INFORMATION:
Giant 2D atlas of the universe helps dark energy spectroscopic survey
2021-01-14
(Press-News.org) The Beijing-Arizona Sky Survey (BASS) team of National Astronomical Observatories of Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC) and their collaborators of the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) project released a giant 2D map of the universe, which paves the way for the upcoming new-generation dark energy spectroscopic survey.
Modern astronomical observations reveal that the universe is expanding and appears to be accelerating. The power driving the expansion of the universe is called dark energy by astronomers. The dark energy is still a mystery and accounts for about 68% of the substance of the universe.
Large-scale redshift measurements of galaxies can describe the 3D distribution of the matter and reveal the effect of dark energy on the expansion of the universe.
The DESI project is a new-generation cosmological redshift survey. ZHAO Gongbo, Deputy Director-General of NAOC and a member of DESI, said "DESI will execute a five-year mission to obtain the redshifts of millions of galaxies and construct the largest 3D universe. It is expected to solve the mystery of dark energy."
"Before DESI begins, researchers need a larger and deeper 2D map of the universe to meet the targeting requirements of such large-scale spectroscopic observations," said ZOU Hu, one of the BASS co-PIs and an associate professor in NAOC.
Nearly 200 researchers from NAOC and DESI collaborators put much effort on the joint observing and data analyzing in the past six years. They stitch together the observed images and form a giant 2D map of the universe.
Nathalie Palanque-Delabrouille, DESI co-spokesperson and a cosmologist at the French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission (CEA), said "DESI wouldn't be getting anywhere without such large imaging surveys."
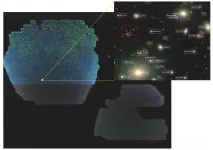
"This is the biggest map by almost any measure. The map covers half of the sky, and digitally sprawls over 10 trillion pixelsand contains about two billion objects," said David Schlegel, the co-project scientist for DESI and leader of the imaging project.
In the 2D map of the universe, the BASS contributes the northern sky. It is an international collaboration between NAOC and University of Arizona in the U.S. XUE Suijian from NAOC said "Chinese astronomers have joined in DESI as the builders due to the BASS contribution."
The DESI imaging team also released eight versions of data specially for the DESI targeting. This data release is the final release. It includes the largest imaging area and the most precise object measurements, according to CUI Chenzhou, the execute director of National Astronomical Data Center.
This release will ensure to implement the DESI project successfully. In addition, the data will become the legacy data for the astronomical community all around the world and play a valuable role on the scientific applications.
BASS was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program and External Cooperation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pillarene hybrid material shows enhanced tunable multicolor luminescence and sensing ability
2021-01-14
Organic luminescent materials have been highlighted as an exciting research topic owing to their prominent potentials in light-emitting diodes, fluorescent sensors, optoelectronic devices, in vivo imaging, anti-counterfeiting, data storage, and information encryption. However, applications of tunable fluorescent materials in the solid states have been largely hampered because these luminescent systems generally require time-consuming organic synthesis procedures and suffer from reduced photoluminescence (PL) owing to the notorious aggregation caused quenching. Aggregation-induced ...
Study the boundary between bulk, nano and molecule scale of gold plasmonic physics
2021-01-14
As an elementary type of collective excitation, plasmon has been found to dominate the optical properties of metals. The collective behavior of electrons in plasmons reflects the important difference between condensed matter and molecule-like ones. It is of great significance to study the evolution of plasmonic response and find out the boundary.
Controversy exists on such interesting questions as the division between the nanoparticle and molecules, and the physics of mesoscopic and microscopic plasmonic evolution. A unified understanding covering the small and large size limit, namely macro / meso / micro scales with sufficiently atomic precision is thus required. Clusters, as the transition from atomic molecules to condensed matter, are the ideal candidate for studying the evolution ...
Temperature scanners of limited value in detecting Covid-19
2021-01-14
Making people stand in front of a scanner to have their body temperature read can result in a large number of false negatives, allowing people with Covid-19 to pass through airports and hospitals undetected.
A new study argues that taking temperature readings of a person's fingertip and eye would give a significantly better and more reliable reading and help identify those with fever.
The study, co-led by human physiologist and an expert in temperature regulation, Professor Mike Tipton, is published in Experimental Physiology.
Professor Tipton, ...
