Geologic history written in garnet sand
2021-01-14
(Press-News.org) On a beach on a remote island in eastern Papua New Guinea, a country located in the southwestern Pacific to the north of Australia, garnet sand reveals an important geologic discovery. Similar to messages in bottles that have traveled across the oceans, sediments derived from the erosion of rocks carry information from another time and place. In this case the grains of garnet sand reveal a story of traveling from the surface to deep into the Earth (~75 miles), and then returning to the surface before ending up on a beach as sand grains. Over the course of this geologic journey, the rock type changed as some minerals were changed, and other materials were included (trapped) within the newly formed garnets. The story is preserved in garnet compositions, as well as in their trapped inclusions: solids (e.g., very rare minerals such as coesite - a high pressure form of quartz), liquids (e.g., water) and gases (e.g., CO2).
Suzanne Baldwin, Thonis Family Professor in the Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences at Syracuse University's College of Arts and Sciences, has led many field expeditions to Papua New Guinea. Her team's latest results on this tectonically active region have just been published in the prestigious journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
By reading the rock record researchers revealed the recycling pathway from the surface to deep within the upper mantle and then back to the surface as a result of tectonic and sedimentary processes. The compositions of that sand also hold various key components that reveal how quickly this recycling happened. In this case, transit through the rock cycle happened in less than ~10 million years. This may seem like a long time, but for these geologic processes, it is actually remarkably short.
The garnet sands are just the latest piece of the puzzle to understand the geologic evolution of this region. It is the only location on Earth where active exhumation of high- and ultrahigh- pressure metamorphic rocks is occurring during the same rock cycle that produced these metamorphic rocks. The international group of researchers, including Joseph Gonzalez '19 Ph.D. from Syracuse University (now a European Research Council postdoctoral researcher at the University of Pavia, Italy), Ph.D. student Jan Schönig and Professor Hilmar von Eynatten from the University Göttingen in Germany, and Professor Hugh Davies (formerly from the University of Papua New Guinea, now at The Australian National University), revealed how the trapped inclusions in garnet sand can be used to determine rock recycling processes within active plate boundary zones.
At active plate boundaries, like the one the team studied in eastern Papua New Guinea, converging tectonic plates slide toward each other with one plate moving underneath the other to form a subduction zone. During this process, rocks are subducted deep into the Earth. Over time, forces on the plate boundaries may change and rocks can be exhumed to the surface through a process known as lithospheric deformation. The trapped inclusions preserve a record of crustal subduction and rapid exhumation linking upper mantle and surface processes on these short geologic timescales. By applying their approach to both modern sediments and sedimentary rocks, researchers can now reveal the tempo of rock recycling processes throughout Earth's history.
INFORMATION:
This study was funded by the Syracuse University Thonis endowment, grants from NSF Division of Earth Sciences, NSF Major Research Instrumentation Grant and a German Research Foundation Grant.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-14
An antibacterial peptide that turns on and off
The researchers solved the 3D molecular structure of an antibacterial peptide named uperin 3.5, which is secreted on the skin of the Australian toadlet (Uperoleia mjobergii) as part of its immune system. They found that the peptide self-assembles into a unique fibrous structure, which via a sophisticated structural adaptation mechanism can change its form in the presence of bacteria to protect the toadlet from infections. This provides unique atomic-level evidence explaining a regulation mechanism of an antimicrobial ...
2021-01-14
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. -- It's not just to hide clutter anymore - add "saving the planet" to the reasons you leave the camera off during your next virtual meeting.
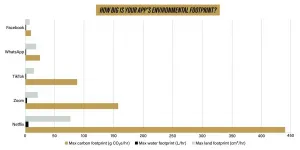
A new study says that despite a record drop in global carbon emissions in 2020, a pandemic-driven shift to remote work and more at-home entertainment still presents significant environmental impact due to how internet data is stored and transferred around the world.
Just one hour of videoconferencing or streaming, for example, emits 150-1,000 grams of carbon dioxide (a gallon of gasoline burned from a car emits about 8,887 grams), requires 2-12 liters of water and demands a land area adding up to about the size of an iPad Mini.
