It takes a lot of nerve: Scientists make cells to aid peripheral nerve repair
2015-08-06
(Press-News.org) Scientists at the University of Newcastle, UK, have used a combination of small molecules to turn cells isolated from human skin into Schwann cells - the specialised cells that support nerves and play a role in nerve repair. This new method generates large and pure populations of Schwann cells and hence is a promising step forward for the repair of peripheral nerve injuries. This research has just been published in the scientific journal Development at http://dev.biologists.org/
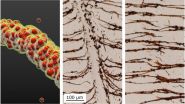
Currently, nerve repair strategies involve taking grafts from patients and using these to repair their damaged peripheral nerves but this approach has several disadvantages and can often itself cause nerve damage. Now, Motoharu Sakaue together with Maya Sieber-Blum, Professor of Stem Cell Sciences at the Institute of Genetic Medicine in Newcastle, investigated the possibility of making Schwann cells, which are known to promote nerve repair. To make these cells, the researchers isolated stem cells from adult skin and coaxed them into Schwann cells by exposing them to small molecules.
"We observed that the bulge, a region within hair follicles, contains skin stem cells that are intermixed with cells derived from the neural crest - a tissue known to give rise to Schwann cells. This observation raised the question whether these neural crest-derived cells are also stem cells and whether they could be used to generate Schwann cells" said Sieber-Blum.
"We then used pertinent small molecules to either enhance or inhibit pathways that are active or inactive, respectively, in the embryo during Schwann cell differentiation" she said.
Using this approach, the scientists were able to generate large and highly pure populations of human Schwann cells. These cells exhibited a morphology that is characteristic of Schwann cells and also expressed relevant Schwann cell markers. The researchers further tested the functionality of these Schwann cells, showing that they could interact with nerves in vitro. "The next step is to determine, for example in animal models of peripheral nerve injury, whether grafts of these Schwann cells are conducive to nerve repair" say the authors.
This study identifies a biologically relevant and accessible source of cells that could be used for generating sufficient quantities of Schwann cells and thus offers great potential in the repair of peripheral nerve injuries.
INFORMATION:
If reporting this story, please mention Development as the source and, if reporting online, please carry a link to: http://dev.biologists.org
REFERENCE:
Sakaue, M. and Sieber-Blum, M. (2015). Human epidermal neural crest stem cells as a source of Schwann cells. Development, doi:10.1242/dev.123034
This article is posted on this site to give advance access to other authorised media who may wish to report on this story. Full attribution is required, and if reporting online, a link to dev.biologists.com is also required.
The story posted here is COPYRIGHTED. Therefore advance permission is required before any and every reproduction of each article in full. PLEASE CONTACT permissions@biologists.com
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-08-05
TORONTO, August 5 2015 -- The term "self-regulation" has started appearing in children's report cards of late, but what it means is often unclear to parents. Thanks to three York University researchers, who have created a clear-cut definition for learning this important psychological concept, parents and teachers can now have a better understanding of what "self-regulation" means and how they can help their children develop that capacity.
"My hope is that every parent whose child has had a meltdown in a mall, and every teacher who has to work hard every day to prevent ...
2015-08-05
PHILADELPHIA -- Moles are benign tumors found on the skin of almost every adult. Scientists have known for years that a mutation in the BRAF gene makes them start growing, but until now haven't understood why they stop. Now, researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania have identified a major genetic factor that keeps moles in their usual non-cancerous, no-growth state. The study was published online first this summer in the journal Cancer Discovery.
"The BRAF mutation that stimulates the initial growth of moles also stimulates the ...
2015-08-05
Glenview, Ill. (August 5, 2015)-- Researchers may be closer to finding the mechanism responsible for loss of lung elastic recoil and airflow limitation in nonsmokers with chronic asthma. The study published today in the journal CHEST Unraveling the Pathophysiology of the Asthma-COPD Overlap Syndrome reported that both nonsmokers and smokers with chronic asthma share features of COPD. This conundrum, often referred to as asthma-COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS), has been assumed to be due to large and especially small airway remodeling.
The study found that many patients with ...
2015-08-05
PITTSBURGH, Aug. 5, 2015 - Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine have figured out how to objectively quantify the beating action of cilia, the tiny, hair-like projections on cells that line nasal passages, the lungs and almost every other body tissue, according to a study published online today in Science Translational Medicine. Such digital signatures could help doctors more quickly and accurately diagnose ciliary motion (CM) defects, which can cause severe respiratory airway clearance defects and also developmental defects including congenital ...
2015-08-05
ROSEMONT, Ill.-- Most patients younger than age 50 with a torn or severely damaged meniscus experienced reduced pain and improved knee function following transplant surgery, according to a study in the August 5 issue of the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery (JBJS). However, many patients required additional surgery within 10 years.
The meniscus is a wedge-shaped piece of fibrocartilage in the knee that acts as a shock absorber between the thighbone and shinbone. A meniscus can be torn during sports or wear away over time as the body ages. For younger patients with knee ...
2015-08-05
Using photosynthetically active microorganisms, researchers at the Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) have succeeded in manufacturing several biocatalysts suitable for industrial application: a crucial step towards sustainable chemical processes, according to Dr Marc Nowaczyk from the Chair for Plant Biochemistry and Jun.-Prof Dr Robert Kourist, Junior Research Group Microbial Biochemistry.
Sustainable manufacture of enzymes for the industry
Seeing as our planet's fossil resources are limited, researchers are looking for new methods for the production of certain substances, ...
2015-08-05
If you want to form very flexible chains of nanoparticles in liquid in order to build tiny robots with flexible joints or make magnetically self-healing gels, you need to revert to childhood and think about sandcastles.
In a paper published this week in Nature Materials, researchers from North Carolina State University and the University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill show that magnetic nanoparticles encased in oily liquid shells can bind together in water, much like sand particles mixed with the right amount of water can form sandcastles.
"Because oil and water don't ...
2015-08-05
Disney Research has developed a new method of rendering high-quality graphics for animated features that efficiently corrects for erroneous pixels while preserving the crisp detail in images, significantly increasing the efficiency of producing animated images.
The new approach enhances the performance of Monte Carlo ray tracing, a method for rendering 3-D scenes by randomly tracing the possible light paths for each pixel in an image. The images produced by ray tracing can be highly realistic, but can require large amounts of computer time to render.
The Disney researchers ...
2015-08-05
The elaborate costumes worn by Rapunzel, the heroine of Disney's "Tangled," are testament to the growing sophistication of cloth animation, but for art directors, who must tweak tens or hundreds of technical parameters, achieving a desired look for simulated clothing can be laborious.
To ease this process, Disney Research and Walt Disney Animation Studios have developed a tool that enables technical directors who must create garments that are soft, silky, wrinkly, heavy, or flowing, to use those same terms to control the computer programs that fashion simulated cloth.
The ...
2015-08-05
Little details, such as the wrinkling or twitching of an eyelid, can have a big impact on whether a digitally rendered face looks real in a film or videogame. Now scientists at Disney Research have devised the first method to capture these subtleties of the eyelids in detail.
Their method, to be presented at ACM SIGGRAPH 2015, the International Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, in Los Angeles Aug. 9-13, captures detailed, dynamic skin features and creates plausible folding and stretching in areas that aren't directly captured during data collection.
Artists ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] It takes a lot of nerve: Scientists make cells to aid peripheral nerve repair