Large transporter protein linked to schizophrenia
Investigations of a cellular protein have uncovered a possible link with schizophrenia
2021-01-02
(Press-News.org) Scientists have suspected mutations in a cellular cholesterol transport protein are associated with psychiatric disorders, but have found it difficult to prove this and to pinpoint how it happens. Now, Kazumitsu Ueda of Kyoto University's Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS) and colleagues in Japan have provided evidence that mice with disrupted ABCA13 protein demonstrate a hallmark behaviour of schizophrenia. The team investigated ABCA13's functions and published their findings in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
ABCA13 belongs to a family of cellular transporter proteins called ATP-binding cassette (ABC) proteins, which are involved in moving cholesterol and other molecules into and out of cells. Ueda and his team have been studying ABC proteins for 35 years, giving them extra leverage for uncovering the elusive roles of what is suspected to be the largest of these proteins, ABCA13.
The scientists studied ABCA13 in different types of human cells. They also turned off the gene that codes for the protein in mice. Finally, they investigated the effects of mutated ABCA13 proteins in human cells. The team found that ABCA13 was a large protein localized in cellular vesicles, and helps transport cholesterol from the cell's membrane into the vesicles.
"We found that ABCA13 accelerates the internalization of cholesterol in cells and that its loss of function is associated with the pathophysiology of some psychiatric disorders," says Ueda.
Mice lacking ABCA13 looked normal and had a normal lifespan. But a series of behavioural investigations showed abnormal results for the 'startle response and prepulse inhibition test'. Normally, a weak 'prepulse' stimulus, like a sound, can reduce the feeling of being startled by a subsequent stronger stimulus. However, people with some psychiatric disorders, still feel startled by a main stimulus despite being preceded by a prepulse. The scientists found that both normal mice and the mice lacking ABCA13 had a normal startle response. But only the engineered mice were startled when the startling stimulus was preceded by a prepulse.
The scientists further wanted to know how ABCA1 deletion affected nerve cells in the brain. They found that vesicles in brain nerve endings in the mice that lacked ABCA1 did not accumulate cholesterol. Synaptic nerve vesicles are vital for the transmission of information from one nerve to another, so this malfunction could contribute to the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders, the researchers say.
Finally, the scientists studied human cells containing mutated versions of ABCA13 thought to be associated with some psychiatric disorders. They found the mutations impaired ABCA13's functions and ability to locate within cellular vesicles.
The team suggests further studies on ABCA13 functions could lead to the development of novel therapeutic strategies for psychiatric disorders like schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and major depression.
INFORMATION:
DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015997
About Kyoto University's Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS):
At iCeMS, our mission is to explore the secrets of life by creating compounds to control cells, and further down the road to create life-inspired materials.
https://www.icems.kyoto-u.ac.jp/
For more information, contact:
I. Mindy Takamiya/Mari Toyama
pe@mail2.adm.kyoto-u.ac.jp
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-02
Philadelphia, December 29, 2020 - Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a complex psychiatric disorder brought on by physical and/or psychological trauma. How its symptoms, including anxiety, depression and cognitive disturbances arise remains incompletely understood and unpredictable. Treatments and outcomes could potentially be improved if doctors could better predict who would develop PTSD. Now, researchers using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have found potential brain biomarkers of PTSD in people with traumatic brain injury (TBI).
The study appears in ...
2021-01-02
What happens in the brain when our conscious awareness fades during general anesthesia and normal sleep? Finnish scientists studied this question with novel experimental designs and functional brain imaging. They succeeded in separating the specific changes related to consciousness from the more widespread overall effects, and discovered that the effects of anesthesia and sleep on brain activity were surprisingly similar. These novel findings point to a common central core brain network fundamental for human consciousness.
Explaining the biological basis of human ...
