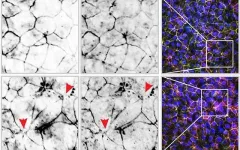
(Press-News.org) Touted by makers as a "healthy" alternative to traditional nicotine cigarettes, new research indicates the chemicals found in e-cigarettes disrupt the gut barrier and trigger inflammation in the body, potentially leading to a variety of health concerns.
In the study, published Jan. 5, 2021 in the journal END
Study: e-cigarettes trigger inflammation in the gut
Chemicals used for vaping break down zipper-like junctions between cells in the gut, leading to chronic inflammation and potential for other health concerns
2021-01-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NYUAD study informs research of child development and learning in conflict-affected areas
2021-01-07
Abu Dhabi, UAE, January 6, 2021: To provide effective aid to children who live in areas of conflict it is necessary to understand precisely how they have been impacted by the crises around them. One area of importance is the effect of conflict and trauma on a child's development and education.
In a new paper, Global TIES for Children researchers J. Lawrence Aber, Carly Tubbs Dolan, Ha Yeon Kim, and Lindsay Brown, present a review of opportunities and challenges they have encountered in designing and conducting rigorous research that advances our understanding of this effect. Global TIES for Children, an international research center based at NYU Abu Dhabi and NYU New York, generates evidence to support the most effective humanitarian and development aid to promote children's ...
New discovery sheds light on the mysterious family life of notorious sabre-toothed tiger
2021-01-07
New research indicates adolescent offspring of the menacing sabre-toothed predator, Smilodon fatalis, were more momma's cubs than independent warriors.
A new study by scientists at the Royal Ontario Museum (ROM) and University of Toronto, published January 7, 2021 in iScience¸ documents a family group of the sabre-toothed cats whose remains were discovered in present-day Ecuador. By studying the fossils, collected for the ROM in the early 1960s, the scientists were able to show that while the supersized Ice Age cats grew quite quickly, they also appeared to stay with their mother for longer than some other large cats before forging their own path.
"This study started out as a simple description ...
COVID-19 accelerates cancer virtual care with quality, convenience and cost savings
2021-01-07
Patients and healthcare providers at the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre rated virtual care during COVID-19 as highly satisfactory overall for quality of care and convenience, while at the same time saving patients millions in costs.
Research led by Princess Margaret Radiation Oncologist Dr. Alejandro Berlin showed that virtual care can be implemented rapidly and safely across a highly-specialized and high-volume cancer centre. Eighty (80) per cent of patients reported they were either very satisfied or satisfied with it, citing convenience as a main ...
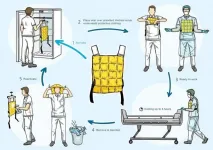
Cooling vests alleviate perceptual heat strain perceived by COVID-19 nurses
2021-01-07
Wearing cooling vests during a COVID-19 shift ensures that nurses experience less heat during their work. During their shifts, nurses wear protective clothing for three hours in a row, during which the temperature can rise to as much as 36 degrees. The cooling vests offer such effective cooling that they are now part of the standard work clothing for nurses in the COVID nursing departments at Radboud university medical center.
Due to the high level of contagiousness present with COVID-19, health care personnel have to work in protective clothing that is not ...
Seafood strategies
2021-01-07
The "Executive Order on Promoting American Seafood Competitiveness and Economic Growth," issued by the Trump administration in May 2020, lays out a plan to expand the U.S. seafood industry, especially aquaculture, and enhance American seafood competitiveness in the global market.
The goals of the directive are focused largely on growth and expansion of the industry, which includes wild-caught fisheries and farm-raised products, as well as recreation, processing and other industries that rely on fishing.
"The seafood industry in general is worth about $200 billion and accounts for 2 million jobs in the United States," ...
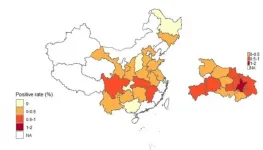
COVID-19 likely lingered longer than reported in Wuhan
2021-01-07
Wuhan City in China was the first place to report COVID-19 in the world and--between December 2019 and May 2020--caused nearly two-thirds of all COVID-19 cases in China. Now, researchers reporting in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases have tested more than 60,000 healthy individuals in China for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and concluded that thousands of Wuhan residents were infected with asymptomatic cases of COVID-19 after the infection was believed to be under control in China.
Rapid antibody tests are used to diagnosis present and past infections with the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19; positive IgG antibodies suggests a previous infection while IgM antibodies mean a current or recent ...
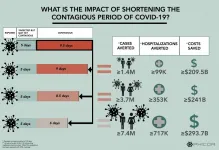
Cutting COVID-19 infectious period could prevent millions of cases
2021-01-07
A new computational analysis suggests that a vaccine or medication that could shorten the infectious period of COVID-19 may potentially prevent millions of cases and save billions of dollars. The study was led by Bruce Lee along with colleagues in the Public Health Informatics, Computational, and Operations Research (PHICOR) team headquartered at the CUNY Graduate School of Public Health and Health Policy and the Lundquist Research Institute at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center, and publishes in the open-access journal PLOS Computational Biology.
While much of the ...
Fatal health threat to young African children reduced by innovative artistic intervention
2021-01-07
The fatal threat from diarrhoea and pneumonia to young children in the world's poorer countries can be drastically reduced by using traditional performing arts to encourage mothers to provide youngsters with safe food and water, a new study reveals.
The Gambia, like many other Low- and Middle-income Countries (LMICs) faces high rates of under-five deaths due to diarrhoea and pneumonia - the two highest causes of death in this age group in this country and globally.
Children transitioning from breastfeeding to eating food are at most risk, as complementary food becomes contaminated. Researchers working in The Gambia discovered that mothers' food safety and hygiene behaviours were massively improved by a low-cost behaviour change community ...
New research reveals how one antibody blocks dangerous effects of dengue virus infection, offering a potential path to prevention
2021-01-07
ANN ARBOR--A team of researchers has discovered an antibody that blocks the ability of the dengue virus to cause disease in mice. The findings open the potential for developing effective treatments and designing a vaccine for dengue and similar diseases.
Dengue virus, a member of a group of viruses called flaviviruses, causes 50 to 100 million cases of dengue disease each year, with no effective treatment or vaccine. Other members of this group include the viruses that cause Zika, yellow fever and West Nile fever.
In a new study scheduled to publish Jan. 8 in the journal Science, researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, and the University of Michigan revealed how an antibody called 2B7 neutralizes one specific protein made ...
Treating an autoimmune disease in mice with an mRNA vaccine
2021-01-07
Christina Krienke and colleagues have designed an mRNA vaccine that delayed the onset of and reduced the severity of multiple sclerosis-like disease in mice. The vaccine restores the body's tolerance to its own proteins, suppressing the characteristic immune overreactivity of the disease. The vaccine developed by Krienke et al. works in a targeted fashion to promote tolerance to specific disease-related proteins, an improvement over other approaches to treating the disease that induce systemic immune suppression that can leave an individual vulnerable to other ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
[Press-News.org] Study: e-cigarettes trigger inflammation in the gutChemicals used for vaping break down zipper-like junctions between cells in the gut, leading to chronic inflammation and potential for other health concerns