(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, January 19, 2021 - Early life experiences can have an outsized effect on brain development and neurobiological health. New research is showing that those effects can be passed down to subsequent generations, reporting that the infant children of mothers who had experienced childhood emotional neglect displayed altered brain circuitry involved in fear responses and anxiety.
The study appears in Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, published by Elsevier.
"These results show that our brain development is not only shaped by what happens in our own life, but is also impacted by things that happened to our parents before we were even conceived," said lead author of the study, Cassandra Hendrix, PhD, Department of Pyschology, Emory University, Atlanta, GA, USA.
Dr. Hendrix and her colleagues studied 48 Black mother-infant pairs starting in the first trimester of pregnancy. Mothers were given a questionnaire to assess childhood trauma (experiences of early abuse or neglect). The mothers were also evaluated for current, prenatal stress levels, and for anxiety and depression. One month after birth, infants underwent a brain scan using resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging, a non-invasive technology that could be used while the babies slept naturally.
"These remarkable results leverage our ability to image the brain and its functioning very early in life," said Cameron Carter, MD, Editor of Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging.
The researchers focused on brain connections between the amygdala, which is central to processing fearful emotions, and two other brain regions: the prefrontal cortex and the anterior cingulate cortex. Both areas play a key role in regulating emotions. Babies whose mothers experienced childhood emotional neglect had stronger functional connections between the amygdala and the cortical regions.
After controlling for mothers' current stress levels, the researchers found that the more emotional neglect a mother had experienced during her own childhood, the more strongly her baby's amygdala was connected to the frontal cortical regions. Physical abuse or neglect of the mother were not correlated with the stronger connectivity. The findings suggest that childhood emotional neglect has intergenerational effects on brain structure and function.
The significance of the stronger connection remains unclear, said Dr. Hendrix. "The neural signature we observed in the 1-month-old infants of emotionally neglected mothers may be a mechanism that leads to increased risk for anxiety, or it could be a compensatory mechanism that promotes resilience in case the infant has less supportive caregivers. In either case, emotional neglect from a mother's own childhood seems to leave behind a neural signature in her baby that may predispose the infant to more readily detect threat in the environment almost from birth. Our findings highlight the importance of emotional support early in life, even for subsequent generations."
"The findings add to evidence of the intergenerational consequences of early life adversity, such as maternal neglect," added Dr. Carter. "Future studies that follow children longitudinally will help us understand the functional significance of these changes in brain function in terms of the emotional and social development of children of mothers who experienced early neglect."
INFORMATION:
Notes for editors
The article is "Maternal childhood adversity associates with frontoamygdala connectivity in neonates," by Cassandra Hendrix, Daniel Dilks, Brooke McKenna, Anne Dunlop, Elizabeth Corwin, and Patricia Brennan (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpsc.2020.11.003). It appears as an Article in Press in Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, published by Elsevier.
Copies of this paper are available to credentialed journalists upon request; please contact Rhiannon Bugno at BPCNNI@sobp.org or +1 254 522 9700. Journalists wishing to interview the authors may contact Cassandra Hendrix at cassandra.hendrix@nyulangone.org or +1 704 490 9445.
The authors' affiliations and disclosures of financial and conflicts of interests are available in the article.
Cameron S. Carter, MD, is Professor of Psychiatry and Psychology and Director of the Center for Neuroscience at the University of California, Davis. His disclosures of financial and conflicts of interests are available here.
About Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging
Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging is an official journal of the Society of Biological Psychiatry, whose purpose is to promote excellence in scientific research and education in fields that investigate the nature, causes, mechanisms and treatments of disorders of thought, emotion, or behavior. In accord with this mission, this peer-reviewed, rapid-publication, international journal focuses on studies using the tools and constructs of cognitive neuroscience, including the full range of non-invasive neuroimaging and human extra- and intracranial physiological recording methodologies. It publishes both basic and clinical studies, including those that incorporate genetic data, pharmacological challenges, and computational modeling approaches. The 2019 Impact Factor score for Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging is 5.335.
http://www.sobp.org/bpcnni
About Elsevier
As a global leader in information and analytics, Elsevier helps researchers and healthcare professionals advance science and improve health outcomes for the benefit of society. We do this by facilitating insights and critical decision-making for customers across the global research and health ecosystems.
In everything we publish, we uphold the highest standards of quality and integrity. We bring that same rigor to our information analytics solutions for researchers, health professionals, institutions and funders.
Elsevier employs 8,100 people worldwide. We have supported the work of our research and health partners for more than 140 years. Growing from our roots in publishing, we offer knowledge and valuable analytics that help our users make breakthroughs and drive societal progress. Digital solutions such as ScienceDirect, Scopus, SciVal, ClinicalKey and Sherpath support strategic research management, R&D performance, clinical decision support, and health education. Researchers and healthcare professionals rely on our 2,500+ digitized journals, including The Lancet and Cell, our 40,000 eBook titles; and our iconic reference works, such as Gray's Anatomy. With the Elsevier Foundation and our external Inclusion & Diversity Advisory Board, we work in partnership with diverse stakeholders to advance inclusion and diversity in science, research and healthcare in developing countries and around the world.
