Research reveals how teeth functioned and evolved in giant mega-sharks
2021-01-13
(Press-News.org) A pioneering study by University of Bristol researchers finds that the evolution of teeth in the giant prehistoric shark Megalodon and its relatives was a by-product of becoming huge, rather than an adaptation to new feeding habits.
The iconic extinct Megalodon was the largest shark to ever roam the seas. Its name translates to 'big tooth', making reference to its massive teeth, which represent the most abundant fossil remains of the species. They are broad and triangular, nothing like the curved, blade-like teeth of the closest relatives of Megalodon.
The differences in tooth shape seen in this group of giant sharks has been traditionally thought to reflect a shift in diet. While the oldest relatives probably used their teeth to pierce small and fast-moving prey like fish, Megalodon most likely used them to bite off big chunks of meat from marine mammals or dismember such prey with powerful lateral head shakes.
In the new study published today in the journal Scientific Reports, scientists used computational tools to understand how the dentitions of these megatooth sharks functioned during feeding.
Antonio Ballell, PhD student at the University of Bristol's School of Earth Sciences, said: "We applied engineering techniques to digitally simulate how different tooth shapes handled bite forces and loads resulting from lateral head movements.
"This method, called Finite Element Analysis, has been previously used to understand how resistant different biological structures are under specific forces.
"We expected to find that Megalodon teeth could resist forces better than those of its older and smaller relatives. Surprisingly, when we removed tooth size from the simulations, we recovered the opposite pattern: Megalodon teeth are relatively weaker than the most gracile teeth of other megatooth sharks."
Dr Humberto Ferrón, postdoctoral researcher and co-author of the study, said: "Our results might seem to be at odds with traditional functional interpretations of the dentitions of these group of giant sharks. We think that other biological processes might be responsible for the evolutionary change in their dentitions.
"For example, modifications in tooth shape that occurred from the older, smaller species to that of the more recent, larger forms like Megalodon are very similar to those observed along the growth of Megalodon.
"That is, juvenile Megalodon individuals have teeth that resemble those of older megatooth sharks. Thus, instead of feeding specialization, we think that the acquisition of its gigantic body size was responsible for the evolution of the peculiar teeth of Megalodon."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-13
DURHAM, N.C. - Glioblastoma brain tumors are especially perplexing. Inevitably lethal, the tumors occasionally respond to new immunotherapies after they've grown back, enabling up to 20% of patients to live well beyond predicted survival times.
What causes this effect has long been the pursuit of researchers hoping to harness immunotherapies to extend more lives.
New insights from a team led by Duke's Preston Robert Tisch Brain Tumor Center provide potential answers. The team found that recurring glioblastoma tumors with very few mutations are far more vulnerable ...
2021-01-13
Even with the COVID-19-related small dip in global carbon emissions due to limited travel and other activities, the ocean temperatures continued a trend of breaking records in 2020. A new study, authored by 20 scientists from 13 institutes around the world, reported the highest ocean temperatures since 1955 from surface level to a depth of 2,000 meters.
The report was published on January 13 in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences and concluded with a plea to the policymakers and others to consider the lasting damage warmer oceans can cause as they attempt to mitigate the ...
2021-01-13
Today, the largest study of genetic diversity in Ukraine was published in the open science journal GigaScience. The project was an international effort, bringing together researchers in Ukraine, the US and China and is the first fruits of this collaboration to set up a new Central Europe Center for Genomic Research in Ukraine. Led by researchers at Uzhhorod National University and Oakland University in the US, the work provides genetic understanding of the historic and pre-historic migration settlements in one of the key intersections of human trade and migration between the Eurasian peoples as well as the identification of genetic variants of medical interest in the Ukrainian population that differ ...
2021-01-13
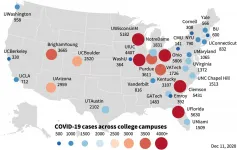
College campuses are at risk of becoming COVID-19 superspreaders for their entire county, according to a new vast study which shows the striking danger of the first two weeks of school in particular.
Looking at 30 campuses across the nation with the highest amount of reported cases, experts saw that over half of the institutions had spikes - at their peak - which were well above 1,000 coronavirus cases per 100,000 people per week within the first two weeks of class.
In some colleges, one in five students had been infected with the virus by the end of the fall term. Four institutions had over 5,000 ...
2021-01-13
A detailed description of how ovarian cancer cells adapt to survive and proliferate in the peritoneal cavity has been published in Frontiers in Oncology. Researchers show that structures inside the cells change as the disease progresses from benign to malignant, helping the cells to grow in an otherwise hostile environment of low nutrients and oxygen. Understanding how these cellular adaptations are regulated could herald new targeted treatment options against the fifth-leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women.
"Our study compared the structures inside cells representing different stages of ovarian cancer, including after aggregation, which enhances their survival," says Eva Schmelz, a Professor and Scientific Director at Virginia Tech University, USA, who led this research. "We found ...
2021-01-13
The remote learning experience of parents who had their children at home in Spring 2020, as schools across the US closed during the United States' COVID-19 lockdown, was more positive than widely believed.
That is the suggestion from a new study published in the Journal of School Choice, which looked at the experience of a nationally representative sample of 1,700 parents stretching right across America.
On average only 44% of parents reported the online learning program required too much of parents, while 38% of parents said it was difficult for them to manage the online provisions.
However, worryingly, most parents (63%) believed remote learning caused their child to fall behind.
While the study focused ...
2021-01-13
Yale researchers have devised a way to peer into the brains of two people simultaneously while are engaged in discussion. What they found will not surprise anyone who has found themselves arguing about politics or social issues.
When two people agree, their brains exhibit a calm synchronicity of activity focused on sensory areas of the brain. When they disagree, however, many other regions of the brain involved in higher cognitive functions become mobilized as each individual combats the other's argument, a Yale-led research team reports Jan. 13 in the journal Frontiers of Human Neuroscience.
"Our entire brain ...
2021-01-13
A loss of biodiversity and accelerating climate change in the coming decades coupled with ignorance and inaction is threatening the survival of all species, including our very own, according to the experts from institutions including Stanford University, UCLA, and Flinders University.
The researchers state that world leaders need a 'cold shower' regarding the state of our environment, both to plan and act to avoid a ghastly future.
Lead author Professor Corey Bradshaw of Flinders University in Australia says he and his colleagues have summarised the state of the natural world in stark form to help clarify the gravity of the human predicament.
"Humanity is causing a ...
2021-01-13
Tsukuba, Japan - Work causes so much stress that it's become a global public health issue. Stress's impact on mental and physical health can also hurt productivity and result in economic loss. A new study now finds that working people who regularly take walks in forests or greenspaces may have higher stress-coping abilities.
In a study published in Public Health in Practice, researchers led by Professor Shinichiro Sasahara at the University of Tsukuba analyzed workers' "sense of coherence" (SOC) scores, demographic attributes, and their forest/greenspace walking habits. SOC comprises the triad of meaningfulness (finding a sense of meaning in life), comprehensibility (recognizing and understanding stress), and ...
2021-01-13
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Jan. 13, 2021)--If you're a bit more forgetful or having more difficulty processing complex concepts than in the past, the problem may be your menopause stage. A new study claims that menopause stage is a key determinant of cognition and, contrary to previous studies, shows that certain cognitive declines may continue into the postmenopause period. Study results are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
It's commonly assumed that people's memories decline with age, as does their ability to learn new things and grasp challenging concepts. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Research reveals how teeth functioned and evolved in giant mega-sharks