2021-01-02
A fascinating substance with unique properties, ice has intrigued humans since time immemorial. Unlike most other materials, ice at very low temperature is not as ordered as it could be. A collaboration between the Scuola Internazionale Superiore di Studi Avanzati (SISSA), the Abdus Salam International Centre for Theoretical Physics (ICTP), the Institute of Physics Rosario (IFIR-UNR), with the support of the Istituto Officina dei Materiali of the Italian National Research Council (CNR-IOM), made new theoretical inroads on the reasons why this happens and on the way in which some of the missing order can be recovered. In that ordered state the team ...
2021-01-02
Small studies have suggested that a group of medications called RAS inhibitors may be harmful in persons with advanced chronic kidney disease, and physicians therefore often stop the treatment in such patients. Researchers at Karolinska Institutet now show that although stopping the treatment is linked to a lower risk of requiring dialysis, it is also linked to a higher risk of cardiovascular events and death. The results are published in The Journal of the American Society of Nephrology.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects approximately ten percent of the global population. Hypertension is ...
2021-01-02
Scientific articles in the field of physics are mostly very short and deal with a very restricted topic. A remarkable exception to this is an article published recently by physicists from the Universities of Münster and Düsseldorf. The article is 127 pages long, cites a total of 1075 sources and deals with a wide range of branches of physics - from biophysics to quantum mechanics.
The article is a so-called review article and was written by physicists Michael te Vrugt and Prof. Raphael Wittkowski from the Institute of Theoretical Physics and the Center for Soft Nanoscience at the University of Münster, together with ...
2021-01-02
Although plants are anchored to the ground, they spend most of their lifetime swinging in the wind. Like animals, plants have 'molecular switches' on the surface of their cells that transduce a mechanical signal into an electrical one in milliseconds. In animals, sound vibrations activate 'molecular switches' located in the ear. Scientists from the CNRS, INRAE, Ecole Polytechnique, Université Paris-Saclay and Université Clermont-Auvergne (1) have found that in plants, rapid oscillations of stems and leaves ...
2021-01-02
How can cells adhere to surfaces and move on them? This is a question which was investigated by an international team of researchers headed by Prof. Michael Hippler from the University of Münster and Prof. Kaiyao Huang from the Institute of Hydrobiology (Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan, China). The researchers used the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii as their model organism. They manipulated the alga by altering the sugar modifications in proteins on the cell surface. As a result, they were able to alter the cellular surface adhesion, also known as adhesion force. The results have now been published in the ...
2021-01-02
Thanks to the marine worm Platynereis dumerilii, an animal whose genes have evolved very slowly, scientists from CNRS, Université de Paris and Sorbonne Université, in association with others at the University of Saint Petersburg and the University of Rio de Janeiro, have shown that while haemoglobin appeared independently in several species, it actually descends from a single gene transmitted to all by their last common ancestor. These findings were published on 29 December 2020 in BMC Evolutionary Biology.
Having red blood is not peculiar to humans or mammals. ...
2021-01-02
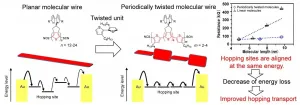
Osaka, Japan - Researchers at Osaka University synthesized twisted molecular wires just one molecule thick that can conduct electricity with less resistance compared with previous devices. This work may lead to carbon-based electronic devices that require fewer toxic materials or harsh processing methods.
Organic conductors, which are carbon-based materials that can conduct electricity, are an exciting new technology. Compared with conventional silicon electronics, organic conductors can be synthesized more easily, and can even be made into molecular wires. However, these structures suffer from reduced electrical conductivity, which prevents ...
2021-01-02
After "COVID-19," the term that most people will remember best from 2020 is likely to be "social distancing." While it most commonly applied to social gatherings with family and friends, it has impacted the way many receive medical care. Historically, the United States has been relatively slow to broadly adopt telemedicine, largely emphasizing in-person visits.
However, the COVID-19 pandemic, especially in the spring of 2020, necessitated increased use of virtual or phone call visits, even prompting the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) to relax some of its regulations, primarily for video-based ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Large transporter protein linked to schizophrenia
Investigations of a cellular protein have uncovered a possible link with schizophrenia