Workaholism leads to mental and physical health problems
Work addiction risk depends on occupation
2021-01-13
(Press-News.org) Workaholism or work addiction risk is a growing public health concern that can lead to many negative mental and physical health outcomes such as depression, anxiety or sleep disorder. Perception of work (job demands and job control) may become a major cause of employees' work addiction. The international group of researchers including the HSE University scientist explored the link between work addiction risk and health-related outcomes using the framework of Job Demand Control Model. The results were published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
Workaholics are people who usually work seven and more hours more than others per week. There are potential reasons for that: financial problems, poor marriage or pressure by their organization or supervisor. What can differentiate a workaholic behaviour from similar behaviour like work engagement? Workaholism is also known as a behavioural disorder, which means the excessive involvement of the individual in work when an employer doesn't require or expect it.
The scientists aimed to demonstrate the extent to which the work addiction risk is associated with the perception of work (job demands and job control), and mental health in four job categories suggested by Karasek's model or Job Demand-Control-Support model (JDCS). The JDCS model assumes four various work environments (four quadrants) in which workers may experience a different level of job demands and job control: passive, low-strain, active, and tense/job-strain. Job control is the extent to which an employee feels control over doing work.
"Passive" jobs (low job control, low job demands) might be satisfying to a worker as long as the workers reach the set goal. "Low strain" jobs have high job control and low job demands. Individuals in this category are not particularly at risk of mental health problems, and it corresponds typically to creative jobs such as architects. "Active" workers have high job demands and high job control. They are highly skilled professionals with responsibilities, such as heads or directors of companies. Those highly skilled workers have very demanding tasks but they have high levels of decision latitude to solve problems. Finally, workers at risk of stress-related disorders are those within the "job strain" group (high demand and low control). For example, healthcare workers from emergency departments are typically in job strain because they cannot control the huge workload.
The study was conducted in France because it is one of the industrial countries with growing numbers of occupations. The authors of the research collected data from 187 out of 1580 (11.8%) French workers who agreed to participate in a cross-sectional study using the WittyFit software online platform. The self-administered questionnaires were the Job Content Questionnaire by Karasek, the Work Addiction Risk Test, the Hospital Anxiety and Depression scale and socio-demographics. The authors of this study divided all the participants based on their occupational groups and investigated the link between work addiction risk and mental and physical health outcomes.
'One of the novelties of this research was to introduce vulnerable occupational groups to organizations or job holders. For example, if we find that work addiction risk can be found more in some occupations and may result in negative outcomes for the health situation then we can give this information to decision makers in this organization or, for example, to the ministry of health. And they could intervene to prevent this problem,' explains Morteza Charkhabi, Associate Professor at the Institute of Education at the HSE University.
The results show that high job demands at work are strongly associated with work addiction risk but the job control level does not play the same role. The prevalence of work addiction risk is higher for active and high-strain workers than for passive and low-strain workers. These two groups of workers appeared to be more vulnerable and therefore can suffer more from the negative outcomes of work addiction risk, in terms of depression, sleep disorder, stress and other health issues.
'We found that job demands could be the most important factor that can develop work addiction risk. So this factor should be controlled or should be investigated by the organization's manager, for example, HR staff, psychologists. Also another conclusion could be the job climate like job demands of each job category can influence the rate of work addiction risk. Thus in this study we actually focused on external factors like job demands not internal factors like the personal characteristics,' adds Morteza Charkhabi.
The researchers found that people with higher work addiction risk compared to people with low work addiction risk have twice the risk of developing depression. Sleep quality was lower to workers with high risk of work addiction compared to workers with low risk of work addiction. Also women had almost twice the work addiction risk than men.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-13
Optical sensors can quantitatively analyze chemical and biological samples by measuring and processing the optical signals produced by the samples. Optical sensors based on infrared absorption spectroscopy can achieve high sensitivity and selectivity in real time, and therefore play a crucial role in a variety of application areas such as environmental sensing, medical diagnostics, industrial process control and homeland security.
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Applications, a team of scientists, led by Dr. Peter Q. Liu from the Department of Electrical Engineering, the State University of New York at Buffalo, have demonstrated a new type of high-performance optical sensor which can utilize ...
2021-01-13
Metal surfaces play a role as catalysts for many important applications - from fuel cells to the purification of car exhaust gases. However, their behaviour is decisively affected by oxygen atoms incorporated into the surface.
