Uncovering how plants see blue light
2021-01-04
(Press-News.org) Plants can perceive and react to light across a wide spectrum. New research from Prof. Nitzan Shabek's laboratory in the Department of Plant Biology, College of Biological Sciences shows how plants can respond to blue light in particular.
"Plants can see much better than we can," Shabek said.
Plants don't have dedicated light-detecting organs, like our eyes. They do have a variety of dedicated receptors that can sense almost every single wavelength. One such are the blue light photoreceptors called cryptochromes. When the cryptochrome detects an incoming photon, it reacts in a way that triggers a unique physiological response.
Cryptochromes probably appeared billions of years ago with the first living bacteria and they are very similar across bacteria, plants and animals. We have cryptochromes in our own eyes, where they are involved in maintaining our circadian clock. In plants, cryptochromes govern a variety of critical processes including seed germination, flowering time and entrainment of the circadian clock. However, the photochemistry, regulation, and light-induced structural changes remain unclear.
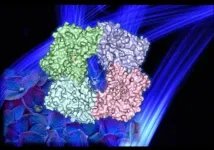
In a new study, published Jan. 4 in Nature Communications Biology, Shabek's lab determined the crystal structure of part of the blue-light receptor, cryptochrome-2, in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana. They found that the light-detecting part of the molecule changes its structure when it reacts with light particles, going from a single unit to a structure made of four units linked together, or tetramer.
Rearrangement leads to gene activation
"This rearrangement process, called photo-induced oligomerization, is also very intriguing because certain elements within the protein undergo changes when exposed to blue light. Our molecular structure suggests that these light-induced changes release transcriptional regulators that control expression of specific genes in plants," Shabek said.
The researchers were able to work out the structure of cryptochrome-2 with the aid of the Advanced Light Source X-ray facility at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
The Shabek lab broadly studies how plants sense their environment from the molecular to the organismal levels.
"This work is part of our long-term goals to understand sensing mechanisms in plants. We are interested in hormone perceptions as well as light signaling pathways," Shabek said.
The team first solved the crystal structure of the blue light receptor two years ago, using X-ray crystallography and biochemical approaches. With recent advances in plant sciences and structural biology, they were able to update the model and reveal the missing piece of the puzzle.
INFORMATION:
Coauthors on the work are Malathy Palayam, Jagadeesan Ganapathy, Angelica Guercio, Lior Tal and Samuel Deck. The Advanced Light Source is a U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science User Facility.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-04
By Karina Ninni | Agência FAPESP – Treatment of depression faces two main challenges. The first is that almost 50% of patients do not respond well to existing antidepressants. The second is that conventional medications take a relatively long time – around three to five weeks – to have the desired effect. A group of researchers affiliated with the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil set out to tackle the second problem by using epigenetic modulators to try to “erase” the consequences of stress. Epigenetic mechanisms are part of a complex system that controls how and when genes are switched on or off.
Exposure to stress, a key trigger of depression, alters certain epigenetic markers in the brain. Many of these alterations ...
2021-01-04
The coronavirus pandemic is creating a large spike in significant psychological distress among Americans, with the first month of the pandemic causing as much distress in the same number of individuals that experienced it during the whole previous year, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Findings from the first longitudinal study of psychological distress during the pandemic show that among a representative sample of Americans, more than 10% reported experiencing symptoms of significant psychological distress during April and May of 2020 -- the same amount they reported experiencing over an entire year during a survey conducted a year earlier.
The study also found that people with distress prior to the ...
2021-01-04
Scientists have long been aware of the dangerous overuse of antibiotics and the increasing number of antibiotic-resistant microbes that have resulted. While over-prescription of antibiotics for medicinal use has unsettling implications for human health, so too does the increasing presence of antibiotics in the natural environment. The latter may stem from the improper disposal of medicines, but also from the biotechnology field, which has depended on antibiotics as a selection device in the lab.
"In biotech, we have for a long time relied on antibiotic and chemical selections to kill cells that we don't want to grow," said UC Santa Barbara chemical engineer Michelle ...
2021-01-04
Following the repeal of the short-lived Cook County, Illinois Sweetened Beverage Tax, sales of sweetened beverages went right back to where they were before the tax went into place, according to a new study led by researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago. The study is published in JAMA Network Open.
The tax, which included both sugar-sweetened and artificially-sweetened diet beverages, was largely pitched as a way to reduce county budget deficits. The tax lasted just four months -- it went into effect on Aug. 2, 2017 and ended on Dec. 1, 2017.
"We ...
2021-01-04
Mollusks build shells to protect their soft tissues from predators. Nacre, also known as the mother of pearl, has an intricate, highly regular structure that makes it an incredibly strong material. Depending on the species, nacres can reach tens of centimeters in length. No matter the size, each nacre is built from materials deposited by a multitude of single cells at multiple different locations at the same time. How exactly this highly periodic and uniform structure emerges from the initial disorder was unknown until now.
Nacre formation starts uncoordinated ...
2021-01-04
Drones, robots and autonomous systems can transform the natural world in and around cities for people and wildlife.
International research, involving over 170 experts and led by the University of Leeds, assessed the opportunities and challenges that this cutting-edge technology could have for urban nature and green spaces.
The researchers highlighted opportunities to improve how we monitor nature, such as identifying emerging pests and ensuring plants are cared for, and helping people engage with and appreciate the natural world around them.
As robotics, autonomous vehicles and drones become more widely used across cities, pollution and traffic ...
2021-01-04
What The Study Did: In this observational study of 5,256 U.S. nursing home residents with COVID-19, increased age, male sex and impaired cognitive and physical function were independent risk factors for all-cause 30-day mortality.
Authors: Orestis A. Panagiotou, M.D., Ph.D., of the Brown University School of Public Health in Providence, Rhode Island, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.7968)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, ...
2021-01-04
What The Study Did: The findings of a survey study using data from California suggests the COVID-19 pandemic was associated with increases in self-reported worry about violence for oneself and others, increased firearm acquisition and changes in firearm storage practices.
Authors: Nicole Kravitz-Wirtz, Ph.D., M.P.H., University of California Firearm Violence Research Center and Violence Prevention Research Program, Department of Emergency Medicine, University of California Davis School of Medicine in Sacramento, is the corresponding ...
2021-01-04
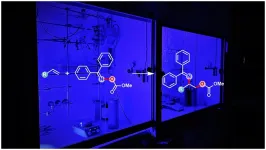
Whether in beta-blockers to treat high blood pressure or in natural products: So-called vicinal aminoalcohols are high-quality organic compounds that are found in many everyday products. However, their production is difficult. For a long time, chemists are trying to develop efficient methods of synthesizing them. In their recent study published in the journal Nature Catalysis, scientists led by Prof. Dr. Frank Glorius of Münster University have found a solution for the production of a special variant of aminoalcohols. "The new method helps to study the properties of the substance and to find applications for these ...
2021-01-04
Assembling tiny chips into unique programmable surfaces, Princeton researchers have created a key component toward unlocking a communications band that promises to dramatically increase the amount data wireless systems can transmit.
The programmable surface, called a metasurface, allows engineers to control and focus transmissions in the terahertz band of the electromagnetic spectrum. Terahertz, a frequency range located between microwaves and infrared light, can transit much more data than current, radio-based wireless systems. With fifth generation (5G) communications systems offering speeds 10 to 100 times faster than the previous generation, demand for bandwidth is ever increasing. Facing the emergence of technologies such as self-driving cars and augmented reality ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Uncovering how plants see blue light