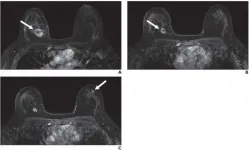
(Press-News.org) Leesburg, VA, January 14, 2021--According to ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), new suspicious findings occurred in 5.5% of breast MRI examinations performed to monitor response to neoadjuvant therapy; none of these new lesions were malignant.
"Our findings suggest that new lesions that arise in the setting of neoadjuvant therapy are highly unlikely to represent a new site of malignancy, particularly if the index malignancy shows treatment response," wrote Donna A. Eckstein and colleagues in the department of radiology and biomedical imaging at the University of California, San Francisco.
Based on a presentation at the ARRS 2019 Annual Meeting, Honolulu, HI, the researchers' retrospective review pinpointed all breast MRI examinations performed to assess response to neoadjuvant therapy between 2010 and 2018. Cases with new suspicious lesions assessed as BI-RADS 4 or 5 and found after the initiation of neoadjuvant treatment were included. Meanwhile, exclusion criteria were cases with no pretreatment MRI, cases in which the suspicious lesion was present on the baseline MRI but remained suspicious, and cases with insufficient follow-up. Pathologic examination determined malignant outcomes, whereas benignity was established by pathologic examination, follow-up imaging, or both.
A total of 419 breast MRI examinations in 297 women (mean patient age, 45 years; range, 32-65 years) were performed to assess response to neoadjuvant treatment. After exclusions, 23 MRI examinations (5.5%) with new suspicious findings distinct from the site of known malignancy comprised the final study cohort. Of these 23 lesions, 13 new suspicious findings (56.5%) were contralateral to the known malignancy, nine (39.1%) were ipsilateral, and one (4.3%) involved the bilateral breasts. Lesion types included mass (16, 69.6%), nonmass enhancement (5, 21.7%), and focus (2, 8.7%).
Noting that, currently, there are no guidelines for the management of new suspicious imaging findings identified on MRI during the course of neoadjuvant systemic breast cancer treatment, "results in this small cohort suggest that these new findings are highly likely to be benign, particularly in the setting of response to therapy, which may potentially obviate biopsies in these patients in the future," wrote Eckstein et al.
"However," the authors of this AJR article concluded, "larger studies across different facilities are needed to confirm whether biopsy may be safely averted in this scenario."
INFORMATION:
Press passes are now available for the ARRS 2021 All-Virtual Annual Meeting:
https://www.arrs.org/AM21
Founded in 1900, the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) is the first and oldest radiological society in North America, dedicated to the advancement of medicine through the profession of radiology and its allied sciences. An international forum for progress in medical imaging since the discovery of the x-ray, ARRS maintains its mission of improving health through a community committed to advancing knowledge and skills with an annual scientific meeting, monthly publication of the peer-reviewed American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), quarterly issues of InPractice magazine, AJR Live Webinars and Podcasts, topical symposia, print and online educational materials, as well as awarding scholarships via The Roentgen Fund®.
Scientists at the University of Tsukuba show that using a layer of graphene just one atom thick improves the catalytic activity of nickel or copper when generating hydrogen gas, which may lead to cheaper fuel for zero-emission automobiles
Tsukuba, Japan - A team of researchers led by the Institute of Applied Physics at the University of Tsukuba has demonstrated a method for producing acid-resistant catalysts by covering them with layers of graphene. They show that using few layers allows for greater proton penetration during a hydrogen evolution reaction, which is crucial for maximizing ...
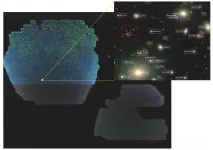
The Beijing-Arizona Sky Survey (BASS) team of National Astronomical Observatories of Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC) and their collaborators of the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) project released a giant 2D map of the universe, which paves the way for the upcoming new-generation dark energy spectroscopic survey.
Modern astronomical observations reveal that the universe is expanding and appears to be accelerating. The power driving the expansion of the universe is called dark energy by astronomers. The dark energy is still a mystery and accounts for about 68% of the substance ...