But leaving your camera off during a web call can ...
2021-01-14
January 14, 2021 - Orthopaedic surgeons have traditionally been taught that certain types of knee symptoms indicate damage to specialized structures called the menisci. But these "meniscal" and "mechanical" symptoms do not reflect what surgeons will find at knee arthroscopy, reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio in partnership with Wolters Kluwer.
Both types of symptoms are strongly related to the overall amount of cartilage damage in the knee joint - but not to the presence of meniscal tears, according to the new research ...
2021-01-14
In today's economy, American businesses often tap into professional management to grow, but most firms in India and other developing countries are family owned and often shun outside managers. A new study co-authored by Yale economist Michael Peters explores the effects that the absence of outside professional management has on India's businesses and the country's economy.
The study, published in the American Economic Review, uses a novel model to compare the relationship between the efficiency of outside managers and firm growth in the United States and India. It shows ...
2021-01-14
Genome analysis can provide information on genes and their location on a strand of DNA, but such analysis reveals little about their spatial location in relation to one another within chromosomes -- the highly complex, three-dimensional structures that hold genetic information.
Chromosomes resemble a fuzzy "X" in microscopy images and can carry thousands of genes. They are formed when DNA winds around proteins -- called histones -- which are further folded into complexes called chromatin, which make up individual chromosomes.
Knowing which genes are located in spatial proximity within the chromatin is important because genes that are near each other generally work together.
Now, researchers at the END ...
2021-01-14
Computational materials science experts at the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory enhanced an algorithm that borrows its approach from the nesting habits of cuckoo birds, reducing the search time for new high-tech alloys from weeks to mere seconds.
The scientists are investigating a type of alloys called high-entropy alloys, a novel class of materials that are highly sought after for a host of unusual and potentially beneficial properties. They are lightweight in relation to their strength, fracture-resistant, highly corrosion and oxidation resistant, and stand up well in high-temperature and high-pressure environments -- making them attractive materials for aerospace industry, space exploration, nuclear energy, and defense applications.
While the promise of these ...
2021-01-14
Researchers from the PTSD Systems Biology Consortium, led by scientists from the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research, have identified distinct biotypes for post-traumatic stress disorder, the first of their kind for any psychological disorder. "These biotypes can refine the development of screening tools and may explain the varying efficacy of PTSD treatments", said Dr. Marti Jett, leader of the consortium and WRAIR chief scientist.
Publishing their work in Molecular Psychiatry in a manuscript first authored by WRAIR's Dr. Ruoting Yang, researchers used blood tests from male, combat-exposed veterans across a three year period to identify two PTSD biotypes, G1--characterized ...
2021-01-14
TROY, N.Y. -- As cancer and tumor cells move inside the human body, they impart and are subject to mechanical forces. In order to understand how these actions affect cancer cell growth, spread, and invasion, a team of engineers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute is developing new models that mimic aspects of the mechanical environment within the body, providing new insight into how and why tumors develop in certain ways.
In research published today in Integrative Biology, a team of engineers from Rensselaer developed an in vitro -- in the lab -- lymphatic vessel model to study the growth of tumor emboli, collections of ...
2021-01-14
Superconductivity already has a variety of practical applications, such as medical imaging and levitating transportation like the ever-popular maglev systems. However, to ensure that the benefits of applied superconductors keep spreading further into other technological fields, we need to find ways of not only improving their performance, but also making them more accessible and simpler to fabricate.
In this regard, magnesium diboride (MgB2) has attracted the attention of researchers since its discovery as a superconductor with multiple advantages. It is a lightweight, easily processible material made from widely abundant ...
2021-01-14
MEDFORD/SOMERVILLE, Mass. (Jan. 14, 2021)-- Exposure to discrimination plays a significant role in the risk of developing anxiety and related disorders, even - in a first - after accounting for potential genetic risks, according to a multidisciplinary team of health researchers led by Tufts University and the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
Researchers determined that even after controlling for genetic risk for anxiety, depression, and neuroticism, greater reports of discrimination experiences remained associated with higher scores of anxiety and related disorders. The findings, recently ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Geologic history written in garnet sand