(Press-News.org) UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- American politicians have long been expected to uphold a certain veneer: powerful, influential and never vulnerable. New Penn State research has found that these idealized forms of masculinity may also help explain support for Donald Trump in the 2016 presidential election and in the days leading up to the 2020 election.
Across several studies, the researchers found that when men and women endorsed "hegemonic masculinity" -- a culturally idealized form of masculinity that says men should be strong, tough, and dominant -- they were more likely to vote for and have positive feelings about Trump.
The researchers found this was true even when they controlled for political party, gender and how much the participants trusted the government.
Nathaniel Schermerhorn, a dual doctoral candidate in psychology and women's, gender, and sexuality studies, said the findings -- published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America -- suggest that while American society seems to be ready for a female president, an active rejection of hegemonic masculinity may need to happen first.
"The pervasiveness of hegemonic masculinity exists because we do not always know that our attitudes and behaviors are contributing to it," Schermerhorn said. "The success of Donald Trump's 2016 campaign shows that even if we, as a society, have made progress in saying that discrimination and prejudice is undesirable, we have not, as a society, fully interrogated the systematic ways in which those prejudices are upheld."
Because American politics are largely dominated by men, the researchers said political campaigns often emphasize traditionally masculine characteristics to convince voters of a candidate's competence and skill.
"Historically, American politics have been a masculinity contest about proving which candidate is better," Schermerhorn said. "Since the 1980s, the Republican party has used this to their rhetorical advantage by presenting the Republican candidate as masculine and feminizing the entire Democratic party, for example by calling them 'snowflakes.'"
Theresa Vescio, professor of psychology and women's, gender, and sexuality studies, said Trump's 2016 campaign was no exception -- he often criticized his opponent's masculinity and displayed sexist attitudes toward Hilary Clinton while positioning himself as a tough, powerful and successful businessman.
Vescio said that while this may resonate with voters who share similar ideals of masculinity, such attitudes may not actually be realistic.
"In contemporary America, idealized forms of masculinity suggest that men should be high in power, status and dominance, while being physically, mentally and emotionally tough," Vescio said. "But this is an incredibly high standard that few can achieve or maintain. Therefore, this is an idea that many men strive to achieve, but few men actually exhibit."
Vescio said that while Trump's success with voters has been attributed to many different possible factors, she and the other researchers were specifically interested in to what extent hegemonic masculinity played a role with constituents.
The researchers recruited a total of 2,007 participants for seven different studies. In the first six studies, participants answered questions about their endorsements of hegemonic masculinity, trust in the government, sexism, racism, homophobia and xenophobia. They also indicated their political affiliation, how they voted in the 2016 presidential election, and their evaluations of Trump and Clinton.
In a seventh and final study, participants answered similar questions but also provided information about how they were going to vote in the 2020 presidential election, as well as their evaluations of Trump and Biden.
After analyzing the data, the researchers found that across all studies, participants who endorsed hegemonic masculinity were more likely to vote for Trump and to evaluate him positively. This was true for women and men, white and non-white participants, Democrats and Republicans, and across level of education.
"Additionally, we found that stronger endorsement of hegemonic masculinity was related to greater sexism, racism, homophobia, xenophobia, and Islamophobia," Vescio said. "But, hegemonic masculinity continued to predict support for Trump even when controlling for these prejudices."
Schermerhorn said the results can help shine a light on how both men and women respond to masculine and feminine candidates. He said that because hegemonic masculinity is embedded in social and political institutions, people may internalize the status quo as beneficial, even when it isn't.
"While endorsing hegemonic masculinity predicted a higher likelihood of supporting Trump, it did not necessarily predict negative support for Democratic candidates," he said. "This could suggest that hegemonic masculinity may actually be a predictor of maintaining the status quo and not the inverse -- working against the status quo."
INFORMATION:
A geosciences team led by the University of South Florida (USF) has developed a new way to reconstruct the sizes of volcanic eruptions that occurred thousands of years ago, creating a first-of-its kind tool that can aid scientists in understanding past explosive eruptions that shaped the earth and improve the way of estimating hazards of future eruptions.
The advanced numerical model the USF team developed allows scientists to reconstruct eruption rates through time by estimating the dimensions of the umbrella clouds that contribute to the accumulation ...
CHICAGO --- While many physicians benefit from social media by networking with potential collaborators or interfacing with patients, a new study from Northwestern University and the University of Chicago found many physicians also report being sexually harassed and personally attacked on these platforms on the basis of their religion, race or medical recommendations.
Although the data were collected before the COVID-19 outbreak, the findings highlight the intensity of online harassment before the pandemic, which has only intensified since the spring, the study authors said.
