High-precision control of nanoparticles for digital applications
2015-08-18
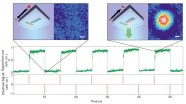
(Press-News.org) For the first time ever, researchers have succeeded in creating arrangements of colloids - tiny particles suspended in a solution - and, importantly, they have managed to control their motion with high precision and speed. Thanks to this new technique developed by scientists at the University of Zurich, colloidal nanoparticles may play a role in digital technologies of the future. Nanoparticles can be rapidly displaced, require little energy and their small footprint offers large storage capacity - all these attributes make them well suited to new data storage applications or high-resolution displays.
Colloids are minute particles that are finely distributed throughout a liquid. Suspensions of colloidal particles are most familiar to us as beverages, cosmetics and paints. At a diameter in the range of ten to one hundred nanometres, a single such particle is invisible to the naked eye. These nanoparticles are constantly in motion due to the principle of Brownian motion. Since the particles are electrically charged, they experience forces of attraction and repulsion that can be harnessed to control and manipulate their behavior. In experiments carried out five years ago, Madhavi Krishnan, Professor of Physical Chemistry at the University of Zurich, succeeded in the controlled spatial manipulation of matter on the nanometer scale. In a new study, she and her colleagues have now demonstrated that it is not only possible to spatially confine nanoparticles, but also to control their position and orientation in time and to do so in a liquid, without using physical contact.
Manipulation using electrical and optical signals
The UZH researchers have developed a method that makes it possible to create nanostructures and manipulate them in a flexible way. They were able to organise the tiny particles into new structures with the utmost precision and then to manipulate their motion. «Manipulation is made possible by the interaction with electrical and optical fields», explains Madhavi Krishnan. This new approach using intermolecular interactions at room termperature does not require ultracold temperatures. The new technology also offers extremely fast and low-friction operation.
Smaller, faster and with more storage capacity
This technique for arranging and manipulating colloid motion makes it possible to develop completely new materials and devices. «Nanoparticles possess properties that are very useful for digital technologies, and each individual particle can now be used to store and retrieve data», explains Madhavi Krishnan. The targeted manipulation of individual nanoparticles opens up new options for their application, including in future data storage media or in displays with resolutions that have thus far been hard to attain. «This makes possible displays along the lines of the Kindle reader with a pixel size that is thousand-times smaller and a much faster response time» the scientist explains.
INFORMATION:
References
Christopher J. Myers, Michele Celebrano and Madhavi Krishnan. Information storage and retrieval in a single levitating colloidal particle. Nature Nanotechnology, August 17, 2015.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.173
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-08-18
In a commentary published in the Aug. 13 issue of JAMA, Johns Hopkins experts say consolidation of hospitals into massive chains threatens healthy competition, reduces patient choice and could drive up medical expenses.
The authors call on the Federal Trade Commission -- the regulatory body overseeing business practices and consumer protection -- to be more vigilant and cautious when hospital systems seek approval to consolidate and to pay particular attention to geographic regions where proposed mergers could create a single dominant hospital system.
"It's really Economics ...
2015-08-18
AMES, Iowa - Mothers are often the caregiver when a child is sick, and that motherly instinct doesn't go away when the child is an adult. In fact, mothers provide more support to adult children with a serious health condition than to their other children, according to new research that will be presented at the American Sociological Association 2015 Annual Meeting.
It's a situation that can put older mothers in a vulnerable position, said Megan Gilligan, lead author and assistant professor of human development and family studies at Iowa State University. Gilligan and ...
2015-08-18
Researchers from North Carolina State University, Institut Langevin and Paris-Descartes University have conducted a proof-of-concept study that raises the possibility of using ultrasound techniques to detect cervical stiffness changes that indicate an increased risk of preterm labor in pregnant women. While additional work needs to be done, it may ultimately give doctors a new tool for determining when to provide treatment that can prevent preterm birth.
Premature births can mean low birthweights and other medical problems for newborns, but there are steps that doctors ...
2015-08-18
An international research team reports results of a three-year study of sediment samples collected offshore from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in a new paper published August 18, 2015, in the American Chemical Society's journal, Environmental Science and Technology.
The research aids in understanding what happens to Fukushima contaminants after they are buried on the seafloor off coastal Japan.
Led by Ken Buesseler, a senior scientist and marine chemist at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), the team found that a small fraction of contaminated ...
2015-08-18
Only 1 in 10 heart failure patients is referred to a cardiac rehabilitation program after being hospitalized, despite strong evidence that such exercise programs improve quality of life and reduce the likelihood of future hospitalizations.
The findings, from a UCLA-led study, appear in the August 25 Journal of the American College of Cardiology. Researchers drew the data from a national database of more than 100,000 people with heart failure who were discharged from hospitals between 2005 and 2014 and were eligible for cardiac rehabilitation programs.
"Although we expected ...
2015-08-18
A new class of fascinating technologies -- including optics in computing, telecommunications links and switches, and virtually any other optical component -- could be created simply by configuring a mesh of light-controlling devices known as interferometers. This is similar to the way electronic semiconductors can fashion the wide array of digital technologies we have at our disposal today.
Optical technologies have the potential to greatly reduce the power consumption of computers, speed telecommunications, and enhance the sensitivity of chemical and biological sensors. ...
2015-08-18
A national survey of more than 750 emergency medical services providers conducted by researchers at Oregon Health & Science University identified airway management skills, personal anxiety and limited pediatric care proficiency among key factors that may contribute to pediatric safety events for children in out-of-hospital emergent care situations. The study, published online today in The Journal of Pediatrics, supports the American Academy of Pediatrics' recommendation for pediatric physician involvement in EMS training, medical oversight and policy development.
"Pediatric ...
2015-08-18
Violent conflicts in Neolithic Europe were held more brutally than has been known so far. This emerges from a recent anthropological analysis of the roughly 7000-year-old mass grave of Schöneck-Kilianstädten by researcher of the Universities of Basel and Mainz. The findings, published in the journal PNAS, show that victims were murdered and deliberately mutilated.
It was during the time when Europeans first began to farm. To what degree conflicts and wars featured in the early Neolithic (5600 to 4900 B.C.), and especially in the so-called Linear Pottery culture ...
2015-08-18
A study of catsharks reveals how alterations in the expression and function of certain genes in limb buds underlie the evolution of fish fins to limbs. The findings are reported by researchers from Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG, Barcelona) and their collaborators in the journal eLife and give new insight into how fish evolved to live on land in the form of early tetrapods.
The first four-legged, land-living creatures - known as early tetrapods - evolved from fish, following the transformation of fins into limbs. This ...
2015-08-18
Patient satisfaction is a very poor proxy for quality of care comparisons in elective cranial neurosurgery. Because deaths are rare events in elective cranial neurosurgery, reporting of surgeon or even department-specific mortality figures cannot differentiate a high or low level of the quality of care.
The current focus on patient safety in health care has led to public quality-of-care comparisons between health care facilities and even between individual health care professionals. In the United States, a new reimbursement method based on patient satisfaction ratings ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] High-precision control of nanoparticles for digital applications