Elsevier is part of RELX, a global provider of information-based analytics and decision tools for professional and business customers. http://www.elsevier.com
Media contact
Rhiannon Bugno, Editorial Office
Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging
+1 254 522 9700
BPCNNI@sobp.org
LA JOLLA, CALIF. - Jan 20, 2020 - Scientists have identified two drugs that are potent against acute myeloid leukemia (AML) when combined, but only weakly effective when used alone. The researchers were able to significantly enhance cancer cell death by jointly administering the drugs that are only partially effective when used as single-agent therapies. The study, a collaboration between Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute and the University of Glasgow, was recently published in the journal Nature Communications.
"Our study shows that two types of drugs, MDM2 inhibitors and BET inhibitors, work synergistically to promote significant anti-leukemia activity," says Peter Adams, Ph.D., a professor at Sanford Burnham Prebys and senior author of the study. "The results ...
New research has demonstrated that a simple, cheap test can help identify who is at risk of developing colorectal cancer, aiding early diagnosis and potentially saving lives.
Led by the University of Exeter, and supported by the Peninsula and the Somerset, Wiltshire, Avon, and Gloucestershire Cancer Alliances, and by the Cancer Research UK CanTest Collaborative, a new study published today in the British Journal of Cancer examined data from nearly 4,000 patients aged 50 and over. The study involved all healthcare providers in the South West of England taking a new approach. ...
Successive governments' approach to obesity policies has destined them to fail, say researchers.
Government obesity policies in England over the past three decades have largely failed because of problems with implementation, lack of learning from past successes or failures, and a reliance on trying to persuade individuals to change their behaviour rather than tackling unhealthy environments. This is the conclusion of new research by a team at the University of Cambridge funded by the NIHR School for Public Health Research.
The researchers say their findings may help to explain why, after nearly thirty years of government obesity policies, obesity prevalence in England has not fallen and substantial inequalities persist. According to a report by NHS Digital in May 2020, ...
Young Seychelles warblers fare better if their elderly parents have help raising them, according to new research from the University of East Anglia (UEA) and the University of Groningen.
Seychelles warblers, a cooperatively breeding species of songbird that lives in small family groups, share the care of young between parents and helpers. This collaboration can compensate for a decline in the ability of elderly parents to provide sufficient care, the researchers found. It may also promote more social behaviour in family groups with older parents.
The findings help explain why social species, such as humans, often do better if they live in groups and cooperate to raise offspring.
The ...
Fried-food intake is linked to a heightened risk of major heart disease and stroke, finds a pooled analysis of the available research data, published online in the journal Heart.
And the risk rises with each additional 114 g weekly serving, the analysis indicates.
It's clear that the Western diet doesn't promote good cardiovascular health, but it's not clear exactly what contribution fried food might make to the risks of serious heart disease and stroke, say the researchers.
To shed some light on this, they trawled research databases, looking for relevant studies published up to April 2020, and found 19.
They pooled the data from 17, involving 562,445 participants ...
We should err on the side of caution and stop the global roll out of 5G (fifth generation) telecoms networks until we are certain this technology is completely safe, urges an expert in an opinion piece published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
There are no health concerns about 5G and COVID-19, despite what conspiracy theorists have suggested.
But the transmitter density required for 5G means that more people will be exposed to radio frequency electromagnetic fields (RF-EMFs), and at levels that emerging evidence suggests, are potentially harmful to health, argues Professor John William Frank, Usher Institute, University of Edinburgh.
The ...
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
1. Primary care physicians account for a minority of spending on low-value care
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M20-6257
URL goes live ...
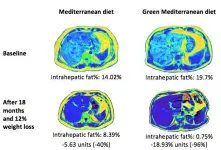
BEER-SHEVA, Israel...January 18, 2021 - A green Mediterranean (MED) diet reduces intrahepatic fat more than other healthy diets and cuts non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in half, according to a long-term clinical intervention trial led by Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers and a team of international colleagues.
The findings were published in Gut, a leading international journal focused on gastroenterology and hepatology.
"Our research team and other groups over the past 20 years have proven through rigorous randomized long-term trials that the Mediterranean diet is the healthiest," says lead researcher Prof. Iris Shai, an epidemiologist in the BGU ...
More people could be protected from life-threatening rabies thanks to an agile approach to dog vaccination using smart phone technology to spot areas of low vaccination coverage in real time.
Vets used a smart phone app to help them halve the time it takes to complete dog vaccination programmes in the Malawian city of Blantyre.
The custom-made app lets them quickly spot areas with low inoculation rates in real time, allowing them to jab more dogs more quickly, and with fewer staff.
Rabies is a potentially fatal disease passed on to humans primarily through dog bites. It is responsible for some 60,000 deaths worldwide each year, 40 per cent of which are children. It places a huge financial burden on some of the world's poorest countries.
Researchers predict that more than one million ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Click beetles can propel themselves more than 20 body lengths into the air, and they do so without using their legs. While the jump's motion has been studied in depth, the physical mechanisms that enable the beetles' signature clicking maneuver have not. A new study examines the forces behind this super-fast energy release and provides guidelines for studying extreme motion, energy storage and energy release in other small animals like trap-jaw ants and mantis shrimps.
The multidisciplinary study, led by University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign mechanical science and ...