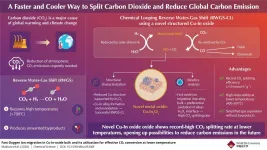
(Press-News.org) With ever-worsening climate change, there is a growing need for technologies that can capture and use up the atmospheric CO2 (carbon dioxide) and reduce our carbon footprint. Within the realm of renewable energy, CO2-based e-fuels have emerged as a promising technology that attempts to convert atmospheric CO2 into clean fuels. The process involves production of synthetic gas or syngas (a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide (CO)). With the help of the reverse water-gas shift (RWGS) reaction, CO2 is broken down into the CO necessary for syngas. While promising in its conversion efficiency, the RWGS reaction requires incredibly high temperatures (>700°C) to proceed, while also generating unwanted byproducts.
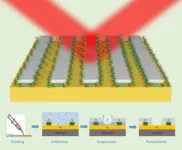
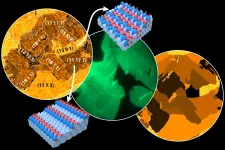
To tackle these problems, scientists developed a modified chemical-looping version of the RWGS reaction that converts CO2 to CO in a two-step method. First, a metal oxide, used as an oxygen storage material, is reduced by hydrogen. Subsequently, it is re-oxidized by CO2, yielding CO. This method is free of undesirable byproducts, makes gas separation simpler, and can be made feasible at lower temperatures depending on the oxide chosen. Consequently, scientists have been looking for oxide materials that exhibit high oxidation-reduction rates without requiring high temperatures.
In a recent END
Copper-indium oxide: A faster and cooler way to reduce our carbon footprint
Scientists set a record for the highest conversion rate of carbon dioxide at low temperatures with copper-modified indium oxide, signifying sustainable e-fuel
2021-01-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Lipid biomarkers in urine can determine the type of asthma
2021-01-13
In a new study, researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have used a urine test to identify and verify a patient's type of asthma. The study, which has been published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, lays the foundation for a more personalized diagnosis and may result in improved treatment of severe asthma in the future.
About 10 percent of the Swedish population suffers from asthma, a disease that has become increasingly widespread over the past 50 years, with annual global mortality of around 400,000 according to the World Health Organization. Asthma is characterized by chronic inflammation in the airways, which can result in symptoms including ...
New studies support blood test for early detection of Alzheimer's disease
2021-01-13
In three recent publications in Molecular Psychiatry, Brain and JAMA Neurology researchers from the University of Gothenburg provide convincing evidence that an in-house developed blood test for Alzheimer's disease can detect the disease early and track its course, which has major implications for a potential use in clinical practice and treatment trials.
"This is an extremely dynamic research field right now, thanks to the technological development and seminal scientific progress in the past years. The dream scenario is to have a blood test for the early detection and screening of Alzheimer's disease up and running. That would give significantly ...
Workaholism leads to mental and physical health problems
2021-01-13
Workaholism or work addiction risk is a growing public health concern that can lead to many negative mental and physical health outcomes such as depression, anxiety or sleep disorder. Perception of work (job demands and job control) may become a major cause of employees' work addiction. The international group of researchers including the HSE University scientist explored the link between work addiction risk and health-related outcomes using the framework of Job Demand Control Model. The results were published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
Workaholics are people who usually work seven and more hours more than ...
High-sensitivity nanophotonic sensors with passive trapping of analyte molecules in hot-spots
2021-01-13
Optical sensors can quantitatively analyze chemical and biological samples by measuring and processing the optical signals produced by the samples. Optical sensors based on infrared absorption spectroscopy can achieve high sensitivity and selectivity in real time, and therefore play a crucial role in a variety of application areas such as environmental sensing, medical diagnostics, industrial process control and homeland security.
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Applications, a team of scientists, led by Dr. Peter Q. Liu from the Department of Electrical Engineering, the State University of New York at Buffalo, have demonstrated a new type of high-performance optical sensor which can utilize ...
Catalysts: worth taking a closer look
2021-01-13
Metal surfaces play a role as catalysts for many important applications - from fuel cells to the purification of car exhaust gases. However, their behaviour is decisively affected by oxygen atoms incorporated into the surface.
This phenomenon has been known for a long time, but until now it has not been possible to precisely investigate the role of oxygen in complex surfaces point by point in order to understand the chemical background at the atomic level. This has now been achieved at TU Wien in cooperation with a team from the Elettra Synchrotron in Trieste. It became possible ...
Could we harness energy from black holes?
2021-01-13
A remarkable prediction of Einstein's theory of general relativity--the theory that connects space, time, and gravity--is that rotating black holes have enormous amounts of energy available to be tapped.
For the last 50 years, scientists have tried to come up with methods to unleash this power. Nobel physicist Roger Penrose theorized that a particle disintegration could draw energy from a black hole; Stephen Hawking proposed that black holes could release energy through quantum mechanical emission; while Roger Blandford and Roman Znajek suggested electromagnetic ...
UCI scientists measure local vibrational modes at individual crystalline faults
2021-01-13
Irvine, Calif., Jan. 11, 2021 - Often admired for their flawless appearance to the naked eye, crystals can have defects at the nanometer scale, and these imperfections may affect the thermal and heat transport properties of crystalline materials used in a variety of high-technology devices.
Employing newly developed electron microscopy techniques, researchers at the University of California, Irvine and other institutions have, for the first time, measured the spectra of phonons - quantum mechanical vibrations in a lattice - at individual crystalline faults, and they discovered the propagation of phonons near the flaws. The team's findings are the subject of a study published recently in Nature.
"Point defects, dislocations, stacking ...
UCI researchers use deep learning to identify gene regulation at single-cell level
2021-01-13
Irvine, Calif., Jan. 5, 2021 -- Scientists at the University of California, Irvine have developed a new deep-learning framework that predicts gene regulation at the single-cell level.
Deep learning, a family of machine-learning methods based on artificial neural networks, has revolutionized applications such as image interpretation, natural language processing and autonomous driving. In a study published recently in Science Advances, UCI researchers describe how the technique can also be successfully used to observe gene regulation at the cellular level. Until now, that process had ...
Research reveals how teeth functioned and evolved in giant mega-sharks
2021-01-13
A pioneering study by University of Bristol researchers finds that the evolution of teeth in the giant prehistoric shark Megalodon and its relatives was a by-product of becoming huge, rather than an adaptation to new feeding habits.
The iconic extinct Megalodon was the largest shark to ever roam the seas. Its name translates to 'big tooth', making reference to its massive teeth, which represent the most abundant fossil remains of the species. They are broad and triangular, nothing like the curved, blade-like teeth of the closest relatives of Megalodon.
The ...
Recurrent GBM brain tumors with few mutations respond best to immunotherapy
2021-01-13
DURHAM, N.C. - Glioblastoma brain tumors are especially perplexing. Inevitably lethal, the tumors occasionally respond to new immunotherapies after they've grown back, enabling up to 20% of patients to live well beyond predicted survival times.
What causes this effect has long been the pursuit of researchers hoping to harness immunotherapies to extend more lives.
New insights from a team led by Duke's Preston Robert Tisch Brain Tumor Center provide potential answers. The team found that recurring glioblastoma tumors with very few mutations are far more vulnerable ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Copper-indium oxide: A faster and cooler way to reduce our carbon footprintScientists set a record for the highest conversion rate of carbon dioxide at low temperatures with copper-modified indium oxide, signifying sustainable e-fuel