Impurities boost performance of organic solar cells
2021-01-05
(Press-News.org) Sunlight offers a potential solution in the search for an energy source that does not harm the planet, but this depends on finding a way to efficiently turn electromagnetic energy into electricity. Researchers from KAUST have shown how a known herbicide can improve this conversion in organic devices.
While solar cells have traditionally been made from inorganic materials such as silicon, organic materials are starting to break through as an alternative because they are light, flexible and relatively inexpensive to make, even offering the possibility for printable manufacture.
For organic photovoltaics to become a realistic replacement for fossil fuels, they must improve their efficiency when converting the fraction of incident solar energy to electrical energy. Key to achieving this is choosing the right combination of materials.
Ph.D. student Yuanbao Lin and Thomas Anthopoulos have now achieved this by developing "an efficient molecular dopant to improve the performance and stability of organic solar cells," according to Lin.
Most photovoltaic devices have two important elements: an n-type region and a p-region, so called because each region has a net negative and positive electric charge, respectively. These charges can be achieved by adding impurities to the semiconductor. An impurity that creates an n-type material is known as a donor, while an acceptor impurity makes a p-type material.
Lin, Anthopoulos and their team used diquat (C12H12Br2N2) as a molecular donor dopant to enhance the conversion efficiency of high-performance organic solar cells.
The dopant was added to two organic material systems that have previously shown excellent photovoltaic performance. In one case, the power conversion efficiency was improved from 16.7 percent to 17.4 percent, while they were able to attain a maximum efficiency of 18.3 percent in the other. These improvements were possible because the molecular diquat dopant increased both the materials' optical absorption and the lifetime of the electrical charges when light was absorbed.
Like many organic n-type dopants, diquat is reactive in an ambient atmosphere; its lack of stability has prevented its use as a molecular dopant so far. However, the KAUST team were able to develop a process that stably created neutral diquat by electrochemically reducing charged diquat, which is stable in air.
This ability makes diquat a promising choice for the next generation of organic solar cells. "The predicted maximum efficiency of the organic solar cell is around 20 percent," explains Lin. "We will try our best to reach this."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-05
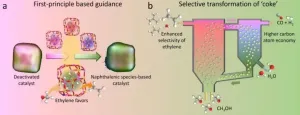
MTO process, which was first commercialized in 2010, is a catalytic process converting methanol, which is typically made from coal, natural gas, biomass, and CO2, over SAPO-34 zeolite catalyst. It's becoming one of the main streams for producing light olefins, including ethylene and propylene, from non-oil resources.
One of the major challenges in MTO is the rapid deactivation of zeolite catalyst due to the coke deposition.
In industrial practices, a fluidized bed reactor-regenerator configuration is normally used in order to maintain the continuous operation, in ...
2021-01-05
Dr. Camilo Ricordi, director of the Diabetes Research Institute (DRI) and Cell Transplant Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, and his team of international collaborators are reporting the results of a groundbreaking randomized controlled trial showing umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell (UC-MSC) infusions safely reduce risk of death and quicken time to recovery for the most severe COVID-19 patients. Dr. Ricordi's peer-reviewed paper has just been published in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine (SCTM) January 2021.
The clinical trial, authorized by the FDA last ...
2021-01-05
Dr. Camilo Ricordi, director of the Diabetes Research Institute (DRI) and Cell Transplant Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, and his team of international collaborators are reporting the results of a groundbreaking randomized controlled trial showing umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell (UC-MSC) infusions safely reduce risk of death and quicken time to recovery for the most severe COVID-19 patients. Dr. Ricordi's peer-reviewed paper has just been published in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine (SCTM) January 2021.
The clinical trial, authorized by the FDA last April, was initiated by The Cure Alliance, a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization of research scientists founded ten years ago by Dr. Ricordi for scientists ...
2021-01-05
Like any other plant, Arabidopsis thaliana or mouse-ear cress, needs nitrogen to survive and thrive. But, like maize, beans and sugar beet, it prefers nitrogen in the form of nitrate, growing better on nitrate rich soil. Whereas, pine and rice for example preferentially grow on ammonium nutrition, another form of the key macronutrient nitrogen. If the concentration or the availability of the different forms of nitrogen fluctuate, plants have to adapt quickly. "One of the most important questions is, what is the role of plant hormones in adaptation to the nitrogen availability? How do the machineries within a plant cope with their changing environment?" asks Eva Benková, developmental biologist and Professor at the Institute of Science and Technology (IST) Austria.
Finding the balance
In ...
2021-01-05
University of Miami Miller School of Medicine researchers led a unique and groundbreaking randomized controlled trial showing umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cell infusions safely reduce risk of death and quicken time to recovery for the severest COVID-19 patients, according to results published in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine in January 2021.
The study's senior author, Camillo Ricordi, M.D., director of the Diabetes Research Institute (DRI) and Cell Transplant Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, said treating COVID-19 with mesenchymal stem cells makes sense.
Results: treatment group vs. ...
2021-01-05
Inspired by the color-changing skin of cuttlefish, octopuses and squids, Rutgers engineers have created a 3D-printed smart gel that changes shape when exposed to light, becomes "artificial muscle" and may lead to new military camouflage, soft robotics and flexible displays.
The engineers also developed a 3D-printed stretchy material that can reveal colors when light changes, according to their study in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
Their invention is modeled after the amazing ability of cephalopods such as cuttlefish, octopuses and squids to change the color and texture of their soft skin for camouflage and communication. This is achieved by the ...
2021-01-05
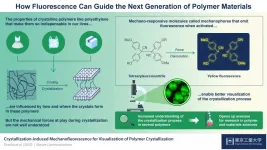
In modern times, manufacturers produce highly specialized materials for a wide array of uses, called polymers. Polymers have a variety of purposes owing to their versatile properties, ranging from being used in construction due to their high tensile strength and resistance to manufacturing plastic bags that require more lightweight, flexible materials, such as nylon or polyethene.
These differences between the properties of different polymers stems from their internal structure. Polymers are made up of long chains of smaller sub-units, called "monomers." Crystallization occurs when crystalline polymers are melted, then cooled down slowly, which enables the chains to organize themselves into neatly arranged ...
2021-01-05
Grasslands are managed worldwide to support livestock production, while remaining natural or semi-natural ones provide critical services that contribute to the wellbeing of both people and the planet. Human activities are however causing grasslands to become a source of greenhouse gas emissions rather than a carbon sink. A new study uncovered how grasslands used by humans have changed our climate over the last centuries.
Grasslands are the most extensive terrestrial biome on Earth and are critically important for animal forage, biodiversity, and ecosystem services. They absorb and release carbon dioxide (CO2), and emit methane (CH4) from grazing livestock and nitrous oxide (N2O) from soils, especially when manure or ...
2021-01-05
A new study out of the University of Chicago Medicine following young adult drinkers for 10 years has found that individuals who reported the highest sensitivity to alcohol's pleasurable and rewarding effects at the start of the trial were more likely to develop an alcohol use disorder (AUD) over the course of the study.
Moreover, when retested on their responses 10 years later, those who became alcoholics had the highest levels of alcohol stimulation, liking and wanting - and these were heightened compared to their baseline with no signs of tolerance to these pleasurable effects.
The research, published on Jan. 5 in the American Journal of Psychiatry, followed a ...
2021-01-05
Bird diets provide a real treasure for research into the distribution and conservation of their prey, such as overlooked and rare bush-cricket species, point out scientists after studying the diet of the Eurasian Eagle Owl (Bubo bubo) in southeastern Bulgaria.
In their END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Impurities boost performance of organic solar cells