"If anything, our data is likely an underestimate of the true ...
LOS ANGELES -- A growing number of women forgoing reconstruction after a mastectomy say they're satisfied with their choice, even as some did not feel supported by their physician, according to a study led by researchers at the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center.
The study, published in the Journal Annals of Surgical Oncology, surveyed 931 women who had a unilateral or bilateral mastectomy without current breast mound reconstruction to assess the motivating factors for forgoing the procedure and to measure whether surgeons provided adequate information and support for "going flat."
Out of the women surveyed, 74% were satisfied with their outcome and 22% experienced "flat denial," where the procedure was not initially offered, the ...
Of the 5,300 children enrolled in the Ohio Behavioral Health Juvenile Justice Initiative since 2006, 21% reported that someone close them had been murdered in the past year. Nearly half of the boys and more than a quarter of the girls in the program have both a substance abuse and mental health disorder.
But there's good news, too: From 2017 through 2019, 81% of the participants--aged 10 through 17--successfully completed the state's juvenile diversion program, and data indicated that 79% of youth reduced their contact with police while in treatment.
Those findings are from a new detailed evaluation of the Ohio Behavioral Health Juvenile Justice Initiative (BHJJ) by researchers at the Jack, Joseph and ...
Boulder, Colo., USA: Europe's largest gas field, the Groningen field in the Netherlands, is widely known for induced subsidence and seismicity caused by gas pressure depletion and associated compaction of the sandstone reservoir. Whether compaction is elastic or partly inelastic, as implied by recent experiments, is key to forecasting system behavior and seismic hazard.
Bart Verberne and colleagues sought evidence for a role of inelastic deformation through comparative microstructural analysis of unique drill-core, recovered from the seismogenic center of the field in 2015, 50 years after gas production started, versus core recovered before production (1965). Quartz grain fracturing, crack healing, and stress-induced Dauphiné twinning are ...
BOSTON - A long-running debate over how an important gene-silencing protein identifies its targets has been resolved by researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH). Their findings, reported in Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, also explain certain mysteries about the behavior of this protein, known as Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2).
PRC2 helps regulate whether genes are active ("on) or silent ("off"). PRC2's role in gene silencing is critical throughout the lifespan, from embryo formation to old age. For example, PRC2 determines whether genes that suppress the growth of malignant tumors are turned on or off, which has made it the focus of pharmaceutical companies ...
If you've ever had a bad case of jet lag, you know how a disruption to your body's circadian rhythm makes it difficult to function. Molecular circadian "clocks" exist in cells throughout the body, governing more than just sleep and wake cycles - they are crucial to many aspects of human health. For more than a decade researchers have been trying to figure out what makes them tick, in search of new insights into diseases like Alzheimer's, cancer and diabetes.
Until now, that research has focused on what is known as clock genes, which encode proteins that drive oscillating cycles of gene expression affecting physiology and behavior. But research just published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences reveals the discovery ...
Plants can perceive and react to light across a wide spectrum. New research from Prof. Nitzan Shabek's laboratory in the Department of Plant Biology, College of Biological Sciences shows how plants can respond to blue light in particular.
"Plants can see much better than we can," Shabek said.
Plants don't have dedicated light-detecting organs, like our eyes. They do have a variety of dedicated receptors that can sense almost every single wavelength. One such are the blue light photoreceptors called cryptochromes. When the cryptochrome detects an incoming photon, it reacts in a way that triggers a unique physiological response.
Cryptochromes probably appeared billions of years ago with the first living ...
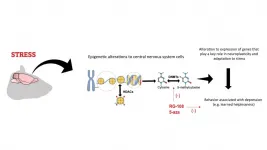
By Karina Ninni | Agência FAPESP – Treatment of depression faces two main challenges. The first is that almost 50% of patients do not respond well to existing antidepressants. The second is that conventional medications take a relatively long time – around three to five weeks – to have the desired effect. A group of researchers affiliated with the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil set out to tackle the second problem by using epigenetic modulators to try to “erase” the consequences of stress. Epigenetic mechanisms are part of a complex system that controls how and when genes are switched on or off.
Exposure to stress, a key trigger of depression, alters certain epigenetic markers in the brain. Many of these alterations ...
The coronavirus pandemic is creating a large spike in significant psychological distress among Americans, with the first month of the pandemic causing as much distress in the same number of individuals that experienced it during the whole previous year, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Findings from the first longitudinal study of psychological distress during the pandemic show that among a representative sample of Americans, more than 10% reported experiencing symptoms of significant psychological distress during April and May of 2020 -- the same amount they reported experiencing over an entire year during a survey conducted a year earlier.
The study also found that people with distress prior to the ...