Anti-transpirant products unnecessary in cycad propagation
2021-01-02
(Press-News.org) In a first-of-its-kind study within cycad horticulture literature, University of Guam researchers have found that the use of anti-transpirants neither help nor hinder successful propagation of cycad stem cuttings.
The Guam-based study, published Oct. 22 in the journal Tropical Conservation Science, investigated whether retaining leaves during the propagation of cycad stem cuttings conferred any benefit to propagation success. Additionally, two anti-transpirant products were utilized to investigate their efficacy during the propagation process.
Leaves perform a variety of critical functions for plants, including the transport of water and nutrients from the roots via transpiration, the synthesis of useful sugars via photosynthesis, and the reduction of water loss via the closing of stomata, or little openings on the undersides of the leaves. Horticulturists sometimes manipulate these openings to the plant's benefit.
Anti-transpirants are products used in the commercial fruit industry to reduce water demands during periods of drought and have been shown to be useful during grafting trials of some plants. Some of these products work by coating the stomata, preventing the escape of gases and thereby water loss. Others purportedly induce chemical reactions within the plant to help reduce water loss. One of each type of anti-transpirant was used for the studies.
The study tested the use of anti-transpirants on two species of Zamia cycads.
"To our knowledge no anti-transpirant product has ever been used on any cycad species prior to these studies," said Benjamin Deloso, a cycad specialist who led the study as part of his master's thesis at UOG.
Numerous traits were measured throughout the duration of the study, including the speed of adventitious root formation, the behavior of the retained leaves, the date of first leaf emergence, and plant survival.
The results revealed that leaf retention on stem cuttings yielded no beneficial or detrimental influence on propagation success or the speed of adventitious root formation and that when cycad plants are healthy, regeneration of roots and leaves is possible from stem cuttings when under the care of an experienced cycad horticulturist.
"You can think of a healthy cycad stem as a bank account. Even if you experience some losses -- loss of roots or leaves -- you still have reserves in the account that can be used to recover," Deloso said.
The University of Guam continues to publish original research and expand knowledge on cycads, the world's most threatened plant group.
Although this latest research did not include Guam's native cycad, Cycas micronesica, known locally as fadang, the research is of interest to its conservation.
"As a native CHamoru, I am concerned about the state of Guam's environment," said C.J. Paulino, an environmental science graduate student at UOG and a co-author of the study. "Given the decline of the island's native fadang, I was happy to contribute to research that would benefit its conservation."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-02
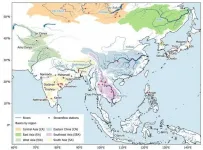
813 years of annual river discharge at 62 stations, 41 rivers in 16 countries, from 1200 to 2012. That is what researchers at the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) produced after two years of research in order to better understand past climate patterns of the Asian Monsoon region.
Home to many populous river basins, including ten of the world's biggest rivers (Figure 1), the Asian Monsoon region provides water, energy, and food for more than three billion people. This makes it crucial for us to understand past climate patterns so that we can better predict long term changes in ...
2021-01-02
COLUMBUS, Ohio - The introduction of computer simulation to the identification of symptoms in children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) has potential to provide an additional objective tool to gauge the presence and severity of behavioral problems, Ohio State University researchers suggest in a new publication.
Most mental health disorders are diagnosed and treated based on clinical interviews and questionnaires - and, for about a century, data from cognitive tests has been ...
2021-01-02
Kraków, 30 December 2020
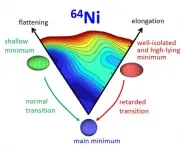
The map of nuclear deformation takes the form of a mountain landscape
Until recently, scientists believed that only very massive nuclei could have excited zero-spin states of increased stability with a significantly deformed shape. Meanwhile, an international team of researchers from Romania, France, Italy, the USA and Poland showed in their latest article that such states also exist in much lighter nickel nuclei. Positive verification of the theoretical model used in these experiments allows describing the properties of nuclei unavailable in Earth laboratories.
