(Press-News.org) Researchers at the UC Davis Violence Prevention Research Program (VPRP) assessed the prevalence of exposure to violence, such as robbery or assault, and its impacts on the mental health and social functioning of California adults. Their study, published in the Journal of Interpersonal Violence, shows the far-reaching psychological effects an incident of gun violence can have on victims and those close to them.
The study's findings are based on data from 2,558 adults who responded to the 2018 California Safety and Wellbeing Survey (CSaWS). CSaWS is an ongoing survey research project on firearm ownership and the consequences of exposure to violence in California. Responses were weighted to be statistically representative of the state's adult population.
These findings come as many localities across the country, including in California, have experienced a historic increase in firearm acquisition and gun-related deaths and injuries over the past year.
"Our study highlights the pervasive socioemotional impacts of violence exposure," said Amanda Aubel, first author on the study and a research data analyst at VPRP. "It points to the urgent need to address not only the physical but also the psychological consequences of violence exposure and the unique, exacerbating influence of firearms."
Prevalence and impact of exposure to violence
According to the study, around 4% of respondents--an estimated 1.2 million California adults--said they or a household member had experienced violence while living in their current neighborhood. Half of these respondents stated that the most recent incident of violence had happened to them directly. Violent events included robbery, physical assault and rape or sexual assault.
The study also found that half of the people exposed to violence reported that the event was "severely" distressing. For 47% of exposed respondents, the event led them to experience significant problems with family members or friends, with their job or schoolwork, or both. For comparison, only 12% of unexposed adults reported having such social functioning problems in the past 12 months.
Weapon involvement in violent events
More than one-third of exposed respondents indicated that a weapon or something that could be used as a weapon was present during the violent event. In 40% of these cases, the weapon was a firearm.
The study explored whether firearm involvement was associated with socioemotional consequences.
"Violence involving firearms may be particularly detrimental for mental health and social functioning," Aubel said. "The mere presence of a firearm during an act of violence can increase the perceived level of threat to one's life."
While the presence of a weapon was not associated with distress levels, when a weapon was present, events considered severely distressing were significantly more likely to involve firearms and less likely to involve other types of weapons. This is consistent with prior studies that have found violence involving firearms has unique negative effects on mental health compared to violence involving other or no weapons.
Exposure to violence and gun ownership
The study is one of few to examine exposure to violence among gun owners and gun purchasing intentions following such exposure.
Compared to unexposed individuals, respondents with exposure to violence were significantly more likely to live in households with guns but not to own guns themselves. The authors note that this finding warrants further investigation, given substantial evidence that household firearm ownership is associated with an elevated risk of firearm death and injury for everyone living in the home.
One-third of exposed respondents said the violent event led them to consider buying a gun. Of that group, only 1% reported personally owning guns at the time of the survey. For comparison, 17% of unexposed respondents considered buying a gun in the past 12 months; 35% were gun owners already.
These findings suggest that experiencing violence may motivate people to buy a firearm who would not have considered doing so otherwise. Yet, these new gun owners could be increasing their risk of harm by bringing a firearm into their home.
"State-level data such as these may be important for designing effective violence prevention programs and policies," said Nicole Kravitz-Wirtz, assistant professor with VPRP and senior author on the study. "Interventions must include trauma-informed services and sustained financial investments in the communities most highly impacted by firearm violence."
INFORMATION:
Article: Aubel, Pallin, Wintemute & Kravitz-Wirtz. (2020) "Exposure to Violence, Firearm Involvement, and Socioemotional Consequences Among California Adults," Journal of Interpersonal Violence, DOI: 10.1177/0886260520983924.
Primer on Carbon Dioxide Removal Provides Vital Resource at Critical Time
--By Julie Chao
Scientists say that any serious plan to address climate change should include carbon dioxide removal (CDR) technologies and policies, which makes the newly launched CDR Primer an especially vital resource, says Berkeley Lab scientist Margaret Torn, one of about three dozen scientists who contributed to this document.
"Atmospheric CO2 concentrations are already 50% over historic natural levels - 270 ppm (parts per million) in pre-industrial times vs 414 ppm today," said Torn. "To slow climate change and avoid its worst impacts, climate scientists tell ...
MADISON, Wis. -- As a new, apparently more transmissible version of the virus that causes COVID-19 has appeared in several countries, new research finds that the transmissibility of viral strains and the population density of a region will play big roles in how vaccination campaigns can help towns and cities return to more normal activities.
