Sweetened beverage sales bounced back quickly after Cook County tax repealed
Study published in JAMA Network Open
2021-01-04
(Press-News.org) Following the repeal of the short-lived Cook County, Illinois Sweetened Beverage Tax, sales of sweetened beverages went right back to where they were before the tax went into place, according to a new study led by researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago. The study is published in JAMA Network Open.
The tax, which included both sugar-sweetened and artificially-sweetened diet beverages, was largely pitched as a way to reduce county budget deficits. The tax lasted just four months -- it went into effect on Aug. 2, 2017 and ended on Dec. 1, 2017.
"We know that the tax worked to bring down demand for sweetened beverages significantly while it was in place," said Lisa Powell, UIC distinguished professor and director of health policy and administration at the School of Public Health and lead author of the paper. "The repeal of the Cook County Sweetened Beverage Tax was a missed public health opportunity. If it had stayed in place, we could have seen a lasting reduction in consumption of sweetened beverages, which are linked to obesity, Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease which, in turn, have recently been found to be associated with increased risk of severe illness from COVID-19."
Previous research by Powell and colleagues showed that while the tax was in effect, it worked to bring down volume sold of sweetened beverages by 27% in Cook County, with a net effect of 21% after taking into account cross-border shopping in response to the tax.
In the new study, Powell and Julien Leider, a senior research specialist at the UIC Institute for Health Research and Policy, compared the price and volume of sweetened beverages sold in Cook County in the two years before the tax, during the four months the tax was in place and in the eight months after the tax was repealed relative to St. Louis, Missouri, which did not have a similar tax.
Employing a different analytical method than they used in their previous research, Powell and Leider found that sweetened beverages increased in price by 1.13 cents per fluid ounce in Cook County while the tax was in place. After the repeal of the tax, the price dropped 1.19 cents per fluid ounce. They also found that the volume of sweetened beverages sold in Cook County dropped by about 26% under the tax and increased by about 30% after the tax was repealed. Ultimately, there was no net change in the volume of sweetened beverages sold pre-tax compared to after the tax was repealed.
"Volume of sweetened beverages sold in Cook County went right back to pre-tax levels following the repeal of the tax," Powell said.
Powell notes that the results suggest that the tax worked to bring down demand for sweetened beverages through price point alone and did not appear to change perceptions regarding the harms linked to consuming sugary beverages. Public messaging about the tax, focused mostly on proceeds being used to address budgetary deficits rather than on public health.
"We don't know if public messaging were more focused on health benefits if there would have been some lasting impact of the tax, but as it stands, we see that the substantial impact from the tax fully disappeared once it w
as repealed," Powell said.
INFORMATION:
This research was funded by a grant from Bloomberg Philanthropies' Obesity Prevention Initiative (49255).
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-04
Mollusks build shells to protect their soft tissues from predators. Nacre, also known as the mother of pearl, has an intricate, highly regular structure that makes it an incredibly strong material. Depending on the species, nacres can reach tens of centimeters in length. No matter the size, each nacre is built from materials deposited by a multitude of single cells at multiple different locations at the same time. How exactly this highly periodic and uniform structure emerges from the initial disorder was unknown until now.
Nacre formation starts uncoordinated ...
2021-01-04
Drones, robots and autonomous systems can transform the natural world in and around cities for people and wildlife.
International research, involving over 170 experts and led by the University of Leeds, assessed the opportunities and challenges that this cutting-edge technology could have for urban nature and green spaces.
The researchers highlighted opportunities to improve how we monitor nature, such as identifying emerging pests and ensuring plants are cared for, and helping people engage with and appreciate the natural world around them.
As robotics, autonomous vehicles and drones become more widely used across cities, pollution and traffic ...
2021-01-04
What The Study Did: In this observational study of 5,256 U.S. nursing home residents with COVID-19, increased age, male sex and impaired cognitive and physical function were independent risk factors for all-cause 30-day mortality.
Authors: Orestis A. Panagiotou, M.D., Ph.D., of the Brown University School of Public Health in Providence, Rhode Island, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.7968)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, ...
2021-01-04
What The Study Did: The findings of a survey study using data from California suggests the COVID-19 pandemic was associated with increases in self-reported worry about violence for oneself and others, increased firearm acquisition and changes in firearm storage practices.
Authors: Nicole Kravitz-Wirtz, Ph.D., M.P.H., University of California Firearm Violence Research Center and Violence Prevention Research Program, Department of Emergency Medicine, University of California Davis School of Medicine in Sacramento, is the corresponding ...
2021-01-04
Whether in beta-blockers to treat high blood pressure or in natural products: So-called vicinal aminoalcohols are high-quality organic compounds that are found in many everyday products. However, their production is difficult. For a long time, chemists are trying to develop efficient methods of synthesizing them. In their recent study published in the journal Nature Catalysis, scientists led by Prof. Dr. Frank Glorius of Münster University have found a solution for the production of a special variant of aminoalcohols. "The new method helps to study the properties of the substance and to find applications for these ...
2021-01-04
Assembling tiny chips into unique programmable surfaces, Princeton researchers have created a key component toward unlocking a communications band that promises to dramatically increase the amount data wireless systems can transmit.
The programmable surface, called a metasurface, allows engineers to control and focus transmissions in the terahertz band of the electromagnetic spectrum. Terahertz, a frequency range located between microwaves and infrared light, can transit much more data than current, radio-based wireless systems. With fifth generation (5G) communications systems offering speeds 10 to 100 times faster than the previous generation, demand for bandwidth is ever increasing. Facing the emergence of technologies such as self-driving cars and augmented reality ...
2021-01-04
What The Study Did: Changes were assessed in abortions performed and at what gestational age following a Texas order postponing nonmedically necessary surgeries due to the COVID-19 pandemic compared with abortions performed during the same months in 2019.
Authors: Kari White, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the University of Texas at Austin, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2020.24096)
Editor's Note: The articles includes conflict of interest and funding/support ...
2021-01-04
What The Viewpoint Says: The rapid spread of scientific misinformation on social media platforms throughout the COVID-19 pandemic is discussed in this Viewpoint, which also proposes strategies to counteract its adverse effects including surveillance of digital data and partnering with trusted messengers to engage the public and advance scientifically sound public health measures.
Authors: Raina M. Merchant, M.D., M.S.H.P., of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2020.24514)
Editor's Note: The ...
2021-01-04
ITHACA, N.Y. - From an observatory high above Chile's Atacama Desert, astronomers have taken a new look at the oldest light in the universe.
Their observations, plus a bit of cosmic geometry, suggest that the universe is 13.77 billion years old - give or take 40 million years. A Cornell University researcher co-authored one of two papers about the findings, which add a fresh twist to an ongoing debate in the astrophysics community.
The new estimate, using data gathered at the National Science Foundation's Atacama Cosmology Telescope (ACT), matches the one provided by the standard ...
2021-01-04
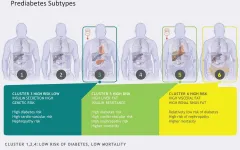
All prediabetes is not the same: in people in the preliminary stages of type 2 diabetes, there are six clearly distinguishable subtypes, which differ in the development of the disease, diabetes risk, and the development of secondary diseases. This is shown in a study by the Institute for Diabetes Research and Metabolic Diseases (IDM) of Helmholtz Zentrum München at the University of Tübingen, Tübingen University Hospital and the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD). The results have now been published in Nature Medicine. The new classification can help in the future to prevent the manifestation of diabetes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Sweetened beverage sales bounced back quickly after Cook County tax repealed
Study published in JAMA Network Open