More than ...
2021-01-02
New Orleans, LA - Research conducted at LSU Health New Orleans Neuroscience Center of Excellence reports that a combination of an LSU Health-patented drug and selected DHA derivatives is more effective in protecting brain cells and increasing recovery after stroke than a single drug. The findings are published in Brain Circulation, available here.
Nicolas Bazan, MD, PhD, Boyd Professor, Professor of Neurology and Director of the Neuroscience Center of Excellence at LSU Health New Orleans School of Medicine, and Ludmila ...
2021-01-02
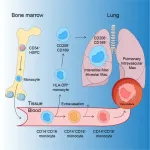
In some cases, immune cells in the lungs can contribute to worsening a virus attack. In a new study, researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden describe how different kinds of immune cells, called macrophages, develop in the lungs and which of them may be behind severe lung diseases. The study, which was published in Immunity, may contribute to future treatments for COVID-19, among other diseases.
The structure of the lungs exposes them to viruses and bacteria from both the air and the blood. Macrophages are immune cells that, among other things, protect the lungs from such attacks. ...
2021-01-02
East Hanover, NJ. December 30, 2020. A team of rehabilitation researchers has studied processing speed deficits in individuals with spinal cord injury (SCI), comparing their brain activation patterns with those of healthy age-matched controls, and older healthy individuals. They found that the SCI group and older controls had similar activation patterns, but the SCI group differed significantly from their age-matched controls.
The article, "The neural mechanisms underlying processing speed deficits in individuals who have sustained a spinal cord injury: A pilot study" (doi: 10.1007/s10548-020-00798-x) was ...
2021-01-02
BOSTON -- A peer-reviewed paper published in The New England Journal of Medicine provides data from the much-anticipated COVE study, which evaluated mRNA-1273, a vaccine candidate against COVID-19 manufactured by Moderna, Inc. Results from the primary analysis of the study, which will continue for two years, provide evidence that the vaccine can prevent symptomatic infection. Among the more than 30,000 participants randomized to receive the vaccine or a placebo, 11 of those in the vaccine group developed symptomatic COVID-19 compared to 185 participants who received the placebo, demonstrating 94.1 percent efficacy in preventing symptomatic COVID-19. Cases ...
2021-01-02
December 30, 2020 - As the COVID-19 pandemic emerged, trauma centers faced unprecedented obstacles to providing care for injured patients. A look at steps taken by trauma centers in response to COVID-19 is provided by a survey in the January/February Journal for Healthcare Quality (JHQ), the peer-reviewed journal of the National Association for Healthcare Quality (NAHQ). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
Trauma centers introduced new processes to optimize use of personal protective equipment (PPE), ICU beds, ventilators, and other limited resources, according to the report by David Bar-Or, MD, of ION Research, Englewood, Colo., ...
2021-01-02
WHAT:
The investigational vaccine known as mRNA-1273 was 94.1% efficacious in preventing symptomatic coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), according to preliminary results from a Phase 3 clinical trial reported in the New England Journal of Medicine. The vaccine also demonstrated efficacy in preventing severe COVID-19. Investigators identified no safety concerns and no evidence of vaccine-associated enhanced respiratory disease (VAERD).
The vaccine was co-developed by Moderna, Inc., a biotechnology company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes ...
2021-01-02
"Today's computer applications generate a large amount of data that needs to be processed by machine learning algorithms," says Yeseong Kim of Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST), who led the effort.
Powerful 'unsupervised' machine learning involves training an algorithm to recognize patterns in large datasets without providing labelled examples for comparison. One popular approach is a clustering algorithm, which groups similar data into different classes. These algorithms are used for a wide variety of data analyses, such as identifying fake news on social media, filtering spam in our e-mails, and detecting ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Anti-transpirant products unnecessary in cycad propagation