Beverage prices, volume sold after sweetened beverage tax repeal in Chicago's county
2021-01-02
(Press-News.org) What The Study Did: This observational study examined whether lasting change in sweetened beverage prices or the volume sold was associated with the implementation and repeal of a sweetened beverage tax in Cook County, Illinois, where Chicago is.
Authors: Lisa M. Powell, Ph.D., of the University of Illinois Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.31083)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study and commentary are linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time
http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.31083?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=122820
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is the new online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-02
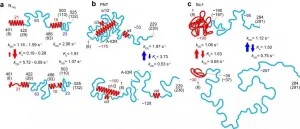
Our understanding of biological proteins does not always correlate with how common or important they are. Half of all proteins, molecules that play an integral role in cell processes, are intrinsically disordered, which means many of the standard techniques for probing biomolecules don't work on them. Now researchers at Kanazawa University in Japan have shown that their home-grown high-speed atomic force microscopy technology can provide information not just on the structures of these proteins but also their dynamics.
Understanding how a protein is put together provides valuable clues to its functions. ...
2021-01-02
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the basis of life on earth. The function of DNA is to store all the genetic information, which an organism needs to develop, function and reproduce. It is essentially a biological instruction manual found in every cell. Biochemists at the University of Münster have now developed a strategy for controlling the biological functions of DNA with the aid of light. This enables researchers to better understand and control the different processes which take place in the cell - for example epigenetics, the key chemical change and regulatory lever in DNA. The ...
2021-01-02
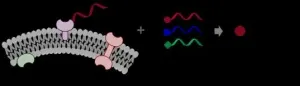
A research team led by Dr Xiaoyu LI from the Research Division for Chemistry, Faculty of Science, in collaboration with Professor Yizhou LI from School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Chongqing University and Professor Yan CAO from School of Pharmacy, Second Military Medical University in Shanghai has developed a new drug discovery method targeting membrane proteins on live cells.
Membrane proteins play important roles in biology, and many of them are high-value targets that are being intensively pursued in the pharmaceutical ...
2021-01-02
New research produced jointly by The Swire Institute of Marine Science (SWIMS), Faculty of Science, The University of Hong Kong (HKU), and The Nature Conservancy (TNC), published recently in the scientific journal Restoration Ecology, shows the enormous potential of restoring lost oyster reefs, bringing significant environmental benefits.
Benefits of oyster reefs
Hong Kong was once home to thriving shellfish reefs, but due to a combination of factors including over-exploitation, coastal reclamation and pollution, shellfish populations have declined drastically. Restoring oyster reefs along urbanized ...
2021-01-02
Angiosarcomas are clinically aggressive tumours that are more prevalent in Asian populations
Study led by Singapore clinician-scientists has found a way to classify angiosarcomas into three subtypes, allowing for more targeted treatment, better outcomes for patients and the development of new therapies
Findings were published in The Journal of Clinical Investigation in October this year
Singapore, 29 December 2020 - A new study led by clinician-scientists from the National Cancer Centre Singapore (NCCS), with collaborators from research institutions worldwide, has found that angiosarcomas have unique genomic and immune profiles which allow them ...
2021-01-02
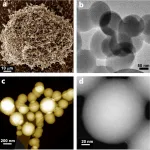
A fast, green and one-step method for producing porous carbon spheres, which are a vital component for carbon capture technology and for new ways of storing renewable energy, has been developed by Swansea University researchers.
The method produces spheres that have good capacity for carbon capture, and it works effectively at a large scale.
Carbon spheres range in size from nanometers to micrometers. Over the past decade they have begun to play an important role in areas such as energy storage and conversion, catalysis, gas adsorption and storage, drug and enzyme delivery, and water treatment.
They are also at the heart of carbon capture technology, ...
2021-01-02
Researchers at the University of Turku have discovered what type of neural mechanisms are the basis for emotional responses to music. Altogether 102 research subjects listened to music that evokes emotions while their brain function was scanned with functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). The study was carried out in the national PET Centre.
The researchers used a machine learning algorithm to map which brain regions are activated when the different music-induced emotions are separated from each other.
- Based on the activation of the auditory and motor cortex, we were able to accurately predict whether the research subject was listening ...
2021-01-02
In a series of commissions awarded by the Federal Joint Committee (G-BA) to the Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG), the question is whether for certain surgical procedures, a correlation can be shown between the volume of services provided per hospital and the quality of treatment results. IQWiG's rapid report on heart transplantations is now available.
According to the findings, a positive correlation can be inferred between the volume of services and the quality of treatment results for heart transplantations in adults: In hospitals with larger case volumes, fewer of the transplanted patients die, both in timely association with the intervention ...
2021-01-02
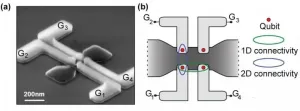
Quantum computer: One of the obstacles for progress in the quest for a working quantum computer has been that the working devices that go into a quantum computer and perform the actual calculations, the qubits, have hitherto been made by universities and in small numbers. But in recent years, a pan-European collaboration, in partnership with French microelectronics leader CEA-Leti, has been exploring everyday transistors--that are present in billions in all our mobile phones--for their use as qubits. The French company Leti makes giant ...
2021-01-02
Imaging techniques enable a detailed look inside an organism. But interpreting the data is time-consuming and requires a great deal of experience. Artificial neural networks open up new possibilities: They require just seconds to interpret whole-body scans of mice and to segment and depict the organs in colors, instead of in various shades of gray. This facilitates the analysis considerably.
How big is the liver? Does it change if medication is taken? Is the kidney inflamed? Is there a tumor in the brain and did metastases already develop? ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Beverage prices, volume sold after sweetened beverage tax repeal in Chicago's county