INFORMATION:
Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 immune response several months post-infection hints at protective immunity
2021-01-06
(Press-News.org) Researchers who studied antibody and immune cell responses in more than 180 men and women who had recovered from COVID-19 report these patients' immune memory to the virus - across all immune cell types studied - was measurable for up to 8 months after symptoms appeared. The results indicate "that durable immunity against secondary COVID-19 disease is a possibility in most individuals," the authors say. As the number of daily COVID-19 cases worldwide continues to mount, whether an initial infection with SARS-CoV-2 leads to long-lasting protective immunity against COVID-19 remains a question. Studying the nature of the humoral response to the virus, which includes an antibody response, and of the cellular immune response, which includes B cells and T cells, over periods of six months after symptoms start could help inform protective immunity's duration. To do this, Jennifer Dan and colleagues recruited more than 180 men and women from the United States who had recovered from the disease. The majority had had mild symptoms that did not require hospitalization, though 7% were hospitalized. Most subjects provided a blood sample at a single time point, between six days and eight months after symptoms took hold, though 43 samples were provided at 6 months or more following symptom onset. In 254 total samples from 188 COVID-19 cases, Dan and colleagues tracked antibodies, B cells (which produce more antibodies), and two types of T cells (which kill cells that are infected). Antibodies, including to viral spike protein components, only exhibited modest declines at six to eight months after symptom onset. T cells, meanwhile, showed only a slight decay in the body, while B cells that recognized features of the SARS-CoV-2 virus grew in number in some cases, the authors say. While the authors caution that "direct conclusions about protective immunity cannot be made on the basis of [their findings] because mechanisms of protective immunity against SARS-CoV-2 or COVID-19 are not defined in humans," they also say that several "reasonable interpretations" can be made from their study. These include support for resting immune memory compartments potentially contributing "in meaningful ways to protective immunity against pneumonia or severe secondary COVID-19," the authors write.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers discover how a bio-pesticide works against spider mites
2021-01-06
Scientists have uncovered why a food-ingredient-based pesticide made from safflower and cottonseed oils is effective against two-spotted spider mites that attack over a thousand species of plants while sparing the mites' natural predators.
An international team of scientists has uncovered how a bio-pesticide works against spider mites while sparing their natural predators.
The findings, published in the journal Engineering in Life Sciences on October 7, 2020, could present farmers and gardeners with an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic pesticides.
Food ingredients have long been used as alternative pesticides against arthropod pests, such as insects, ticks, and mites, because they tend to be less toxic to mammals and pose less impact to the environment. The ...
Identifying strategies to advance research on traumatic brain injury's effect on women
2021-01-06
Analysis from a workshop convened by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) in 2017 reveals gaps in and opportunities for research to improve understanding of the effects of traumatic brain injury (TBI) in women. A new paper in the Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation summarizes and updates the findings presented during the "Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury in Women" workshop and provides strategies for advancing research efforts in this area. NINDS is part of the National Institutes of Health.
"We are making advances in understanding ...
Sexual dysfunction hits some women harder than others as they age
2021-01-06
CLEVELAND, Ohio (January 5, 2021)--Sexual dysfunction often accompanies the menopause transition. Yet, not all women experience it the same. A new study identified the determinants that affect a woman's risk of sexual dysfunction and sought to determine the effectiveness of hormone therapy in decreasing that risk and modifying sexual behavior. Study results are published online in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
Although hot flashes easily rank as the most common symptom of menopause, the transition is often accompanied by other issues, including changes that affect a woman's ...
Link between dietary fiber and depression partially explained by gut-brain interactions
2021-01-06
CLEVELAND, Ohio (January 5, 2021)--Fiber is a commonly recommended part of a healthy diet. That's because it's good for your health in so many ways--from weight management to reducing the risk of diabetes, heart disease, and some types of cancer. A new study also finds that it might be linked with a reduced risk of depression, especially in premenopausal women. Study results are published online in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
Depression is a common and serious mental health condition that not only affects a person's ability to perform daily activities but can also lead to suicide. ...
