(Press-News.org) Researchers from the University of Cambridge, the University of Milan and Google Research have used machine learning techniques to predict how proteins, particularly those implicated in neurological diseases, completely change their shapes in a matter of microseconds.
They found that when amyloid beta, a key protein implicated in Alzheimer's disease, adopts a highly disordered shape, it actually becomes less likely to stick together and form the toxic clusters which lead to the death of brain cells.
The results, reported in the journal Nature Computational Science, could aid in the future development of treatments for diseases involving disordered proteins, such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.
"We are used to thinking of proteins as molecules that fold into well-defined structures: finding out how this process happens has been a major research focus over the last 50 years," said Professor Michele Vendruscolo from Cambridge's Centre for Misfolding Diseases, who led the research. "However, about a third of the proteins in our body do not fold, and instead remain in disordered shapes, sort of like noodles in a soup."
We do not know much about the behaviour of these disordered proteins, since traditional methods tend to address the problem of determining static structures, not structures in motion. The approach developed by the researchers harnesses the power of Google's computer network to generate large numbers of short trajectories. The most common motions show up multiple times in these 'movies', making it possible to define the frequencies by which disordered proteins jumps between different shapes.
"By counting these motions, we can predict which states the protein occupies and how quickly it transitions between them," said first author Thomas Löhr from Cambridge's Yusuf Hamied Department of Chemistry.
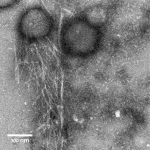
The researchers focused their attention on the amyloid beta peptide, a protein fragment associated with Alzheimer's disease, which aggregates to form amyloid plaques in the brains of affected individuals. They found that amyloid beta hops between widely different states millions of times per second without ever stopping in any particular state. This is the hallmark of disorder, and the main reason for which amyloid beta has been deemed 'undruggable' so far.
"The constant motion of amyloid beta is one of the reasons it's been so difficult to target - it's almost like trying to catch smoke in your hands," said Vendruscolo.
However, by studying a variant of amyloid beta, in which one of the amino acids is modified by oxidation, the researchers obtained a glimpse on how to make it resistant to aggregation. They found that oxidated amyloid beta changes shape even faster than its unmodified counterpart, providing a rationale to explain the decreased tendency for aggregation of the oxidated version.
"From a chemical perspective, this modification is a minor change. But the effect on the states and transitions between them is drastic," said Löhr.
"By making disordered proteins even more disordered, we can prevent them from self-associating in aberrant manners," said Vendruscolo.
The approach provides a powerful tool to investigate a class of proteins with fast and disordered motions, which have remained elusive so far despite their importance in biology and medicine.
INFORMATION:
Decades after the industrialized world largely eliminated lead poisoning in children, the potent neurotoxin still lurks in one in three children globally. A new study in Bangladesh by researchers at Stanford University and other institutions finds that a relatively affordable remediation process can almost entirely remove lead left behind by unregulated battery recycling - an industry responsible for much of the lead soil contamination in poor and middle-income countries - and raises troubling questions about how to effectively eliminate the poison from children's bodies.
"Once the lead is in the environment, it stays there pretty much indefinitely ...
A new University of Saskatchewan (USask) study has found that stretching is superior to brisk walking for reducing blood pressure in people with high blood pressure or who are at risk of developing elevated blood pressure levels.
Walking has long been the prescription of choice for physicians trying to help their patients bring down their blood pressure. High blood pressure (hypertension) is a leading risk factor for cardiovascular disease and among the top preventable risk factors affecting overall mortality.
This new finding, published December 18, 2020 in the Journal of Physical Activity ...
On a beach on a remote island in eastern Papua New Guinea, a country located in the southwestern Pacific to the north of Australia, garnet sand reveals an important geologic discovery. Similar to messages in bottles that have traveled across the oceans, sediments derived from the erosion of rocks carry information from another time and place. In this case the grains of garnet sand reveal a story of traveling from the surface to deep into the Earth (~75 miles), and then returning to the surface before ending up on a beach as sand grains. Over the course of this geologic journey, the rock type changed as some minerals were changed, and other materials were included (trapped) within the newly formed garnets. The story is preserved ...
