(Press-News.org) Fried-food intake is linked to a heightened risk of major heart disease and stroke, finds a pooled analysis of the available research data, published online in the journal Heart.
And the risk rises with each additional 114 g weekly serving, the analysis indicates.
It's clear that the Western diet doesn't promote good cardiovascular health, but it's not clear exactly what contribution fried food might make to the risks of serious heart disease and stroke, say the researchers.
To shed some light on this, they trawled research databases, looking for relevant studies published up to April 2020, and found 19.
They pooled the data from 17, involving 562,445 participants and 36,727 major cardiovascular 'events', such as a heart attack or stroke, to assess cardiovascular disease risk.
And they pooled the data from six, involving 754,873 participants and 85,906 deaths over an average monitoring period of 9.5 years, to assess the potential link between fried food consumption and deaths from cardiovascular disease and from any cause.
Their analysis showed that compared with the lowest category of weekly fried food consumption, the highest was associated with a 28% heightened risk of major cardiovascular events; a 22% heightened risk of coronary heart disease; and a 37% heightened risk of heart failure.
These associations held true when stratified by various study and participant characteristics. What's more, a linear association emerged between fried food consumption and major cardiovascular events, coronary heart disease, and heart failure.
These risks substantially increased by 3%, 2%, and 12%, respectively, in tandem with each additional 114 g weekly serving.
Several studies included only one type of fried food, such as fried fish, potatoes, or snacks, rather than total fried food intake, which may have underestimated the associations found, suggest the researchers.
No associations were found for deaths from cardiovascular disease or from any cause, but this might be because of the relatively small numbers involved, say the researchers.
The design of the included studies varied considerably, added to which, they all relied on memory--factors that should be taken into consideration when interpreting the results, caution the researchers.
And how exactly fried foods might influence the development of cardiovascular disease isn't entirely clear, they point out, but suggesting several possible explanations.
Fried foods boost energy intake because of their fat content and they generate harmful trans fatty acids from the hydrogenated vegetable oils often used to cook them.
Frying also boosts the production of chemical by-products involved in the body's inflammatory response, while foods, such as fried chicken and French fries, are usually high in added salt, and often accompanied by sugar-sweetened drinks, particularly when served in fast food restaurants, they say.
INFORMATION:
Externally peer reviewed? Yes
Evidence type: Meta-analysis
Subjects: People
We should err on the side of caution and stop the global roll out of 5G (fifth generation) telecoms networks until we are certain this technology is completely safe, urges an expert in an opinion piece published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
There are no health concerns about 5G and COVID-19, despite what conspiracy theorists have suggested.
But the transmitter density required for 5G means that more people will be exposed to radio frequency electromagnetic fields (RF-EMFs), and at levels that emerging evidence suggests, are potentially harmful to health, argues Professor John William Frank, Usher Institute, University of Edinburgh.
The ...
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
1. Primary care physicians account for a minority of spending on low-value care
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M20-6257
URL goes live ...
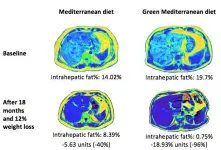
BEER-SHEVA, Israel...January 18, 2021 - A green Mediterranean (MED) diet reduces intrahepatic fat more than other healthy diets and cuts non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in half, according to a long-term clinical intervention trial led by Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers and a team of international colleagues.
The findings were published in Gut, a leading international journal focused on gastroenterology and hepatology.
"Our research team and other groups over the past 20 years have proven through rigorous randomized long-term trials that the Mediterranean diet is the healthiest," says lead researcher Prof. Iris Shai, an epidemiologist in the BGU ...
More people could be protected from life-threatening rabies thanks to an agile approach to dog vaccination using smart phone technology to spot areas of low vaccination coverage in real time.
Vets used a smart phone app to help them halve the time it takes to complete dog vaccination programmes in the Malawian city of Blantyre.
The custom-made app lets them quickly spot areas with low inoculation rates in real time, allowing them to jab more dogs more quickly, and with fewer staff.
Rabies is a potentially fatal disease passed on to humans primarily through dog bites. It is responsible for some 60,000 deaths worldwide each year, 40 per cent of which are children. It places a huge financial burden on some of the world's poorest countries.
Researchers predict that more than one million ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Click beetles can propel themselves more than 20 body lengths into the air, and they do so without using their legs. While the jump's motion has been studied in depth, the physical mechanisms that enable the beetles' signature clicking maneuver have not. A new study examines the forces behind this super-fast energy release and provides guidelines for studying extreme motion, energy storage and energy release in other small animals like trap-jaw ants and mantis shrimps.
The multidisciplinary study, led by University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign mechanical science and ...
Scientists in Australia have developed a method for the rapid synthesis of safe vaccines, an approach that can be used to test vaccine strategies against novel pandemic pathogens such as SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
Led by Professor Richard Payne at the University of Sydney and Professor Warwick Britton at the Centenary Institute, the team has demonstrated application of the method with a new vaccine for use against tuberculosis (TB), which has generated a powerful protective immune response in mice.
Researchers are keen to develop the vaccine strategy further to assist in the rapid pre-clinical testing of new vaccines, particularly for respiratory illnesses.
"Tuberculosis infects 10 million and kills more than 1.4 million people every year," ...
Cell velocity, or how fast a cell moves, is known to depend on how sticky the surface is beneath it, but the precise mechanisms of this relationship have remained elusive for decades. Now, researchers from the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association (MDC) and Ludwig Maximilians Universität München (LMU) have figured out the precise mechanics and developed a mathematical model capturing the forces involved in cell movement. The findings, reported in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), provide new insight for developmental biology and potential cancer treatment.
Cell ...
Imagine going to a surgeon to have a diseased or injured organ switched out for a fully functional, laboratory-grown replacement. This remains science fiction and not reality because researchers today struggle to organize cells into the complex 3D arrangements that our bodies can master on their own.
There are two major hurdles to overcome on the road to laboratory-grown organs and tissues. The first is to use a biologically compatible 3D scaffold in which cells can grow. The second is to decorate that scaffold with biochemical messages in the correct configuration to trigger the formation of the desired organ or tissue.
In a major step toward transforming this hope into reality, researchers at the University of Washington have developed a technique to ...
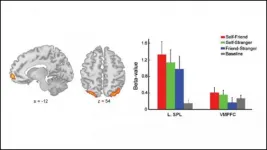
A brain region involved in processing information about ourselves biases our ability to remember, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
People are good at noticing information about themselves, like when your eye jumps to your name in a long list or you manage to hear someone address you in a noisy crowd. This self-bias extends to working memory, the ability to actively think about and manipulate bits of information: people are also better at remembering things about themselves.
To pinpoint the source of this bias, Yin et al. measured participants' brain activity in an fMRI scanner while they tried to remember the location of different colored dots representing themselves, a friend, or a stranger. The participants' fastest response ...
The core mass of the giant exoplanet WASP-107b is much lower than what was thought necessary to build up the immense gas envelope surrounding giant planets like Jupiter and Saturn, astronomers at Université de Montréal have found.
This intriguing discovery by Ph.D. student Caroline Piaulet of UdeM's Institute for Research on Exoplanets (iREx) suggests that gas-giant planets form a lot more easily than previously believed.
Piaulet is part of the groundbreaking research team of UdeM astrophysics professor Björn Benneke that in 2019 announced the first detection of water on an exoplanet located in its star's habitable zone.
Published today in the Astronomical Journal with colleagues ...