The findings suggest that directing vaccines toward densely populated counties would help to interrupt transmission of the disease. Current vaccination distribution plans don't take density into account.
Tony Ives at the University of Wisconsin-Madison and Claudio Bozzuto of the independent data research company Wildlife ...
Researchers from the University of Cambridge, the University of Milan and Google Research have used machine learning techniques to predict how proteins, particularly those implicated in neurological diseases, completely change their shapes in a matter of microseconds.
They found that when amyloid beta, a key protein implicated in Alzheimer's disease, adopts a highly disordered shape, it actually becomes less likely to stick together and form the toxic clusters which lead to the death of brain cells.
The results, reported in the journal Nature Computational Science, could aid in the future development of treatments ...
Decades after the industrialized world largely eliminated lead poisoning in children, the potent neurotoxin still lurks in one in three children globally. A new study in Bangladesh by researchers at Stanford University and other institutions finds that a relatively affordable remediation process can almost entirely remove lead left behind by unregulated battery recycling - an industry responsible for much of the lead soil contamination in poor and middle-income countries - and raises troubling questions about how to effectively eliminate the poison from children's bodies.
"Once the lead is in the environment, it stays there pretty much indefinitely ...
A new University of Saskatchewan (USask) study has found that stretching is superior to brisk walking for reducing blood pressure in people with high blood pressure or who are at risk of developing elevated blood pressure levels.
Walking has long been the prescription of choice for physicians trying to help their patients bring down their blood pressure. High blood pressure (hypertension) is a leading risk factor for cardiovascular disease and among the top preventable risk factors affecting overall mortality.
This new finding, published December 18, 2020 in the Journal of Physical Activity ...
On a beach on a remote island in eastern Papua New Guinea, a country located in the southwestern Pacific to the north of Australia, garnet sand reveals an important geologic discovery. Similar to messages in bottles that have traveled across the oceans, sediments derived from the erosion of rocks carry information from another time and place. In this case the grains of garnet sand reveal a story of traveling from the surface to deep into the Earth (~75 miles), and then returning to the surface before ending up on a beach as sand grains. Over the course of this geologic journey, the rock type changed as some minerals were changed, and other materials were included (trapped) within the newly formed garnets. The story is preserved ...
An antibacterial peptide that turns on and off
The researchers solved the 3D molecular structure of an antibacterial peptide named uperin 3.5, which is secreted on the skin of the Australian toadlet (Uperoleia mjobergii) as part of its immune system. They found that the peptide self-assembles into a unique fibrous structure, which via a sophisticated structural adaptation mechanism can change its form in the presence of bacteria to protect the toadlet from infections. This provides unique atomic-level evidence explaining a regulation mechanism of an antimicrobial ...
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. -- It's not just to hide clutter anymore - add "saving the planet" to the reasons you leave the camera off during your next virtual meeting.
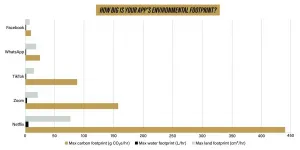
A new study says that despite a record drop in global carbon emissions in 2020, a pandemic-driven shift to remote work and more at-home entertainment still presents significant environmental impact due to how internet data is stored and transferred around the world.
Just one hour of videoconferencing or streaming, for example, emits 150-1,000 grams of carbon dioxide (a gallon of gasoline burned from a car emits about 8,887 grams), requires 2-12 liters of water and demands a land area adding up to about the size of an iPad Mini.
But leaving your camera off during a web call can ...
January 14, 2021 - Orthopaedic surgeons have traditionally been taught that certain types of knee symptoms indicate damage to specialized structures called the menisci. But these "meniscal" and "mechanical" symptoms do not reflect what surgeons will find at knee arthroscopy, reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio in partnership with Wolters Kluwer.
Both types of symptoms are strongly related to the overall amount of cartilage damage in the knee joint - but not to the presence of meniscal tears, according to the new research ...
In today's economy, American businesses often tap into professional management to grow, but most firms in India and other developing countries are family owned and often shun outside managers. A new study co-authored by Yale economist Michael Peters explores the effects that the absence of outside professional management has on India's businesses and the country's economy.
The study, published in the American Economic Review, uses a novel model to compare the relationship between the efficiency of outside managers and firm growth in the United States and India. It shows ...