New molecular structures associated with ALS
2021-01-13
(Press-News.org) Researchers from the University of Seville and the University of Pavia have identified a link between Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) and the accumulation of DNA-RNA hybrids in the genome. The accumulation of these hybrids causes increased genomic damage and boosts genetic instability. This finding will make it possible to better understand the molecular basis of the disease, as well as to propose new solutions to curb it.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system, characterised by progressive degeneration of motor neurons leading to muscle paralysis. Classified as a rare disease, there is no cure despite efforts to understand the disease's molecular basis and research devoted to identifying therapies that can at least slow its evolution.
At the CABIMER centre, the group from the University of Seville led by Professor Andrés Aguilera, in collaboration with the group led by Dr. Cristina Cereda from the Mondino Foundation at the University of Pavia, have identified a link between this disease and the accumulation of DNA-RNA hybrids in the genome. The researchers have observed that patient-derived mutations in TDP-43, a protein of the RNA metabolism whose deficiency is associated with ALS, result in the accumulation of these hybrids in both neuronal and non-neuronal cells, thereby causing increased genomic damage and genetic instability.
This discovery has led to a new perception of the disease's molecular basis related to the role of the TDP-43 protein in the cellular cytoplasm. The mutations analysed cause a TDP-43 deficiency in the cell nucleus, thus leading to the accumulation of these aberrant structures in the DNA. This research opens up new avenues of exploration to understand the disease's molecular basis, as well as new approaches to try to slow its evolution.
INFORMATION:
The study conducted at CABIMER involved, among others, the pre-doctoral student Marta Giannini under the Erasmus+ programme, Aleix Bayona-Feliu under a Juan de la Cierva contract and Sonia Barroso, as part of an ERC Advanced project.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-13
The descendants of regular wild-type bacteria can evolve to survive for a long time on metallic copper surfaces that would usually kill them within a few minutes. An international research team led by Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the Bundeswehr Institute of Microbiology was able to produce these tiny survivalists in the lab and has been able to study them more closely. The team reports on its findings in Applied and Environmental Microbiology.
Bacterial infections are usually treated with antibiotics. However, in recent decades many pathogenic bacteria have developed an increasing tolerance to common drugs. So-called multidrug-resistant bacteria are of particular concern as ...
2021-01-13
It is politically agreed and necessary for climate protection reasons that our entire economy becomes climate-neutral in the coming decades - and that applies to air travel, too. This is a technically feasible goal, and there are numerous ways to achieve it. ETH Professor Marco Mazzotti and his team have now compared the options that appear to be the easiest to implement in the short and medium term and evaluated them according to factors such as cost-effectiveness.
The ETH researchers conclude that the most favourable option is to continue powering aircraft with fossil fuels in future, but then remove the associated CO2 emissions from the atmosphere ...
2021-01-13
Fuchs' corneal dystrophy is one of the most common eye diseases diagnosed in almost 5% of the population of Europe aged 40 years or over. It is a hereditary eye disease that causes vision impairment and typically manifests in middle age. The first symptoms of the disease - blisters on the surface of your cornea - resemble cataract at first glance. The disease progresses from the centre of the cornea affecting all layers of the cornea. The progression of the disease varies from individual to individual and in severe cases results in vision loss.
The molecular neurobiology ...
2021-01-13
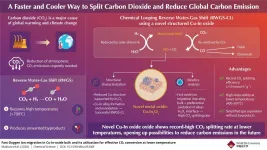
With ever-worsening climate change, there is a growing need for technologies that can capture and use up the atmospheric CO2 (carbon dioxide) and reduce our carbon footprint. Within the realm of renewable energy, CO2-based e-fuels have emerged as a promising technology that attempts to convert atmospheric CO2 into clean fuels. The process involves production of synthetic gas or syngas (a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide (CO)). With the help of the reverse water-gas shift (RWGS) reaction, CO2 is broken down into the CO necessary for syngas. While promising in its conversion efficiency, the RWGS reaction requires incredibly high temperatures (>700°C) to proceed, while also generating ...
2021-01-13
In a new study, researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have used a urine test to identify and verify a patient's type of asthma. The study, which has been published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, lays the foundation for a more personalized diagnosis and may result in improved treatment of severe asthma in the future.
About 10 percent of the Swedish population suffers from asthma, a disease that has become increasingly widespread over the past 50 years, with annual global mortality of around 400,000 according to the World Health Organization. Asthma is characterized by chronic inflammation in the airways, which can result in symptoms including ...
2021-01-13
In three recent publications in Molecular Psychiatry, Brain and JAMA Neurology researchers from the University of Gothenburg provide convincing evidence that an in-house developed blood test for Alzheimer's disease can detect the disease early and track its course, which has major implications for a potential use in clinical practice and treatment trials.
"This is an extremely dynamic research field right now, thanks to the technological development and seminal scientific progress in the past years. The dream scenario is to have a blood test for the early detection and screening of Alzheimer's disease up and running. That would give significantly ...
2021-01-13
Workaholism or work addiction risk is a growing public health concern that can lead to many negative mental and physical health outcomes such as depression, anxiety or sleep disorder. Perception of work (job demands and job control) may become a major cause of employees' work addiction. The international group of researchers including the HSE University scientist explored the link between work addiction risk and health-related outcomes using the framework of Job Demand Control Model. The results were published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
Workaholics are people who usually work seven and more hours more than ...
2021-01-13
Optical sensors can quantitatively analyze chemical and biological samples by measuring and processing the optical signals produced by the samples. Optical sensors based on infrared absorption spectroscopy can achieve high sensitivity and selectivity in real time, and therefore play a crucial role in a variety of application areas such as environmental sensing, medical diagnostics, industrial process control and homeland security.
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Applications, a team of scientists, led by Dr. Peter Q. Liu from the Department of Electrical Engineering, the State University of New York at Buffalo, have demonstrated a new type of high-performance optical sensor which can utilize ...
2021-01-13
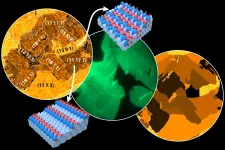
Metal surfaces play a role as catalysts for many important applications - from fuel cells to the purification of car exhaust gases. However, their behaviour is decisively affected by oxygen atoms incorporated into the surface.
This phenomenon has been known for a long time, but until now it has not been possible to precisely investigate the role of oxygen in complex surfaces point by point in order to understand the chemical background at the atomic level. This has now been achieved at TU Wien in cooperation with a team from the Elettra Synchrotron in Trieste. It became possible ...
2021-01-13
A remarkable prediction of Einstein's theory of general relativity--the theory that connects space, time, and gravity--is that rotating black holes have enormous amounts of energy available to be tapped.
For the last 50 years, scientists have tried to come up with methods to unleash this power. Nobel physicist Roger Penrose theorized that a particle disintegration could draw energy from a black hole; Stephen Hawking proposed that black holes could release energy through quantum mechanical emission; while Roger Blandford and Roman Znajek suggested electromagnetic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New molecular structures associated with ALS