Focusing on diversion yields positive results for kids with behavioral issues
Researchers at Case Western Reserve University evaluating effectiveness of Ohio's Behavioral Health/Juvenile Justice Initiative
2021-01-04
(Press-News.org) Of the 5,300 children enrolled in the Ohio Behavioral Health Juvenile Justice Initiative since 2006, 21% reported that someone close them had been murdered in the past year. Nearly half of the boys and more than a quarter of the girls in the program have both a substance abuse and mental health disorder.
But there's good news, too: From 2017 through 2019, 81% of the participants--aged 10 through 17--successfully completed the state's juvenile diversion program, and data indicated that 79% of youth reduced their contact with police while in treatment.
Those findings are from a new detailed evaluation of the Ohio Behavioral Health Juvenile Justice Initiative (BHJJ) by researchers at the Jack, Joseph and Morton Mandel School of Applied Social Sciences at Case Western Reserve University.
The key conclusion: Many youthful offenders can benefit from community-based diversion programs designed to address mental health and substance use issues in lieu of commitment to local or state-run detention centers.
"The majority of justice-involved youth have a history of mental health and/or substance-use issues, and have experienced a great deal of trauma," said Jeff Kretschmar, co-author of the study and the research associate professor at the university's Begun Center for Violence Prevention Research and Education. "However, local jurisdictions are often ill-equipped to accurately assess youth for behavioral health problems and provide appropriate treatment. Ohio's Behavioral Health Juvenile Justice Initiative was intended to transform and expand the local systems' options to better serve these youths."
The report focused on youth currently enrolled in the program rather than retrospectively, Kretschmar said, to "identify emerging behavioral health trends and better understand the effectiveness of the model as it operates across Ohio today."
Report highlights include:
Youth reported a significant decrease in trauma symptoms and problem severity from intake to termination, and a significant improvement in functioning.
Since 2015, only 3.8% of youth enrolled in BHJJ were committed to a state-run detention facility after enrollment.
BHJJ costs about $5,200 per child, compared with $196,000 per child who enters a state-run detention facility.
"The breadth of the data provides us with an opportunity to examine outcomes for youth in BHJJ from a variety of angles and provides practitioners with enough information to match programming with behavioral health needs," said Fredrick Butcher, research assistant professor at the Begun Center.
INFORMATION:
BHJJ was launched 20 years ago at the request of Ohio juvenile court judges, with help from the Department of Mental Health and Addiction Services and the Ohio Department of Youth Services. The Begun Center has served as the evaluation partner since 2005.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-04
Boulder, Colo., USA: Europe's largest gas field, the Groningen field in the Netherlands, is widely known for induced subsidence and seismicity caused by gas pressure depletion and associated compaction of the sandstone reservoir. Whether compaction is elastic or partly inelastic, as implied by recent experiments, is key to forecasting system behavior and seismic hazard.
Bart Verberne and colleagues sought evidence for a role of inelastic deformation through comparative microstructural analysis of unique drill-core, recovered from the seismogenic center of the field in 2015, 50 years after gas production started, versus core recovered before production (1965). Quartz grain fracturing, crack healing, and stress-induced Dauphiné twinning are ...
2021-01-04
BOSTON - A long-running debate over how an important gene-silencing protein identifies its targets has been resolved by researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH). Their findings, reported in Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, also explain certain mysteries about the behavior of this protein, known as Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2).
PRC2 helps regulate whether genes are active ("on) or silent ("off"). PRC2's role in gene silencing is critical throughout the lifespan, from embryo formation to old age. For example, PRC2 determines whether genes that suppress the growth of malignant tumors are turned on or off, which has made it the focus of pharmaceutical companies ...
2021-01-04
If you've ever had a bad case of jet lag, you know how a disruption to your body's circadian rhythm makes it difficult to function. Molecular circadian "clocks" exist in cells throughout the body, governing more than just sleep and wake cycles - they are crucial to many aspects of human health. For more than a decade researchers have been trying to figure out what makes them tick, in search of new insights into diseases like Alzheimer's, cancer and diabetes.