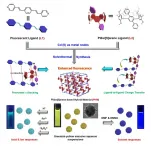
Organic luminescent materials have been highlighted as an exciting research topic owing to their prominent potentials in light-emitting diodes, fluorescent sensors, optoelectronic devices, in vivo imaging, anti-counterfeiting, data storage, and information encryption. However, applications of tunable fluorescent materials in the solid states have been largely hampered because these luminescent systems generally require time-consuming organic synthesis procedures and suffer from reduced photoluminescence (PL) owing to the notorious aggregation caused quenching. Aggregation-induced ...
As an elementary type of collective excitation, plasmon has been found to dominate the optical properties of metals. The collective behavior of electrons in plasmons reflects the important difference between condensed matter and molecule-like ones. It is of great significance to study the evolution of plasmonic response and find out the boundary.
Controversy exists on such interesting questions as the division between the nanoparticle and molecules, and the physics of mesoscopic and microscopic plasmonic evolution. A unified understanding covering the small and large size limit, namely macro / meso / micro scales with sufficiently atomic precision is thus required. Clusters, as the transition from atomic molecules to condensed matter, are the ideal candidate for studying the evolution ...
Making people stand in front of a scanner to have their body temperature read can result in a large number of false negatives, allowing people with Covid-19 to pass through airports and hospitals undetected.
A new study argues that taking temperature readings of a person's fingertip and eye would give a significantly better and more reliable reading and help identify those with fever.
The study, co-led by human physiologist and an expert in temperature regulation, Professor Mike Tipton, is published in Experimental Physiology.
Professor Tipton, ...
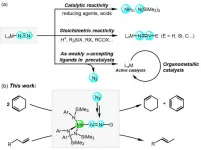
Dinitrogen (N2) fixation is considered as one of the most essential tasks in basic science, providing straightforward methods to produce ammonia and nitrogen-containing molecules. Exploring the reactivity of N2 units of transition metal-nitrogen complexes is of great significance and challenging in the chemistry. Since the first Ru-N2 complex was prepared in 1965, important progress has been made in the synthesis and reactivity of transition metal nitrogen complexes. In many cases, terminal end-on M-N2 complexes as the most prevalent bonding mode were proved ...
In a new study, an international research team led by Sebastian Stumpf from the University of Vienna describes an exceptionally well-preserved skeleton of the ancient shark Asteracanthus. This extremely rare fossil find comes from the famous Solnhofen limestones in Bavaria, which was formed in a tropical-subtropical lagoon landscape during the Late Jurassic, about 150 million years ago. The almost complete skeleton shows that Asteracanthus was two-and-a-half meters long in life, which makes this ancient shark one of the largest of its time. The study is published in the journal Papers in Palaeontology.
Cartilaginous fishes, which include sharks and rays, are one of the most successful vertebrate groups still ...
Climate and changes in it have direct impacts on species of plant and animals - but climate may also shape more complex biological systems like food webs. Now a research group from the University of Helsinki has investigated how micro-climate shapes each level of the ecosystem, from species' abundances in predator communities to parasitism rates in key herbivores, and ultimately to damage suffered by plants. The results reveal how climate change may drastically reshape northern ecosystems.
Understanding the impact of climatic conditions on species interactions is imperative, as these interactions include such potent ecological forces as herbivory, pollination and parasitism.
Lead researcher Tuomas Kankaanpaa from the Faculty of Agriculture and Forestry, University of Helsinki, investigated ...
Astronomers using images from Kitt Peak National Observatory and Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory have created the largest ever map of the sky, comprising over a billion galaxies. The ninth and final data release from the ambitious DESI Legacy Imaging Surveys sets the stage for a ground-breaking 5-year survey with the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI), which aims to provide new insights into the nature of dark energy. The map was released today at the January 2021 meeting of the American Astronomical Society.
For millennia humans have used maps to understand and navigate our world and put ourselves in context: we rely on maps to show us where we are, where we came from, and where we're going. Astronomical maps continue this tradition on a vast scale. They ...
University of Otago researchers have added another piece to the puzzle about how best to translocate New Zealand lizards for conservation purposes - confine them.
In a paper just published in the New Zealand Journal of Ecology, the Department of Zoology researchers outlined how they translocated 19 barking geckos to Mana Island, using the method of penned release - enclosing them in a 100m² pen for three months so they get used to the site and hopefully establish a breeding population.
It was the first time such a method had been used with the species and the researchers found it worked well. The geckos' area use decreased over time, indicating ...