Catalyticity of molybdenum-dinitrogen complexes in organic reactions
2021-01-14
Dinitrogen (N2) fixation is considered as one of the most essential tasks in basic science, providing straightforward methods to produce ammonia and nitrogen-containing molecules. Exploring the reactivity of N2 units of transition metal-nitrogen complexes is of great significance and challenging in the chemistry. Since the first Ru-N2 complex was prepared in 1965, important progress has been made in the synthesis and reactivity of transition metal nitrogen complexes. In many cases, terminal end-on M-N2 complexes as the most prevalent bonding mode were proved ...
Spectacular fossil discovery:
2021-01-14
In a new study, an international research team led by Sebastian Stumpf from the University of Vienna describes an exceptionally well-preserved skeleton of the ancient shark Asteracanthus. This extremely rare fossil find comes from the famous Solnhofen limestones in Bavaria, which was formed in a tropical-subtropical lagoon landscape during the Late Jurassic, about 150 million years ago. The almost complete skeleton shows that Asteracanthus was two-and-a-half meters long in life, which makes this ancient shark one of the largest of its time. The study is published in the journal Papers in Palaeontology.
Cartilaginous fishes, which include sharks and rays, are one of the most successful vertebrate groups still ...
Micro-climate moulds and reshapes northern insect communities, herbivory and predation
2021-01-14
Climate and changes in it have direct impacts on species of plant and animals - but climate may also shape more complex biological systems like food webs. Now a research group from the University of Helsinki has investigated how micro-climate shapes each level of the ecosystem, from species' abundances in predator communities to parasitism rates in key herbivores, and ultimately to damage suffered by plants. The results reveal how climate change may drastically reshape northern ecosystems.
Understanding the impact of climatic conditions on species interactions is imperative, as these interactions include such potent ecological forces as herbivory, pollination and parasitism.
Lead researcher Tuomas Kankaanpaa from the Faculty of Agriculture and Forestry, University of Helsinki, investigated ...
Giant map of the sky sets stage for ambitious DESI survey
2021-01-14
Astronomers using images from Kitt Peak National Observatory and Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory have created the largest ever map of the sky, comprising over a billion galaxies. The ninth and final data release from the ambitious DESI Legacy Imaging Surveys sets the stage for a ground-breaking 5-year survey with the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI), which aims to provide new insights into the nature of dark energy. The map was released today at the January 2021 meeting of the American Astronomical Society.
For millennia humans have used maps to understand and navigate our world and put ourselves in context: we rely on maps to show us where we are, where we came from, and where we're going. Astronomical maps continue this tradition on a vast scale. They ...
Penned release of green geckos has potential to help preserve threatened native species
2021-01-14
University of Otago researchers have added another piece to the puzzle about how best to translocate New Zealand lizards for conservation purposes - confine them.
In a paper just published in the New Zealand Journal of Ecology, the Department of Zoology researchers outlined how they translocated 19 barking geckos to Mana Island, using the method of penned release - enclosing them in a 100m² pen for three months so they get used to the site and hopefully establish a breeding population.
It was the first time such a method had been used with the species and the researchers found it worked well. The geckos' area use decreased over time, indicating ...
Researchers identify promising model for studying human aging
2021-01-14
There are many components to aging, both mental and physical. When it comes to the infrastructure of the human body - the musculoskeletal system that includes muscles, bones, tendons and cartilage - age-associated decline is inevitable, and the rate of that decline increases the older we get. The loss of muscle function -- and often muscle mass -- is scientifically known as sarcopenia or dynapenia.
For adults in their 40s, sarcopenia is hardly noticeable -- about 3% muscle mass is lost each decade. For those aged 65 years and older, however, muscle decline can become much more rapid, with an average loss of 1% muscle mass each year. More importantly, sarcopenia is also marked by a decrease ...
Eastern and central China become brighter due to clean air action
2021-01-14
Since 2013, China has implemented the strictest ever air pollution control policies, which resulted in substantial reductions in aerosol concentrations.
However, extreme and persistent haze events frequently occur during wintertime in China. In winter haze events, aerosol-related reductions of surface solar radiation (SSR) have comparable impacts on clouds over eastern provinces.
Recently, researchers from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics (IAP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory of the United States (PNNL) and their collaborators conducted a study to further understand the underlying chemical mechanisms driving winter haze events and how ...