow River network and its implications for riverine carbon cycle, Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences
Use of a forest sapwood area index to explain long-term variability in mean annual evapotranspiration and streamflow in moist eucalypt forests, Water Resources Research
Tamarix transpiration along a semiarid river has negligible impact on water resources, Water Resources Research
INFORMATION:
Find research spotlights from AGU journals and sign up for weekly E-Alerts, including research spotlights, on eos.org. Register for access to AGU journal papers in the AGU newsroom.
The American Geophysical Union is dedicated to advancing the Earth and space sciences for the benefit of humanity through its scholarly publications, conferences, and outreach programs. AGU is a not-for-profit, professional, scientific organization representing more than 60,000 members in 139 countries. Join our conversation on Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, and other social media channels.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-07-08
Researchers have developed a new approach for better integrating medical devices with biological systems. The researchers, led by Bozhi Tian, assistant professor in chemistry at the University of Chicago, have developed the first skeleton-like silicon spicules ever prepared via chemical processes.
"Using bone formation as a guide, the Tian group has developed a synthetic material from silicon that shows potential for improving interaction between soft tissue and hard materials," said Joe Akkara, a program director in the National Science Foundation materials research ...
2015-07-08
Tropical Depression 4E formed in the Eastern Pacific and crossed the 140 West longitude line as of the 0300 UTC time, which brought it into the Central Pacific Ocean. NOAA's GOES-West satellite captured an infrared image of the depression at 0900 UTC (5 a.m. EDT) on July 8 that showed the large storm in the Central Pacific.
At 8 p.m. PDT/11 p.m. EDT on July 7, (0300 UTC on July 8), the center of newly formed Tropical Depression Four-E was located near latitude 15.4 North, longitude 140.2 West. The depression was moving toward the west-northwest near 17 mph (28 kph) and ...
2015-07-08
Rice University researchers have built a simulation to show how cancerous tumors manipulate blood-vessel growth for their own benefit.
Like all cells, those in tumors need access to the body's fine network of blood vessels to bring them oxygen and carry away waste. Tumors have learned to game the process called angiogenesis in which new vessels sprout from existing ones, like branches from a tree.
But some details have been hidden until now.
The ability to stop tumors through anti-angiogenesis is one goal of cancer therapy. The new work by scientists at Rice's Center ...
2015-07-08
July 8, 2015 - A recent CDC report calls into question the widely reported belief that Black fathers are more absent in their children's lives than White fathers - showing that while more Black fathers live apart from their children, they are just as involved with their children as members of other racial groups in the same living situations. So why is it that messages about Black absentee fathers, such as Obama's 2008 Father's Day address, are so pervasive in society?
A new paper, published today in Social Psychological and Personality Science, suggests that such messages ...
2015-07-08
CAMBRIDGE, Mass--When you spill a bit of water onto a tabletop, the puddle spreads -- and then stops, leaving a well-defined area of water with a sharp boundary.
There's just one problem: The formulas scientists use to describe such a fluid flow say that the water should just keep spreading endlessly. Everyone knows that's not the case -- but why?
This mystery has now been solved by researchers at MIT -- and while this phenomenon might seem trivial, the finding's ramifications could be significant: Understanding such flowing fluids is essential for processes from the ...
2015-07-08
CHICAGO (July 8, 2015): Work hour restrictions for resident physicians, revised nationally four years ago largely to protect patients against physician trainees' fatigue-related errors, have not had the desired effect of lowering postoperative complication rates in several common surgical specialties, according to new study results. The study was published as an "article in press" on the Journal of the American College of Surgeons website in advance of print publication later this year.
There was no significant difference in measured surgical patient outcomes between ...
2015-07-08
Natural killer cells of the immune system can fend off malignant lymphoma cells and thus are considered a promising therapeutic approach. However, in the direct vicinity of the tumor they lose their effect. Scientists of Helmholtz Zentrum München have now elucidated which mechanisms block the natural killer cells and how this blockade could be lifted. The results were recently published in the European Journal of Immunology.
Natural killer cells (NK cells) are part of the immune system and provide an innate immunity against exogenous and altered endogenous structures. ...
2015-07-08
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- The number of women across the globe filing patents with the U.S. Patent and Trade Office over the past 40 years has risen fastest within academia compared to all other sectors of the innovation economy, according to a new study from Indiana University.
The analysis, which examined 4.6 million utility patents issued from 1976 to 2013, was led by Cassidy R. Sugimoto, an associate professor of informatics at the School of Informatics and Computing at IU Bloomington.
The results of "The Academic Advantage: Gender Disparities in Patenting" are reported ...
2015-07-08
This news release is available in French. At population level, vaccines contribute to reducing mortality associated with infectious diseases such as measles, diphtheria, tetanus, hepatitis B or bacterial meningitis. The community general physician, at the centre of this preventive strategy, remains the main source of information for families. In an article published in the journal Ebiomedecine, Pierre Verger (Inserm Unit 912, "Economics and Social Sciences Applied to Health and Analysis of Medical Information - SESSTIM") and his collaborators present and analyse the ...
2015-07-08
This news release is available in German.
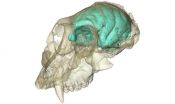
The oldest known Old World monkey, Victoriapithecus, first made headlines in 1997 when its fossilized skull was discovered on an island in Kenya's Lake Victoria, where it lived 15 million years ago. An international team led by Fred Spoor of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany, and University College London (UCL), UK, has now visualized this monkey's brain for the first time: The creature's tiny but remarkably wrinkled brain supports the idea that brain complexity can evolve before ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] This week from AGU: Ice cave collapse, learning geoscience and 4 new research papers