Preserving workers' hearing health by improving earplug efficiency
Work carried out by researchers from ÉTS and the IRSST
2021-01-08
(Press-News.org) Noise exposure accounts for 22% of worldwide work-related health problems. Excessive noise not only causes hearing loss and tinnitus, but also increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. To provide protection, workers normally wear earplugs. However, commonly available earplugs are often uncomfortable, since they don't fit everyone's ears equally well.
How could we improve the comfort and effectiveness of these earplugs? What aspects of the ear canal must be taken into account? To answer these questions, researchers from the École de technologie supérieure (ÉTS University) and the Institut de recherche en santé et sécurité du travail (IRSST) analyzed the varying structure of ear canals to find a correlation between their shapes and the effectiveness of three commonly-used models of earplugs.
Each one is unique
Just like fingerprints, ear canals are unique. So, to find the best compromise between comfort and efficiency, you need to understand the relationship between the shapes of ear canals and of earplugs.
Earplugs must not only fit properly inside the ear canal, but must also exert pressure against the walls of the canal in order to make a tight seal. However, if the plugs put too much pressure on the ear canal walls, they will cause the wearer pain.
The methodology
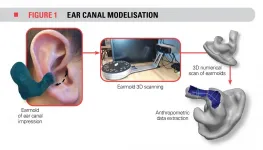
To study these aspects, 3D models of volunteer workers' ear canals were created. These people wore three different types of earplugs. To obtain the geometry of their ear canals, a moulding material was injected to create canal moulds. These moulds were then scanned by measurement software to establish the geometric characteristics of the ear canal, such as the width at various locations and the overall length.
The noise attenuation of the three models of earplugs was then measured for each volunteer. Two miniature microphones were installed in and around the plugs to measure the noise outside and inside the ear plug.
A statistical analysis as well as algorithms based on artificial intelligence helped categorize the morphology of ear canals as a function of the degree of noise mitigation of each earplug.
Concrete applications
The results of the study show that the area of the ear canal called the "first elbow" is closely linked to noise attenuation by earplugs. Groups of similar structures created using artificial intelligence will allow researchers to develop a multitude of tools for manufacturers, who will then be able to produce a range of more comfortable ear plugs. This will allow prevention professionals to suggest models suited to each worker's ear canals.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-08
Non-violent offenders serving time for drug use or possession should be freed immediately and their convictions erased, according to research published in the peer-reviewed The American Journal of Bioethics.
More than 60 international experts including bioethicists, psychologists and drug experts have joined forces to call for an end to the war on drugs which they argue feeds racism.
All drugs currently deemed illicit - even crack cocaine and heroin - should be decriminalized as a matter of urgency, according to this new alliance. Legalisation and regulation should then follow with restrictions on age, advertising and licensing, they say.
They have analysed evidence from over 150 studies and reports, concluding that prohibition unfairly affects Black people, damages communities, ...
2021-01-08
A new study has found that spending time outdoors and switching off our devices is associated with higher levels of happiness during a period of COVID-19 restrictions.
Previous academic studies have indicated how being outdoors, particularly in green spaces, can improve mental health by promoting more positive body image, and lowering levels of depression and anxiety.
Jointly led by academics from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) in the UK, the Karl Landsteiner University of Health Sciences in Austria, and Perdana University in Malaysia, this new research examined how levels ...
2021-01-08
PHILADELPHIA--Medications to treat high blood pressure did not affect outcomes among patients hospitalized with COVID-19, found an international team led by researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. The study, published today in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, is the first randomized controlled trial to show there is no risk for patients continuing these medications while hospitalized for COVID-19.
As part of the REPLACE COVID trial, investigators examined whether ACE inhibitors (ACEIs) or Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs) -- two classes of medications to treat high blood pressure -- ...
2021-01-07
Touted by makers as a "healthy" alternative to traditional nicotine cigarettes, new research indicates the chemicals found in e-cigarettes disrupt the gut barrier and trigger inflammation in the body, potentially leading to a variety of health concerns.
In the study, published Jan. 5, 2021 in the journal END ...
2021-01-07
Abu Dhabi, UAE, January 6, 2021: To provide effective aid to children who live in areas of conflict it is necessary to understand precisely how they have been impacted by the crises around them. One area of importance is the effect of conflict and trauma on a child's development and education.
In a new paper, Global TIES for Children researchers J. Lawrence Aber, Carly Tubbs Dolan, Ha Yeon Kim, and Lindsay Brown, present a review of opportunities and challenges they have encountered in designing and conducting rigorous research that advances our understanding of this effect. Global TIES for Children, an international research center based at NYU Abu Dhabi and NYU New York, generates evidence to support the most effective humanitarian and development aid to promote children's ...
2021-01-07
New research indicates adolescent offspring of the menacing sabre-toothed predator, Smilodon fatalis, were more momma's cubs than independent warriors.
A new study by scientists at the Royal Ontario Museum (ROM) and University of Toronto, published January 7, 2021 in iScience¸ documents a family group of the sabre-toothed cats whose remains were discovered in present-day Ecuador. By studying the fossils, collected for the ROM in the early 1960s, the scientists were able to show that while the supersized Ice Age cats grew quite quickly, they also appeared to stay with their mother for longer than some other large cats before forging their own path.
"This study started out as a simple description ...
2021-01-07
Patients and healthcare providers at the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre rated virtual care during COVID-19 as highly satisfactory overall for quality of care and convenience, while at the same time saving patients millions in costs.
Research led by Princess Margaret Radiation Oncologist Dr. Alejandro Berlin showed that virtual care can be implemented rapidly and safely across a highly-specialized and high-volume cancer centre. Eighty (80) per cent of patients reported they were either very satisfied or satisfied with it, citing convenience as a main ...
2021-01-07
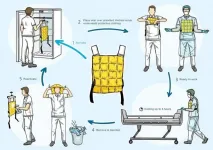
Wearing cooling vests during a COVID-19 shift ensures that nurses experience less heat during their work. During their shifts, nurses wear protective clothing for three hours in a row, during which the temperature can rise to as much as 36 degrees. The cooling vests offer such effective cooling that they are now part of the standard work clothing for nurses in the COVID nursing departments at Radboud university medical center.
Due to the high level of contagiousness present with COVID-19, health care personnel have to work in protective clothing that is not ...
2021-01-07
The "Executive Order on Promoting American Seafood Competitiveness and Economic Growth," issued by the Trump administration in May 2020, lays out a plan to expand the U.S. seafood industry, especially aquaculture, and enhance American seafood competitiveness in the global market.
The goals of the directive are focused largely on growth and expansion of the industry, which includes wild-caught fisheries and farm-raised products, as well as recreation, processing and other industries that rely on fishing.
"The seafood industry in general is worth about $200 billion and accounts for 2 million jobs in the United States," ...
2021-01-07
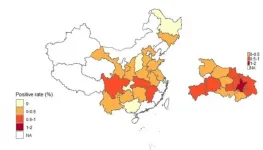
Wuhan City in China was the first place to report COVID-19 in the world and--between December 2019 and May 2020--caused nearly two-thirds of all COVID-19 cases in China. Now, researchers reporting in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases have tested more than 60,000 healthy individuals in China for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and concluded that thousands of Wuhan residents were infected with asymptomatic cases of COVID-19 after the infection was believed to be under control in China.
Rapid antibody tests are used to diagnosis present and past infections with the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19; positive IgG antibodies suggests a previous infection while IgM antibodies mean a current or recent ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Preserving workers' hearing health by improving earplug efficiency
Work carried out by researchers from ÉTS and the IRSST