This phenomenon has been known for a long time, but until now it has not been possible to precisely investigate the role of oxygen in complex surfaces point by point in order to understand the chemical background at the atomic level. This has now been achieved at TU Wien in cooperation with a team from the Elettra Synchrotron in Trieste. It became possible ...
2021-01-13
A remarkable prediction of Einstein's theory of general relativity--the theory that connects space, time, and gravity--is that rotating black holes have enormous amounts of energy available to be tapped.
For the last 50 years, scientists have tried to come up with methods to unleash this power. Nobel physicist Roger Penrose theorized that a particle disintegration could draw energy from a black hole; Stephen Hawking proposed that black holes could release energy through quantum mechanical emission; while Roger Blandford and Roman Znajek suggested electromagnetic ...
2021-01-13
Irvine, Calif., Jan. 11, 2021 - Often admired for their flawless appearance to the naked eye, crystals can have defects at the nanometer scale, and these imperfections may affect the thermal and heat transport properties of crystalline materials used in a variety of high-technology devices.
Employing newly developed electron microscopy techniques, researchers at the University of California, Irvine and other institutions have, for the first time, measured the spectra of phonons - quantum mechanical vibrations in a lattice - at individual crystalline faults, and they discovered the propagation of phonons near the flaws. The team's findings are the subject of a study published recently in Nature.
"Point defects, dislocations, stacking ...
2021-01-13
Irvine, Calif., Jan. 5, 2021 -- Scientists at the University of California, Irvine have developed a new deep-learning framework that predicts gene regulation at the single-cell level.
Deep learning, a family of machine-learning methods based on artificial neural networks, has revolutionized applications such as image interpretation, natural language processing and autonomous driving. In a study published recently in Science Advances, UCI researchers describe how the technique can also be successfully used to observe gene regulation at the cellular level. Until now, that process had ...
2021-01-13
A pioneering study by University of Bristol researchers finds that the evolution of teeth in the giant prehistoric shark Megalodon and its relatives was a by-product of becoming huge, rather than an adaptation to new feeding habits.
The iconic extinct Megalodon was the largest shark to ever roam the seas. Its name translates to 'big tooth', making reference to its massive teeth, which represent the most abundant fossil remains of the species. They are broad and triangular, nothing like the curved, blade-like teeth of the closest relatives of Megalodon.
The ...
2021-01-13
DURHAM, N.C. - Glioblastoma brain tumors are especially perplexing. Inevitably lethal, the tumors occasionally respond to new immunotherapies after they've grown back, enabling up to 20% of patients to live well beyond predicted survival times.
What causes this effect has long been the pursuit of researchers hoping to harness immunotherapies to extend more lives.
New insights from a team led by Duke's Preston Robert Tisch Brain Tumor Center provide potential answers. The team found that recurring glioblastoma tumors with very few mutations are far more vulnerable ...
2021-01-13
Even with the COVID-19-related small dip in global carbon emissions due to limited travel and other activities, the ocean temperatures continued a trend of breaking records in 2020. A new study, authored by 20 scientists from 13 institutes around the world, reported the highest ocean temperatures since 1955 from surface level to a depth of 2,000 meters.
The report was published on January 13 in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences and concluded with a plea to the policymakers and others to consider the lasting damage warmer oceans can cause as they attempt to mitigate the ...
2021-01-13
Today, the largest study of genetic diversity in Ukraine was published in the open science journal GigaScience. The project was an international effort, bringing together researchers in Ukraine, the US and China and is the first fruits of this collaboration to set up a new Central Europe Center for Genomic Research in Ukraine. Led by researchers at Uzhhorod National University and Oakland University in the US, the work provides genetic understanding of the historic and pre-historic migration settlements in one of the key intersections of human trade and migration between the Eurasian peoples as well as the identification of genetic variants of medical interest in the Ukrainian population that differ ...
2021-01-13
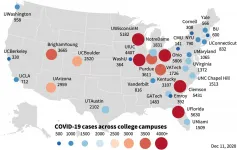
College campuses are at risk of becoming COVID-19 superspreaders for their entire county, according to a new vast study which shows the striking danger of the first two weeks of school in particular.
Looking at 30 campuses across the nation with the highest amount of reported cases, experts saw that over half of the institutions had spikes - at their peak - which were well above 1,000 coronavirus cases per 100,000 people per week within the first two weeks of class.
In some colleges, one in five students had been infected with the virus by the end of the fall term. Four institutions had over 5,000 ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Workaholism leads to mental and physical health problems
Work addiction risk depends on occupation