A subtle change in the DNA may predispose to polyneuropathy after gut infection
2021-01-07
(Press-News.org) Tokyo, Japan - Guillain-Barré syndrome is an infamous autoimmune neuropathy, yet genetic variants predisposing individuals to this disease have yet to be described. In a new study, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) discovered two novel genetic variants in a protein made by antibody-forming immune cells, providing a mechanism for the development of the disease.
The body's immune system is supposed to fight off invaders; however, in autoimmune diseases this defense goes rogue and attacks the host instead through the production of autoantibodies. Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is an acutely developing, autoimmune peripheral neuropathy that leads to muscle weakness and numbness. It is based on the production of autoantibodies against gangliosides, a specific type of lipid molecules on the membranes of cells of the nervous system, which in turn damage those neurons and result in polyneuropathy. That is, damage to multiple peripheral nerves that may cause muscle weakness and numbness. GBS is often preceded by an immune stimulation such as an infection. Indeed, infection with the bacterium Campylobacter jejuni, causing a diarrheal illness, is the most common event before GBS develops. However, as not all patients with this bacterial illness then develop GBS, it has long been thought that genetic variants (small differences in the DNA between individuals) may be what predisposes patients with GBS to the polyneuropathy.
"GBS remains somewhat of a medical mystery. We do not fully understand why patients develop this disease," says corresponding author of the study Professor Takeshi Tsubata. "The goal of our study was to identify genetic variants in patients with GBS and provide a potential mechanism for the production of autoantibodies that lead to the development of polyneuropathy in these patients."
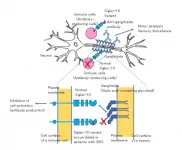
To achieve their goal, the researchers focused on the protein Siglec-10. Siglec-10 is produced by B lymphocytes, a specific type of immune cell that produces antibodies, and binds to gangliosides. The researchers hypothesized that Siglec-10 may play an inhibitory role in the production of antibodies against gangliosides, and in turn that genetic variants in Siglec-10 may diminish this inhibitory role and thus facilitate the development of GBS. By analyzing the DNA sequence encoding for the protein Siglec-10 in patients with GBS, the researchers identified two rare variants that change the amino acid sequence in the protein in GBS patients. There were no patients with only one of the two variants probably because these two variants are located very closely in the Siglec-10 gene.
The researchers then made the GBS-specific Siglec-10 protein in the lab to understand how it differs from the normal Siglec-10 protein at the molecular level. They found that only one of the two variants was responsible for the deleterious effects of the alternate protein, causing a marked alteration in the molecular structure of the protein and in turn a significant impairment of the protein to bind gangliosides.
"These are striking results that show how Siglec-10 suppresses antibody production of gangliosides, and in turn how a variant protein may predispose to the development of Guillain-Barré syndrome. These findings help us understand the pathophysiology of the disease," says first author of the study Amin Alborzian Deh Sheikh.
INFORMATION:
The article, "A Guillain-Barré syndrome-associated SIGLEC10 rare variant impairs its recognition of gangliosides" was published in Journal of Autoimmunity at DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102571
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-07
Using synchrotron radiation at SPring-8 - a large-scale synchrotron radiation facility - Tohoku University, Toshiba Corporation, and the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI) have successfully imaged the magnetization dynamics of a hard disk drive (HDD) write head for the first time, with a precision of one ten-billionth of a second. The method makes possible precise analysis of write head operations, accelerating the development of the next-generation write heads and further increasing HDD capacity.
Details of the research were published in the Journal of Applied Physics on October 6 and presented at the 44th Annual Conference on Magnetics in Japan, on December 14.
International Data Corporation predicts a five-fold increase ...
2021-01-07
The genomes of egg-laying monotreme mammals, platypus and echidna, have been published in the prestigious journal Nature, providing a valuable public resource for research in mammalian biology and evolution, with applications for their conservation and health.
Monotremes display a unique mix of mammalian and reptilian features and form the most distantly related, and least understood, group of living mammals. Their genetic blueprint provides fundamental insights into their unique biology and into the evolution of all mammals.
"The platypus and ...
2021-01-07
The perception of our own voice depends on sound transmission through air (air-conducted) as well as through the skull bone (bone-conducted or BC). The transmission properties of BC speech are, however, not well understood. Now, scientists from Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology report their latest findings on BC transmission under the influence of oral cavity sound pressure, which can boost BC-based technology and basic research on hearing loss and speech impairment.