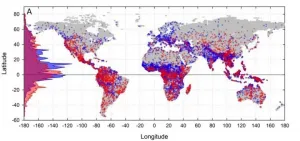
New work provides insight into the relationship between complexity and diversity
2021-01-06
Most forms of life -- species of mammals, birds, plants, reptiles, amphibians, etc. -- are most diverse at Earth's equator and least diverse at the poles. This distribution is called the latitudinal gradient of biodiversity.
A group of Santa Fe Institute collaborators was intrigued by the fact that human cultural diversity shows exactly the same distribution with latitude: human cultures are more diverse near the equator and least at the poles. Their big question was: why? Life is more diverse within richer environments, but it's not clear why human cultural diversity would show this pattern too.
To find answers, the group conducted a biogeographic and macroecological study of the distribution of mammal species ...
COVID-19 generally 'mild' in young children: Evidence review
2021-01-06
A systematic review and meta-analysis of international COVID-19 literature, led by UNSW Sydney, has confirmed that while children under five years old were likely to recover from the infection, half of those infected were infants and almost half of the infected under-fives were asymptomatic.
These findings will help to inform future policy and decision-making about potential COVID-19 vaccination for young children and maternal immunisation programs during pregnancy - but the scientists say future research is needed to explore the potential risk of transmission from infants to their mothers, families and other caregivers, and to find out more about whether asymptomatic under-fives can spread the disease.
The collaborative study between researchers from UNSW Sydney, Telethon ...
Researchers featured in Medical Research Journal for Artificial Intelligence Studies
2021-01-06
Memphis, Tenn. (January 5, 2021) - A paper written by Arash Shaban-Nejad, PhD, MPH, an assistant professor, and Nariman Ammar, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow, both at the Center for Biomedical Informatics in the Department of Pediatrics at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, was recently published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research - Medical Informatics. The paper discussed how an artificial intelligence system developed by the researchers was used to diagnose and treat children and adults who suffer from Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs).
Their research study was named among the Top Milestones on Explainable AI In 2020.
Adverse ...
Majority of media stories fail to label 'preprint' COVID-19 research -- study
2021-01-06
A new SFU-led study finds that less than half of media stories in early 2020 featuring COVID-19 "preprint" research--research that has not yet been peer-reviewed--accurately framed the studies as being preprints or unverified research.
SFU PhD student Alice Fleerackers, a researcher in the Scholarly Communications Lab, and publishing program professor Juan Pablo Alperin collaborated with an international team of researchers to analyze more than 500 mentions in over 450 stories from digital news outlets covering preprint COVID-19 research. The study was published this week in Health Communication.
Their analysis ...
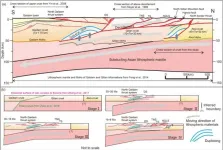
The revelation of the crustal geometry of the western Qilian Mountains, NE Tibetan Plateau
2021-01-06
As the largest orogenic plateau on earth, the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau was caused by a complex crustal deformation process during the continuous collision and compression process between the Indian and Eurasian continents starting at least 60-50 Ma ago. The formation of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau records the collision of the two continents and the deformation process and mechanism within the continents. Therefore, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is considered as a natural ideal laboratory for the study of continent-continent collision and dynamics. At present, the continuous collision between Eurasia and Indian continents is still ongoing, ...
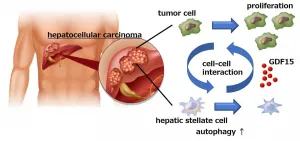
Liver cancer cells manipulate stromal cells involved in fibrosis to promote tumor growth
2021-01-06
Osaka, Japan - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), frequently seen in patients with liver cirrhosis caused by alcohol abuse or chronic viral hepatitis, is the most common form of liver cancer worldwide. As such, it is the third-most common cause of cancer-related death and has a notoriously poor prognosis. At present, surgery is the most effective treatment for HCC, but is only successful in the 10%-20% of cases where cancer cells have not spread beyond the liver.
Given the lack of treatment options for HCC, a group of researchers led by Osaka University decided to focus on specific cells and processes that occur in the area around liver tumors in the hope of finding a novel target for drug development.
The results of their study were published in a recent issue of Gastroenterology.
"Hepatic ...