Until now, that research has focused on what is known as clock genes, which encode proteins that drive oscillating cycles of gene expression affecting physiology and behavior. But research just published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences reveals the discovery ...
2021-01-04
Plants can perceive and react to light across a wide spectrum. New research from Prof. Nitzan Shabek's laboratory in the Department of Plant Biology, College of Biological Sciences shows how plants can respond to blue light in particular.
"Plants can see much better than we can," Shabek said.
Plants don't have dedicated light-detecting organs, like our eyes. They do have a variety of dedicated receptors that can sense almost every single wavelength. One such are the blue light photoreceptors called cryptochromes. When the cryptochrome detects an incoming photon, it reacts in a way that triggers a unique physiological response.
Cryptochromes probably appeared billions of years ago with the first living ...
2021-01-04
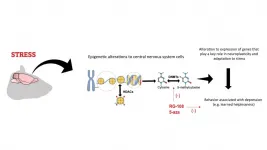
By Karina Ninni | Agência FAPESP – Treatment of depression faces two main challenges. The first is that almost 50% of patients do not respond well to existing antidepressants. The second is that conventional medications take a relatively long time – around three to five weeks – to have the desired effect. A group of researchers affiliated with the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil set out to tackle the second problem by using epigenetic modulators to try to “erase” the consequences of stress. Epigenetic mechanisms are part of a complex system that controls how and when genes are switched on or off.
Exposure to stress, a key trigger of depression, alters certain epigenetic markers in the brain. Many of these alterations ...
2021-01-04
The coronavirus pandemic is creating a large spike in significant psychological distress among Americans, with the first month of the pandemic causing as much distress in the same number of individuals that experienced it during the whole previous year, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Findings from the first longitudinal study of psychological distress during the pandemic show that among a representative sample of Americans, more than 10% reported experiencing symptoms of significant psychological distress during April and May of 2020 -- the same amount they reported experiencing over an entire year during a survey conducted a year earlier.
The study also found that people with distress prior to the ...
2021-01-04
Scientists have long been aware of the dangerous overuse of antibiotics and the increasing number of antibiotic-resistant microbes that have resulted. While over-prescription of antibiotics for medicinal use has unsettling implications for human health, so too does the increasing presence of antibiotics in the natural environment. The latter may stem from the improper disposal of medicines, but also from the biotechnology field, which has depended on antibiotics as a selection device in the lab.
"In biotech, we have for a long time relied on antibiotic and chemical selections to kill cells that we don't want to grow," said UC Santa Barbara chemical engineer Michelle ...
2021-01-04
Following the repeal of the short-lived Cook County, Illinois Sweetened Beverage Tax, sales of sweetened beverages went right back to where they were before the tax went into place, according to a new study led by researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago. The study is published in JAMA Network Open.
The tax, which included both sugar-sweetened and artificially-sweetened diet beverages, was largely pitched as a way to reduce county budget deficits. The tax lasted just four months -- it went into effect on Aug. 2, 2017 and ended on Dec. 1, 2017.
"We ...
2021-01-04
Mollusks build shells to protect their soft tissues from predators. Nacre, also known as the mother of pearl, has an intricate, highly regular structure that makes it an incredibly strong material. Depending on the species, nacres can reach tens of centimeters in length. No matter the size, each nacre is built from materials deposited by a multitude of single cells at multiple different locations at the same time. How exactly this highly periodic and uniform structure emerges from the initial disorder was unknown until now.
Nacre formation starts uncoordinated ...
2021-01-04
Drones, robots and autonomous systems can transform the natural world in and around cities for people and wildlife.
International research, involving over 170 experts and led by the University of Leeds, assessed the opportunities and challenges that this cutting-edge technology could have for urban nature and green spaces.
The researchers highlighted opportunities to improve how we monitor nature, such as identifying emerging pests and ensuring plants are cared for, and helping people engage with and appreciate the natural world around them.
As robotics, autonomous vehicles and drones become more widely used across cities, pollution and traffic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Focusing on diversion yields positive results for kids with behavioral issues
Researchers at Case Western Reserve University evaluating effectiveness of Ohio's Behavioral Health/Juvenile Justice Initiative