Ever wondered why your voice sounds different in a recording compared to how you perceive it as you speak? You are not alone. The ...
2021-01-07
Infectious diseases are caused by pathogenic viruses, bacteria, fungi or parasites. The treatment of bacterial and fungal infections relies particularly on antimicrobial drugs, while the focus in treating viral infections is the alleviation of symptoms.
Initial therapy for infection is often empiric and guided by clinical presentation. Its efficacy on the pathogen is, however, only seldom understood at therapy initiation. Although methods for assessing treatment responses exist, the effectiveness is mainly determined through monitoring symptoms and signs of infections.
Advances in sequencing technology have made characterization of genomes and gene expression products increasingly practical. The technology has also made it possible ...
2021-01-07
Combining electronic structure calculations and machine learning (ML) techniques has become a common approach in the atomistic modelling of matter. Using the two techniques together has allowed researchers, for instance, to create models that use atomic coordinates as the only inputs to inexpensively predict any property that can be computed by the first-principles calculations that had been used to train them.
While the earliest and by now most advanced efforts have focused on using predictions of total energies and atomic forces to construct interatomic potentials, more recent efforts have targeted additional properties of crystals and molecules such as ionization energies, NMR chemical shieldings, dielectric response properties and charge density. In the paper "Learning ...
2021-01-07
It is during rare merging events that galaxies undergo dramatic changes in their appearance and in their stellar content. These systems are excellent laboratories to trace the formation of star clusters under extreme physical conditions.
The Milky Way typically forms star clusters with masses that are 10 thousand times the mass of our Sun. This doesn't compare to the masses of the star clusters forming in colliding galaxies, which can reach millions of times the mass of our Sun.
These dense stellar systems are also very luminous. Even after the collision, when the resulting galactic system begins to fade into a more quiescent phase, these very massive star clusters will shine throughout their host galaxy, as long-lasting witnesses of past merging events.
By studying the six galaxy ...
2021-01-07
Autoimmune diseases are diseases of "mistaken identity", where the immune system - which is supposed to protect us against infectious diseases and neoplasias - mistakenly attacks and destroys components of our own body. The incidence of autoimmune diseases is increasing on a worldwide basis, and these diseases - including type 1 diabetes (T1D), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), multiple sclerosis (MS) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) - now affect up to 5% of the population in different regions. There is no cure for autoimmune diseases, and while the immune target of T1D, SLE, MS, and RA are distinct, they share several similar elements, including up to 50% common genetic risk, chronic local inflammation and mechanisms ...
2021-01-07
Researchers at the University of Gothenburg now suggest a possible cure for children with hard-to-treat forms of neuroblastoma using a new combination of drugs. In a new study in the journal Cancer Research, they describe how a two small molecule-based drug combination likely inhibit the tumor's growth.
Neuroblastoma is the most common form of childhood cancer, derived from the peripheral nervous system, i.e., the part of the nervous system that is not the brain or spinal cord. The disease can occur in the chest, neck, abdomen and adrenal glands and can also spread to the spine. Symptoms include general aches, anemia and skeletal pain.
The ...
2021-01-07
Stomach cancer, or gastric cancer, is a common gastrointestinal malignancy. Peritoneal metastasis occurs in a majority of patients with advanced stomach cancer and is considered as an aggressive disease with poor outcomes.
Patients with peritoneal metastasis are typically not eligible for curative surgery. Therefore, preoperative detection and diagnosis of peritoneal metastasis are critical to inform treatment decision-making and avoid unnecessary surgery.
A new study published in the JAMA Network Open on Jan. 5 shows that deep learning can help predicting the occult peritoneal metastasis in stomach cancer. It provides a novel and noninvasive approach for ...
2021-01-07
Olduvai (now Oldupai) Gorge, known as the Cradle of Humankind, is a UNESCO World Heritage site in Tanzania, made famous by Louis and Mary Leakey. New interdisciplinary field work has led to the discovery of the oldest archaeological site in Oldupai Gorge as reported in Nature Communications, which shows that early human used a wide diversity of habitats amidst environmental changes across a 200,000 year-long period.
Located in the heart of eastern Africa, the Rift System is a prime region for human origins research, boasting extraordinary records of extinct human species and environmental records spanning several million years. For more than a century, archaeologists and human palaeontologists have been exploring the East African Rift outcrops and unearthing hominin fossils in surveys ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A subtle change in the DNA may predispose to polyneuropathy after gut infection