An antibacterial peptide that turns on and off
The researchers solved the 3D molecular structure of an antibacterial peptide named uperin 3.5, which is secreted on the skin of the Australian toadlet (Uperoleia mjobergii) as part of its immune system. They found that the peptide self-assembles into a unique fibrous structure, which via a sophisticated structural adaptation mechanism can change its form in the presence of bacteria to protect the toadlet from infections. This provides unique atomic-level evidence explaining a regulation mechanism of an antimicrobial ...
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. -- It's not just to hide clutter anymore - add "saving the planet" to the reasons you leave the camera off during your next virtual meeting.
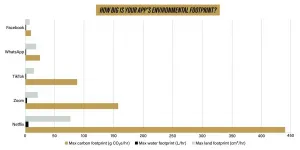
A new study says that despite a record drop in global carbon emissions in 2020, a pandemic-driven shift to remote work and more at-home entertainment still presents significant environmental impact due to how internet data is stored and transferred around the world.
Just one hour of videoconferencing or streaming, for example, emits 150-1,000 grams of carbon dioxide (a gallon of gasoline burned from a car emits about 8,887 grams), requires 2-12 liters of water and demands a land area adding up to about the size of an iPad Mini.
But leaving your camera off during a web call can ...
January 14, 2021 - Orthopaedic surgeons have traditionally been taught that certain types of knee symptoms indicate damage to specialized structures called the menisci. But these "meniscal" and "mechanical" symptoms do not reflect what surgeons will find at knee arthroscopy, reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio in partnership with Wolters Kluwer.
Both types of symptoms are strongly related to the overall amount of cartilage damage in the knee joint - but not to the presence of meniscal tears, according to the new research ...
In today's economy, American businesses often tap into professional management to grow, but most firms in India and other developing countries are family owned and often shun outside managers. A new study co-authored by Yale economist Michael Peters explores the effects that the absence of outside professional management has on India's businesses and the country's economy.
The study, published in the American Economic Review, uses a novel model to compare the relationship between the efficiency of outside managers and firm growth in the United States and India. It shows ...
Genome analysis can provide information on genes and their location on a strand of DNA, but such analysis reveals little about their spatial location in relation to one another within chromosomes -- the highly complex, three-dimensional structures that hold genetic information.
Chromosomes resemble a fuzzy "X" in microscopy images and can carry thousands of genes. They are formed when DNA winds around proteins -- called histones -- which are further folded into complexes called chromatin, which make up individual chromosomes.
Knowing which genes are located in spatial proximity within the chromatin is important because genes that are near each other generally work together.
Now, researchers at the END ...
Computational materials science experts at the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory enhanced an algorithm that borrows its approach from the nesting habits of cuckoo birds, reducing the search time for new high-tech alloys from weeks to mere seconds.
The scientists are investigating a type of alloys called high-entropy alloys, a novel class of materials that are highly sought after for a host of unusual and potentially beneficial properties. They are lightweight in relation to their strength, fracture-resistant, highly corrosion and oxidation resistant, and stand up well in high-temperature and high-pressure environments -- making them attractive materials for aerospace industry, space exploration, nuclear energy, and defense applications.
While the promise of these ...
Researchers from the PTSD Systems Biology Consortium, led by scientists from the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research, have identified distinct biotypes for post-traumatic stress disorder, the first of their kind for any psychological disorder. "These biotypes can refine the development of screening tools and may explain the varying efficacy of PTSD treatments", said Dr. Marti Jett, leader of the consortium and WRAIR chief scientist.
Publishing their work in Molecular Psychiatry in a manuscript first authored by WRAIR's Dr. Ruoting Yang, researchers used blood tests from male, combat-exposed veterans across a three year period to identify two PTSD biotypes, G1--characterized ...